Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablet
- 25mg
- 50mg
- 100mg
Oral suspension (CaroSpir)
- 5mg/mL
Primary Hyperaldosteronism
Tablet only
Short-term preoperative treatment of patients with primary hyperaldosteronism
Long-term maintenance therapy for patients with discrete aldosterone-producing adrenal adenomas who are not candidates for surgery or for patients with bilateral micro or macronodular adrenal hyperplasia (idiopathic hyperaldosteronism)
100-400 mg PO qDay in preparation for surgery initially
May be used as long-term maintenance therapy at the lowest effective for patients who are considered unsuitable for surgery
Edematous Conditions
Management of edema in patients with cirrhosis of the liver when edema are unresponsive to fluid and sodium restriction or nephrotic syndrome when treatment of the underlying disease, fluid restriction and sodium intake, and the use of other diuretics produce an inadequate response
Tablet
- 100 mg qDay or divided q12hr for 5 days initially; then adjust does based on patient response; range: 25-200 mg PO qDay or divided q12hr
PO suspension
- 75 mg PO qDay or divided doses initially; if sole therapy, administer for ≥5 days before increasing dose to obtain effect
Essential Hypertension
Adjunctive therapy for hypertension, to lower blood pressure
Tablets
- 25-100mg PO qDay or divided q12hr initially; may adjust dosage to patient response q2weeks
PO suspension
- 20-75 mg PO qDay or divided doses initially; may adjust dosage to patient response q2weeks
- See Dosing Considerations
Congestive Heart Failure
Indicated for treatment of NYHA Class III-IV heart failure and reduced ejection fraction (EF) to increase survival, manage edema, and reduce the need for hospitalization for heart failure
ACC/AHA guidelines recommend aldosterone antagonist to be added to an ACE inhibitor or ARB, plus a beta-blocker; patient conditions may also require additional medications (eg, loop diuretics, hydralazine, nitrates, digoxin)
Tablet
- 25mg/day PO initially if serum potassium ≤5 mEq/L and eGFR >50 mL/min/1.73 m²; if tolerated, may increase to 50 mg/day as clinically indicated; if 25 mg/day not tolerated, reduce frequency to qoD
PO suspension
- 20 mg PO qDay; if initial 20 mg dose is tolerated, dosage can be increased to 37.5 mg as clinically indicated
Hypokalemia
Range: 25-100 mg PO qDay
Hirsutism (Off-label)
Women with hirsutism
50-200 mg PO qDay or divided q12hr
Acne (Off-label)
Females with hormonal acne
50-200 mg PO qDay or divided q12hr
Dosing Modifications
Renal impairment
- Patients with renal impairment are at increased risk of hyperkalemia; monitor potassium closely
- PO suspension for treatment of patients who develop hyperkalemia on 20 mg PO qDay may reduce dose to 20 mg PO qOD
- Patients who develop hyperkalemia on 25 mg PO qDay may reduce to 25 mg PO qOD
- CrCl >50 mL/min/1.73 m²: 20 mg qDay (oral suspension); 25 mg qDay (tablets)
- CrCl 30-50 mL/min/1.73 m²: Consider initiating at 10 mg qDay (oral suspension) and 25 mg qOD (tablets)
Overdose Management
May use normal saline for volume replacement
May use dopamine or norepinephrine to treat hypotension
Treat hyperkalemia with IV glucose (dextrose 25% in water), concurrently with rapid-acting insulin and IV sodium bicarbonate; oral/rectal solutions of Kayexalate in sorbitol can be used if needed
If dysrhythmia due to decreased K+ or Mg+ suspected, replace aggressively
Discontinue treatment if no symptoms after 6 hr
Dosing Considerations
Oral formulation
- PO suspension formulation is not therapeutically equivalent to tablet
- If PO suspension requires a dose titration >100 mg, use tablet
- For hypertension: Doses >75 mg/day may not provide additional reductions in blood pressure
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablet
- 25mg
- 50mg
- 100mg
Edema (Off-label)
CHF, cirrhosis, ascites, and nephrotic syndrome
1-3.3 mg/kg/day PO or divided q12hr; not to exceed 3.3 mg/kg/day or up to 100 mg/day
Hypertension (Off-label)
Among therapeutic options recommended by the National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents
1-3.3 mg/kg/day PO or divided q12hr; not to exceed 3.3 mg/kg/day or 100 mg/day
Hyperaldosteronism (Orphan)
Orphan designation for primary hyperaldosteronism
Sponsor
- CMP Pharma, Inc; PO Box 147, 8026 US Highway 264A; Farmville, NC 27828
Substantially excreted by the kidney, and risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function; monitor renal function
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results

Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor

Contraindicated (0)
Serious - Use Alternative (11)
- abiraterone
spironolactone increases toxicity of abiraterone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated. Spironolactone binds to androgen receptor and may increase prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels in abiraterone-treated prostate cancer patients.
- amiloride
amiloride and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
amiloride, spironolactone. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated. Hyperkalemia. - cyclosporine
spironolactone and cyclosporine both increase serum potassium. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration not recommended
- drospirenone
drospirenone and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
drospirenone, spironolactone. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated. Hyperkalemia. - eplerenone
spironolactone, eplerenone. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated. Hyperkalemia.
- lofexidine
lofexidine, spironolactone. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration with other drugs that decrease pulse or blood pressure to mitigate risk of excessive bradycardia and hypotension.
- potassium acid phosphate
spironolactone and potassium acid phosphate both increase serum potassium. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- potassium chloride
spironolactone and potassium chloride both increase serum potassium. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- potassium citrate
spironolactone and potassium citrate both increase serum potassium. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- potassium phosphates, IV
spironolactone and potassium phosphates, IV both increase serum potassium. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- triamterene
spironolactone and triamterene both increase serum potassium. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
spironolactone, triamterene. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated. Hyperkalemia.
Monitor Closely (148)
- acebutolol
acebutolol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- aceclofenac
spironolactone and aceclofenac both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- acemetacin
spironolactone and acemetacin both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- albuterol
spironolactone increases and albuterol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- aldesleukin
aldesleukin increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypotension.
- amifostine
amifostine, spironolactone. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration with blood pressure lowering agents may increase the risk and severity of hypotension associated with amifostine. When amifostine is used at chemotherapeutic doses, withhold blood pressure lowering medications for 24 hr prior to amifostine; if blood pressure lowering medication cannot be withheld, do not administer amifostine.
- ampicillin
ampicillin increases effects of spironolactone by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyperkalemia.
- arformoterol
spironolactone increases and arformoterol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- aspirin
spironolactone and aspirin both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
aspirin decreases effects of spironolactone by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. When used concomitantly, spironolactone dose may need to be titrated to higher maintenance dose and the patient should be observed closely to determine if the desired effect is obtained. - aspirin rectal
spironolactone and aspirin rectal both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
aspirin rectal decreases effects of spironolactone by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. When used concomitantly, spironolactone dose may need to be titrated to higher maintenance dose and the patient should be observed closely to determine if the desired effect is obtained. - aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate
spironolactone and aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate decreases effects of spironolactone by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. When used concomitantly, spironolactone dose may need to be titrated to higher maintenance dose and the patient should be observed closely to determine if the desired effect is obtained. - atenolol
atenolol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- avanafil
avanafil increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypotension.
- benazepril
benazepril and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bendroflumethiazide
spironolactone increases and bendroflumethiazide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- betaxolol
betaxolol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- bisoprolol
bisoprolol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- bretylium
spironolactone, bretylium. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Each drug may cause hypotension.
- bumetanide
spironolactone increases and bumetanide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- buprenorphine, long-acting injection
buprenorphine, long-acting injection decreases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Opioids can reduce diuretic efficacy by inducing antidiuretic hormone release.
- canagliflozin
spironolactone and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- candesartan
candesartan and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- captopril
captopril, spironolactone. Either increases toxicity of the other by Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Both drugs lower blood pressure. Risk of hyperkalemia. Monitor blood pressure and potassium.
- carbenoxolone
spironolactone increases and carbenoxolone decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- carbidopa
carbidopa increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Therapy with carbidopa, given with or without levodopa or carbidopa-levodopa combination products, is started, dosage adjustment of the antihypertensive drug may be required.
- carvedilol
carvedilol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- celecoxib
spironolactone and celecoxib both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- celiprolol
celiprolol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- chlorothiazide
spironolactone increases and chlorothiazide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- chlorthalidone
spironolactone increases and chlorthalidone decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- cholestyramine
cholestyramine, spironolactone. unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyperkalemic metabolic acidosis reported when coadministered.
- cholic acid
spironolactone increases toxicity of cholic acid by decreasing elimination. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid concomitant use of inhibitors of the bile salt efflux pump (BSEP). May exacerbate accumulation of conjugated bile salts in the liver and result in clinical symptoms. If concomitant use is necessary, monitor serum transaminases and bilirubin.
- choline magnesium trisalicylate
spironolactone and choline magnesium trisalicylate both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- cyclopenthiazide
spironolactone increases and cyclopenthiazide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dalteparin
spironolactone, dalteparin. Either increases toxicity of the other by serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor. Both drugs may increase serum potassium levels.
- dichlorphenamide
dichlorphenamide, spironolactone. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Both drugs can cause metabolic acidosis.
- diclofenac
spironolactone and diclofenac both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- diflunisal
spironolactone and diflunisal both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- digoxin
spironolactone and digoxin both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
spironolactone, digoxin. Mechanism: decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. False digoxin assay results may be obtained.
spironolactone increases levels of digoxin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Spironolactone may cause false elevation of digoxin assay. - disopyramide
spironolactone increases effects of disopyramide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive cardiovascular depression.
- dobutamine
spironolactone increases and dobutamine decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dopexamine
spironolactone increases and dopexamine decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- empagliflozin
empagliflozin, spironolactone. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of empagliflozin with diuretics results in increased urine volume and frequency of voids, which might enhance the potential for volume depletion.
- enalapril
enalapril, spironolactone. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hyperkalemia.
- enoxaparin
spironolactone, enoxaparin. Either increases toxicity of the other by serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor. Both drugs may increase serum potassium levels.
- ephedrine
spironolactone increases and ephedrine decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- epinephrine
spironolactone increases and epinephrine decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- epinephrine racemic
spironolactone increases and epinephrine racemic decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- eprosartan
eprosartan and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- esmolol
esmolol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ethacrynic acid
spironolactone increases and ethacrynic acid decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- etodolac
spironolactone and etodolac both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- fenbufen
spironolactone and fenbufen both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- fenoprofen
spironolactone and fenoprofen both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- fentanyl
fentanyl decreases effects of spironolactone by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Fentanyl can reduce the efficacy of diuretics by inducing antidiuretic hormone release. Fentanyl may also lead to acute urinary retention by causing bladder sphincter spasm (particularly in men with enlarged prostates).
- fentanyl intranasal
fentanyl intranasal decreases effects of spironolactone by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Fentanyl can reduce the efficacy of diuretics by inducing antidiuretic hormone release. Fentanyl may also lead to acute urinary retention by causing bladder sphincter spasm (particularly in men with enlarged prostates).
- fentanyl transdermal
fentanyl transdermal decreases effects of spironolactone by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Fentanyl can reduce the efficacy of diuretics by inducing antidiuretic hormone release. Fentanyl may also lead to acute urinary retention by causing bladder sphincter spasm (particularly in men with enlarged prostates).
- fentanyl transmucosal
fentanyl transmucosal decreases effects of spironolactone by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Fentanyl can reduce the efficacy of diuretics by inducing antidiuretic hormone release. Fentanyl may also lead to acute urinary retention by causing bladder sphincter spasm (particularly in men with enlarged prostates).
- finerenone
spironolactone and finerenone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Finerenone dose adjustment based on current serum potassium concentration. Monitor serum potassium and adjust finerenone dose as described in the prescribing information as necessary.
- flurbiprofen
spironolactone and flurbiprofen both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- formoterol
spironolactone increases and formoterol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- fosinopril
fosinopril, spironolactone. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hyperkalemia.
- furosemide
spironolactone increases and furosemide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- gentamicin
spironolactone increases and gentamicin decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- heparin
spironolactone, heparin. Either increases toxicity of the other by serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor. Both drugs may increase serum potassium levels.
- hydrochlorothiazide
spironolactone increases and hydrochlorothiazide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ibuprofen
spironolactone and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ibuprofen IV
spironolactone and ibuprofen IV both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- imidapril
imidapril, spironolactone. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hyperkalemia.
- indapamide
spironolactone increases and indapamide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- indomethacin
spironolactone and indomethacin both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- irbesartan
irbesartan and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- isoproterenol
spironolactone increases and isoproterenol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- juniper
juniper, spironolactone. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Juniper may potentiate or interfere with diuretic therapy. Juniper has diuretic effects, but may cause kidney damage at large doses.
- ketoprofen
spironolactone and ketoprofen both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ketorolac
spironolactone and ketorolac both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ketorolac intranasal
spironolactone and ketorolac intranasal both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- labetalol
labetalol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- levalbuterol
spironolactone increases and levalbuterol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- levodopa
levodopa increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider decreasing dosage of antihypertensive agent.
- lisinopril
lisinopril, spironolactone. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hyperkalemia.
- loperamide
spironolactone will increase the level or effect of loperamide by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lornoxicam
spironolactone and lornoxicam both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- losartan
losartan and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- lurasidone
lurasidone increases effects of spironolactone by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Potential for increased risk of hypotension with concurrent use. Monitor blood pressure and adjust dose of antihypertensive agent as needed.
- maraviroc
maraviroc, spironolactone. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of orthostatic hypotension.
- meclofenamate
spironolactone and meclofenamate both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- mefenamic acid
spironolactone and mefenamic acid both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- meloxicam
spironolactone and meloxicam both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- metaproterenol
spironolactone increases and metaproterenol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- methyclothiazide
spironolactone increases and methyclothiazide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. .
- methylphenidate transdermal
methylphenidate transdermal decreases effects of spironolactone by anti-hypertensive channel blocking. Use Caution/Monitor.
- metolazone
spironolactone increases and metolazone decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- metoprolol
metoprolol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- midazolam
spironolactone will increase the level or effect of midazolam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. midazolam dose may need to be adjusted
- mitotane
spironolactone decreases effects of mitotane by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- moexipril
moexipril, spironolactone. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hyperkalemia.
- nabumetone
spironolactone and nabumetone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- nadolol
nadolol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- naproxen
spironolactone and naproxen both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- nebivolol
nebivolol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- nitroglycerin rectal
nitroglycerin rectal, spironolactone. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Observe for possible additive hypotensive effects during concomitant use. .
- noni juice
spironolactone and noni juice both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- norepinephrine
spironolactone increases and norepinephrine decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- olanzapine/samidorphan
olanzapine/samidorphan increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor blood pressure and reduce antihypertensive drug dosage in accordance with its product labeling.
- oliceridine
oliceridine decreases effects of spironolactone by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Opioids can reduce the efficacy of diuretics by inducing the release of antidiuretic hormone. Monitor for signs of diminished diuresis and/or effects on blood pressure and increase dosage of the diuretic as needed. .
- olmesartan
olmesartan and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ospemifene
spironolactone, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- oxaprozin
spironolactone and oxaprozin both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- parecoxib
spironolactone and parecoxib both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- penbutolol
penbutolol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- perindopril
perindopril, spironolactone. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hyperkalemia.
- pindolol
pindolol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- pirbuterol
spironolactone increases and pirbuterol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- piroxicam
spironolactone and piroxicam both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- pivmecillinam
pivmecillinam increases effects of spironolactone by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyperkalemia.
- potassium citrate/citric acid
spironolactone and potassium citrate/citric acid both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- propranolol
propranolol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- pseudoephedrine
spironolactone decreases effects of pseudoephedrine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quinapril
quinapril, spironolactone. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hyperkalemia.
- ramipril
ramipril, spironolactone. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hyperkalemia.
- repaglinide
spironolactone will increase the level or effect of repaglinide by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Spironolactone inhibits CYP2C8; repaglinice dose may need to be adjusted as it is metabolized by CYP2C8
- sacubitril/valsartan
sacubitril/valsartan and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- salicylates (non-asa)
spironolactone and salicylates (non-asa) both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- salmeterol
spironolactone increases and salmeterol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- salsalate
spironolactone and salsalate both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- sirolimus
spironolactone will increase the level or effect of sirolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. sirolimus dose may need to be adjusted
- sotalol
sotalol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- sparsentan
sparsentan and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor serum potassium frequently.
- succinylcholine
spironolactone and succinylcholine both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- sulfasalazine
spironolactone and sulfasalazine both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- sulindac
spironolactone and sulindac both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- tacrolimus
spironolactone will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. tacrolimus dose may need to be adjusted
- tadalafil
tadalafil increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypotension.
- telmisartan
telmisartan and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- temocillin
temocillin increases effects of spironolactone by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyperkalemia.
- terbutaline
spironolactone increases and terbutaline decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ticarcillin
ticarcillin increases effects of spironolactone by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hyperkalemia.
- timolol
timolol and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- tolfenamic acid
spironolactone and tolfenamic acid both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- tolmetin
spironolactone and tolmetin both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- tolvaptan
spironolactone and tolvaptan both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- torsemide
spironolactone increases and torsemide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- trandolapril
trandolapril, spironolactone. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hyperkalemia.
- trimethoprim
trimethoprim and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor. Trimethoprim decreases urinary potassium excretion. May cause hyperkalemia, particularly with high doses, renal insufficiency, or when combined with other drugs that cause hyperkalemia.
- valsartan
valsartan and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- voclosporin
voclosporin and spironolactone both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- xipamide
xipamide increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
Minor (34)
- agrimony
agrimony increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ammonium chloride
spironolactone, ammonium chloride. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of systemic acidosis.
- birch
birch increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- brimonidine
brimonidine increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- cadexomer iodine
cadexomer iodine, spironolactone. Mechanism: decreasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown. Hyperkalemia.
- calcium acetate
spironolactone decreases levels of calcium acetate by increasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- calcium carbonate
spironolactone decreases levels of calcium carbonate by increasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- calcium chloride
spironolactone decreases levels of calcium chloride by increasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- calcium citrate
spironolactone decreases levels of calcium citrate by increasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- calcium gluconate
spironolactone decreases levels of calcium gluconate by increasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- cornsilk
cornsilk increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- epoprostenol
epoprostenol increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive hypotensive effects.
- forskolin
forskolin increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- goldenrod
goldenrod increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- iodinated glycerol
iodinated glycerol, spironolactone. Mechanism: decreasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown. Hyperkalemia.
- iodine
iodine, spironolactone. Mechanism: decreasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown. Hyperkalemia.
- magnesium chloride
spironolactone increases levels of magnesium chloride by decreasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- magnesium citrate
spironolactone increases levels of magnesium citrate by decreasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- magnesium hydroxide
spironolactone increases levels of magnesium hydroxide by decreasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- magnesium oxide
spironolactone increases levels of magnesium oxide by decreasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- magnesium sulfate
spironolactone increases levels of magnesium sulfate by decreasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- maitake
maitake increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- minoxidil
spironolactone increases effects of minoxidil by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- nitazoxanide
nitazoxanide, spironolactone. Either increases levels of the other by Mechanism: plasma protein binding competition. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- octacosanol
octacosanol increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- patiromer
patiromer, spironolactone. cation binding in GI tract. Minor/Significance Unknown. No observed clinically important interaction. No separation of dosing required.
- reishi
reishi increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- shepherd's purse
shepherd's purse, spironolactone. Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Comment: Theoretically, shepherd's purse may interfere with BP control.
- sulfadiazine
spironolactone increases levels of sulfadiazine by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sulfamethoxazole
spironolactone, sulfamethoxazole. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Hyperkalemia.
spironolactone increases levels of sulfamethoxazole by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. - sulfisoxazole
spironolactone increases levels of sulfisoxazole by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- tizanidine
tizanidine increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of hypotension.
- treprostinil
treprostinil increases effects of spironolactone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- trimethoprim
spironolactone, trimethoprim. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Hyperkalemia.
Adverse Effects
Frequency Not Defined
Gastric bleeding
Ulceration
Gastritis
Decreased libido
Inability to achieve or maintain erection
Postmenopausal bleeding
Breast and nipple pain
Thrombocytopenia
Fever
Urticaria
Maculopapular or erythematous cutaneous eruptions
Anaphylactic reactions
Vasculitis
Hyperkalemia
Electrolyte disturbances
Hyponatremia
Hypovolemia
Lethargy
Mental confusion
Ataxia
Dizziness
Headache
Drowsiness
Renal dysfunction (including renal failure)
Chloasma
Drowsiness
Lethargy
Headache
Mental confusion
Rash
Urticaria
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS)
Gynecomastia
Impotence
Menstrual disorders
Abdominal cramping
Diarrhea
Gastritis
Nausea
Vomiting
Breast pain
Leukopenia
Electrolyte disturbances
Leg cramps
Dizziness
Alopecia
Pruritus
Warnings
Black Box Warnings
Spironolactone has been shown to be a tumorigen in chronic toxicity studies in rats; use only for specified indications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity
Addison disease or other conditions associated with hyperkalemia
Coadministration with eplerenone
Cautions
Gynecomastia reported and usually reversible
Hyponatremia, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, hypochloremic alkalosis, and hyperglycemia may occur
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia can occur and rarely gout may occur; monitor serum electrolytes, uric acid, and blood glucose periodically In cirrhosis, avoid electrolyte and acid/base imbalances that might lead to hepatic encephalopathy
Hyperkalemia may occur; monitor serum potassium within 1 week of initiation or titration of spironolactone and regularly thereafter; if hyperkalemia occurs, reduce dose or discontinue treatment and treat hyperkalemia
Excessive diuresis may cause symptomatic dehydration, hypotension and worsening renal function, particularly in salt-depleted patients or those taking angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)
Drug interactions overview
- Coadministration of PO suspension and lithium reduces the renal clearance of lithium, inducing a high risk of lithium toxicity
- Reported that of coadministration of PO suspension and an NSAID can reduce the diuretic, natriuretic, and antihypertensive effect of loop, potassium-sparing, and thiazide diuretics
- NSAID administration can reduce diuretic, natriuretic, and antihypertensive effect of diuretics; when spironolactone and NSAIDs are used concomitantly, monitor closely to determine if the desired effect of the diuretic is obtained
- Acetylsalicylic acid may reduce the efficacy of spironolactone; coadministration with acetylsalicylic acid may need to be titrated to higher maintenance dose and monitor closely to determine if the desired effect is obtained
- Coadministration of spironolactone with potassium supplementation, salt substitutes containing potassium, a diet rich in potassium, or drugs that can increase potassium (eg, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, NSAIDs, heparin and low molecular weight heparin) may lead to severe hyperkalemia
- Risk of worsening of renal function can also occur with concomitant use of nephrotoxic drugs (eg, aminoglycosides, cisplatin, NSAIDs); monitor volume status and renal function periodically
- Spironolactone and its metabolites interfere with radioimmunoassays for digoxin and increase the apparent exposure to digoxin; use an assay that does not interact with spironolactone
- Hyperkalemic metabolic acidosis reported in patients given spironolactone concurrently with cholestyramine
- Spironolactone and its metabolites increase the apparent exposure to digoxin; in patients taking concomitant digoxin, measure serum digoxin concentrations before initiating spironolactone using an assay that does not interact with spironolactone; reduce digoxin concentrations by decreasing dose by approximately 15-30% or by modifying dosing frequency and continue monitoring
- Spironolactone is an irreversible inhibitor for CYP2C8 and CYP3A4/5 in vitro; may increase exposure of other coadministered drugs that are metabolized by CYP2C8 and CYP3A4/5; dosage adjustments of drugs metabolized by CYP2C8 (eg, repaglinide) and CYP3A4/5 (eg, midazolam, sirolimus, and tacrolimus) may be necessary if they are given concurrently with spironolactone
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
Based on mechanism of action and findings in animal studies, spironolactone may affect sex differentiation of the male during embryogenesis; rat embryofetal studies report feminization of male fetuses and endocrine dysfunction in females exposed to spironolactone in utero
Limited available data did not demonstrate an association of major malformations or other adverse pregnancy outcomes with spironolactone; risks may occur to the mother and fetus associated with heart failure, cirrhosis, and poorly controlled hypertension during pregnancy
Potential risk to the male fetus due to antiandrogenic properties of spironolactone; avoid spironolactone in pregnant women or advise a pregnant woman of the potential risk to a male fetus
Disease-associated maternal and embryo/fetal risks
- Pregnant women with CHF are at increased risk for preterm birth; stroke volume and heart rate increase during pregnancy, increasing cardiac output, especially during the first trimester; closely monitor pregnant patients with CHF
- Pregnant women with symptomatic cirrhosis generally have poor outcomes (eg, hepatic failure, variceal hemorrhage, preterm delivery, fetal growth restriction, and maternal death); pregnant women with cirrhosis of the liver should be monitored and managed accordingly
- Hypertension in pregnancy increases the maternal risk for preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, premature delivery, and delivery complications (eg, need for cesarean delivery, postpartum hemorrhage); hypertension increases the fetal risk for intrauterine growth restriction and death
Lactation
Not present in breastmilk; however, limited data from a lactating woman at 17 days postpartum reports the presence of the active metabolite, canrenone, in human breast milk in low amounts that are expected to be clinically inconsequential; in this case, there were no adverse effects reported for the breastfed infant after short term exposure to spironolactone; however, long term effects on a breastfed infant are unknown; there are no data on spironolactone effects on milk production
Consider the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding along with the mother’s clinical need for the drug, and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from the drug or from the underlying maternal condition
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Aldosterone antagonist with diuretic and antihypertensive effects; competitive binding of receptors at aldosterone-dependent Na-K exchange site in distal tubules results in increased excretion of Na+, Cl-, and water and retention of K+ and H+
Increases testosterone clearance and estradiol production; blocks conversion of potent androgens to weaker ones in peripheral tissues
Absorption
Bioavailability: 73% (tablet)
Onset: 2-4 hr (tablet)
Duration: 2-3 days (tablet)
Peak serum time: 2.6-4.3 hr (tablet); 0.5-1.5 hr (PO suspension); 2.5-5 hr (PO suspension, active metabolite)
A high fat and high calorie meal (57% of the ~1000 kcal of the meal were from fat) increased the bioavailability of spironolactone (as measured by AUC) by ~90%
Distribution
Protein bound: 90%
Metabolism
Metabolized by the liver and kidneys
Metabolites: Canrenone, 7-alpha-thiomethylspirolactone, 6-beta-hydroxy-7-alpha-thiomethylspirolactone (active)
Elimination
Half-life (tablet): 1.3-1.4 hr (parent drug); 16.5 hr (canrenone); 13.8 hr (7-α-[thiomethyl] spirolactone [TMS]); 15 hr (6-ß-hydroxy-7-α-[thiomethyl] spirolactone [HTMS])
Half-life (PO suspension): 1-2 hr (parent drug); 10-35 hr (canrenone, 7-α-[thiomethyl] spirolactone [TMS], 6-ß-hydroxy-7-α-[thiomethyl] spirolactone [HTMS])
Excretion (tablet): Urine (47-57%); feces (35-41%)
Excretion (PO suspension): Urine
Administration
Oral Administration
Take with or without food; take consistently with respect to food
Storage
Tablet: Store below 77°F (25°C)
PO suspension: Store at 68-77°F (20-25°C); excursions permitted to 59-86°F (15-30°C); shake well before use, dispense in a tight container as defined in the USP
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| CaroSpir oral - | 25 mg/5 mL suspension |  | |
| CaroSpir oral - | 25 mg/5 mL suspension |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 25 mg tablet | 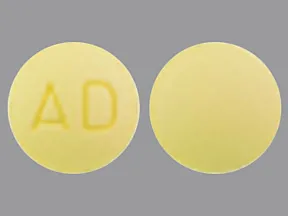 | |
| spironolactone oral - | 25 mg tablet | 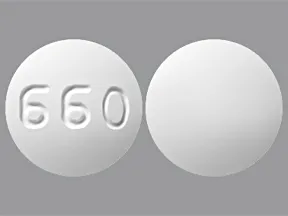 | |
| spironolactone oral - | 50 mg tablet | 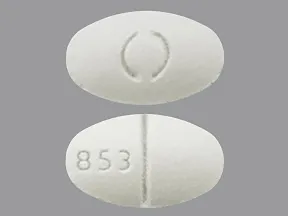 | |
| spironolactone oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 25 mg tablet | 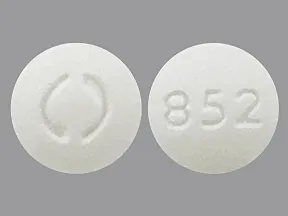 | |
| spironolactone oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 25 mg/5 mL suspension |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 25 mg/5 mL suspension |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| spironolactone oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| Aldactone oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| Aldactone oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| Aldactone oral - | 25 mg tablet |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
spironolactone oral
SPIRONOLACTONE - ORAL
(spir-ON-oh-LAK-tone)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Aldactone
USES: Spironolactone is used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. Lowering high blood pressure helps prevent strokes, heart attacks, and kidney problems. It is also used to treat swelling (edema) caused by certain conditions (such as heart failure, liver disease) by removing excess fluid and improving symptoms such as breathing problems.This medication is also used to treat conditions in which the body is making too much of a natural substance (aldosterone).Spironolactone is known as a "water pill" (potassium-sparing diuretic).
HOW TO USE: Take this medication by mouth as directed by your doctor. If stomach upset occurs, take it with food or milk. It is best to take your dose early in the day (before 6 p.m.) to prevent having to get up during the night to urinate. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions.If you are using the liquid form of this medication, shake the bottle well before each dose. Carefully measure the dose using a special measuring device/spoon. Do not use a household spoon because you may not get the correct dose. You may take the liquid form of this medication with or without food, but it is important to choose one way and take it the same way with every dose.The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. In children, the dosage is also based on body weight.Take this medication regularly in order to get the most benefit from it. Remember to use it at the same time(s) each day as directed. Keep taking this medication even if you feel well. Most people with high blood pressure do not feel sick.Take this medication exactly as prescribed. Do not increase your dose, take it more often than prescribed, or stop using this medicine without first consulting your doctor. Your condition may become worse when the drug is suddenly stopped.Tell your doctor if your condition does not get better or if it gets worse (for example, your blood pressure readings remain high or increase).
SIDE EFFECTS: Drowsiness, dizziness, lightheadedness, stomach upset, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, or headache may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.To reduce the risk of dizziness and lightheadedness, get up slowly when rising from a sitting or lying position.Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.Spironolactone may cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. Tell your doctor right away if you have any symptoms of dehydration or electrolyte imbalance, including unusual dry mouth/thirst, muscle cramps/weakness, slow/fast/irregular heartbeat, or confusion.Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: signs of kidney problems (such as change in the amount of urine), fainting, menstrual period changes, breast pain, breast enlargement (gynecomastia) in men, sexual function problems, signs of infection (such as sore throat that doesn't go away, fever), vomit that looks like coffee grounds, signs of liver problems (such as nausea/vomiting that doesn't stop, dark urine, stomach/abdominal pain, yellowing eyes/skin), easy bruising/bleeding.A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: Before taking spironolactone, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: kidney problems, liver problems, untreated mineral imbalance (such as high potassium, low sodium), decreased adrenal gland function (Addison's disease).Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).This medication may increase your potassium levels. Before using potassium supplements or salt substitutes that contain potassium, consult your doctor or pharmacist.This drug may make you dizzy or drowsy. Alcohol or marijuana (cannabis) can make you more dizzy or drowsy. Do not drive, use machinery, or do anything that needs alertness until you can do it safely. Limit alcoholic beverages. Talk to your doctor if you are using marijuana (cannabis).Severe sweating, diarrhea, or vomiting may cause dehydration and cause you to feel lightheaded. Tell your doctor if you have severe diarrhea or vomiting. To prevent dehydration, drink plenty of fluids unless your doctor tells you not to.Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects of this drug, especially high potassium blood levels.During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.This medication passes into breast milk but is unlikely to harm a nursing infant. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: See also Precautions section.Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.Some products that may interact with this drug include: lithium, drugs that may increase the level of potassium in the blood (such as amiloride, cyclosporine, eplerenone, tacrolimus, triamterene, birth control pills containing drospirenone).Some products have ingredients that could raise your blood pressure or worsen your swelling. Tell your pharmacist what products you are using, and ask how to use them safely (especially cough-and-cold products, diet aids, or NSAIDs such as ibuprofen/naproxen).This medication may interfere with certain lab tests (such as digoxin or cortisol levels), possibly causing false test results. Make sure lab personnel and all your doctors know you use this drug.
OVERDOSE: If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others.Lab and/or medical tests (such as kidney/liver function, blood mineral levels such as potassium) should be done while you are taking this medication. Keep all medical and lab appointments. Consult your doctor for more details.If you are taking this medication for high blood pressure, lifestyle changes such as stress reduction programs, exercise, and dietary changes may increase the effectiveness of this medicine. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist about lifestyle changes that might benefit you.Have your blood pressure checked regularly while taking this medication. Discuss with your doctor and learn how to monitor your own blood pressure. Inform your doctor of your blood pressure readings.
MISSED DOSE: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose. Take your next dose at the regular time. Do not double the dose to catch up.
STORAGE: Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Information last revised January 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.




