Dosing & Uses
Hypercholesterolemia
Indicated as adjunctive therapy to diet in adults with hypertriglyceridemia, hyperlipidemia, mixed dyslipidemia, or primary dysbetalipoproteinemia
Tablets and capsules: 10-20 mg PO qDay; not to exceed 40 mg/day
After initiation or upon titration, analyze lipid levels within 2-4 weeks and adjust dosage accordingly
Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Indicated as adjunctive therapy in adults with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia
Tablets and capsules: 20 mg PO qDay; not to exceed 40 mg/day
After initiation or upon titration, analyze lipid levels within 2-4 weeks and adjust dosage accordingly
Slowing Progression of Atherosclerosis
Indicated as adjunctive therapy to diet to slow the progression of atherosclerosis in adult patients as part of a treatment strategy to lower total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol to target levels
Tablets and capsules: 10-20 mg PO qDay; not to exceed 40 mg/day
After initiation or upon titration, analyze lipid levels within 2-4 weeks and adjust dosage accordingly
Primary Prevention
Indicated to reduce the risk of stroke, myocardial infarction, and arterial revascularization procedures in individuals without clinically evident coronary heart disease with risk factors
Risk factors
- Age (>50 years in men; >60 years in women), AND
- Elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein level (>2 mg/L), AND
- Presence of ≥1 additional cardiovascular risk factor (eg, high blood pressure, low HDL cholesterol, smoking, family history of premature heart disease)
Dosage Modifications
Dosing in Asian patients
- Consider starting at 5 mg PO qDay, owing to increased rosuvastatin plasma concentrations
- May increase up to 20 mg/day if patients are not adequately controlled
Dosage adjustment for rosuvastatin with concomitant therapy
- Coadministered with cyclosporine or vadadustat: Do not exceed rosuvastatin 5 mg qDay
- Coadministered with gemfibrozil: Avoid use; if use cannot be avoided, initiate rosuvastatin at 5 mg qDay; not to exceed 10 mg/day
- Coadministered with atazanavir and ritonavir, lopinavir and ritonavir, or simeprevir: Initiate rosuvastatin at 5 mg qDay; not to exceed 10 mg/day
Renal impairment
- Mild or moderate (CrCl ≥30 mL/min/1.73m²): No dosage adjustment necessary
- Severe (CrCl <30 mL/min/1.73m²) and not on hemodialysis: Decrease starting dose to 5 mg PO qDay; not to exceed 10 mg/day
Hepatic impairment
- Active liver disease: Contraindicated
- Chronic alcoholic liver disease: Use with caution; known to increase rosuvastatin exposure
Dosing Considerations
Initiating therapy or switching from another HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor: Start on appropriate dose and then titrate based on patient’s response and individualized goal of therapy
Limitation of use: Not studied in Fredrickson type I and V dyslipidemias
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablet (Crestor)
- 5mg
- 10mg
- 20mg
- 40mg
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Heterozygous
- Adjunctive therapy to diet to reduce total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and ApoB levels in children and adolescents (8-17 years) with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia after an inadequate response to diet therapy
- Inadequate response defined as when the following findings are present: LDL cholesterol >190 mg/dL OR >160 mg/dL with a positive family history of premature cardiovascular disease (CVD) or ≥2 CVD risk factors
- <8 years: Safety and efficacy not established
- 8 to <10 years: 5-10 mg PO qDay
- 10-17 years: 5-20 mg PO qDay; may adjust dose at intervals of at least 4 wk; not to exceed 20 mg/day
Homozygous
- Adjunctive therapy to diet to reduce LDL cholesterol, total cholesterol, non-HDL cholesterol, and ApoB in children and adolescents (7-17 year) with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, either alone or with other lipid-lowering treatments (eg, LDL apheresis)
- <7 years: Safety and efficacy not established
- 7-17 years: 20 mg PO qDay
Dosage Modifications
Dosing in Asian patients
- Consider starting at 5 mg PO qDay, owing to increased rosuvastatin plasma concentrations
- May increase up to 20 mg/day if patients are not adequately controlled
Dosage adjustment for rosuvastatin with concomitant therapy
- Coadministered with cyclosporine: Do not exceed rosuvastatin 5 mg qDay
- Coadministered with gemfibrozil: Avoid use; if use cannot be avoided, initiate rosuvastatin at 5 mg qDay; not to exceed 10mg/day
- Coadministered with atazanavir and ritonavir, lopinavir and ritonavir, or simeprevir: Initiate rosuvastatin at 5 mg qDay; not to exceed 10mg/day
Renal impairment
- Mild or moderate (CrCl ≥30 mL/min/1.73m²): No dosage adjustment necessary
- Severe (CrCl <30 mL/min/1.73m²) and not on hemodialysis: Decrease starting dose to 5 mg PO qDay; not to exceed 10 mg/day
Hepatic impairment
- Active liver disease: Contraindicated
- Chronic alcoholic liver disease: Use with caution; known to increase rosuvastatin exposure
Dosing Considerations
Initiating therapy or switching from another HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor: Start on appropriate dose and then titrate based on patient’s response and individualized goal of therapy
Limitation of use: Not studied in Fredrickson type I and V dyslipidemias
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results

Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor

Contraindicated (2)
- gemfibrozil
gemfibrozil increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Contraindicated. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- red yeast rice
rosuvastatin, red yeast rice. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated. May increase creatine kinase levels and increase risk of myopathy or rhabdomyolysis; red yeast rice contains monocolin K (reportedly identical to lovastatin).
Serious - Use Alternative (24)
- atazanavir
atazanavir increases levels of rosuvastatin by unknown mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potential for increased toxicity. Use alternatives if available. Increased risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. Limit rosuvastatin dose to 10 mg/day; ritonavir component of atazanavir/ritonavir regimen decreases rosuvastatin metabolism.
- ceftobiprole medocaril sodium
ceftobiprole medocaril sodium will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Ceftobiprole (an OATP1B1/1B3 inhibitor) may increase plasma concentrations of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 substrates.
- clarithromycin
clarithromycin increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- colchicine
colchicine, rosuvastatin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Increased risk of rhabdomyolysis (incl a fatality).
- cyclosporine
cyclosporine increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- darolutamide
darolutamide will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Darolutamide is a BCRP inhibitor. Avoid coadministration with BCRP inhibitors. If use is unavoidable, closely monitor for adverse reactions; dose of rosuvastatin should not exceed 5 mg once daily (refer BCRP substrate prescribing information).
- eltrombopag
eltrombopag increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- fenofibrate
fenofibrate, rosuvastatin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Fenofibrate may further increase risk for rhabdomyolysis when added to optimal statin regimen to further decrease TG and increase HDLs.
- fenofibrate micronized
fenofibrate micronized, rosuvastatin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Fenofibrate may further increase risk for rhabdomyolysis when added to optimal statin regimen to further decrease TG and increase HDLs.
- fenofibric acid
fenofibric acid, rosuvastatin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Fenofibrate may further increase risk for rhabdomyolysis when added to optimal statin regimen to further decrease TG and increase HDLs.
- gemfibrozil
gemfibrozil, rosuvastatin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Gemfibrozil may further increase risk for rhabdomyolysis when added to optimal statin regimen to further decrease TG and increase HDLs. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, initiate rosuvastatin at 5 mg once daily; the dose of rosuvastatin should not exceed 10 mg once daily.
- indinavir
indinavir increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis increased when atorvastatin coadministered with CYP3A4 inhibitors; use lowest statin dose possible.
indinavir increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy. - ketoconazole
ketoconazole increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- lasmiditan
lasmiditan increases levels of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Lasmiditan inhibits BCRP in vitro. Avoid coadministration of lasmiditan with BCRP substrates.
- leniolisib
leniolisib will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Leniolisib, a BCRP, OATP1B1, and OATP1B3 inhibitor, may increase systemic exposure of these substrates
- levoketoconazole
levoketoconazole increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- lopinavir
lopinavir increases levels of rosuvastatin by decreasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Limit rosuvastatin dose to 10 mg/day; ritonavir component of lopinavir/ritonavir decreases rosuvastatin metabolism.
- mifepristone
mifepristone increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nelfinavir
nelfinavir increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- niacin
niacin, rosuvastatin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Increased risk of rhabdomyolysis (>1 g/day niacin).
- ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC)
ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC) increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ritonavir
ritonavir increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- saquinavir
saquinavir increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- trofinetide
trofinetide will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Trofinetide (an OATP131 and OATP13B inhibitor) may increase plasma levels of OATP131 or OATP13B substrates. Avoid coadministration with sensitive substrates.
Monitor Closely (64)
- acalabrutinib
acalabrutinib increases levels of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Acalabrutinib may increase exposure to coadministered BCRP substrates by inhibition of intestinal BCRP.
- aluminum hydroxide
aluminum hydroxide decreases levels of rosuvastatin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Separate by 2 hours.
- apalutamide
apalutamide will decrease the level or effect of rosuvastatin by increasing elimination. Use Caution/Monitor. Apalutamide induces UGT and weakly induces BCRP and OATP1B1. Drugs that are eliminated via these pathways may have decreased systemic exposure if coadministered with apalutamide.
- asciminib
asciminib will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Asciminib is an OATP1B and BCRP inhibitor; closely monitor for adverse reactions in patients treated at all recommended doses with concomitant use of other OATP1B or BCRP substrates; reduce dosage of other OATP1B or BCRP substrates as recommended in their Prescribing Information when used concomitantly at all recommended doses
- atazanavir
atazanavir increases levels of rosuvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Potential for increased toxicity. Use alternatives if available. Increased risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. .
- calcium carbonate
calcium carbonate decreases levels of rosuvastatin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Separate by 2 hours.
- carbamazepine
carbamazepine increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- caspofungin
caspofungin increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- cholestyramine
cholestyramine decreases levels of rosuvastatin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clotrimazole
clotrimazole increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- cobicistat
cobicistat will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. For HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors that are not contraindicated with cobicistat, dose should not exceed 20 mg/day.
- crofelemer
crofelemer increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Crofelemer has the potential to inhibit transporters MRP2 and OATP1A2 at concentrations expected in the gut; unlikely to inhibit systemically because minimally absorbed.
- danicopan
danicopan will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Danicopan increases plasma concentrations of BCRP substrates; consider dose reduction of BCRP substrate according to its prescribing information.
- daptomycin
rosuvastatin, daptomycin. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Coadministration of daptomycin with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors may increase CPK levels and risk for myopathy; consider temporary suspension of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors during daptomycin therapy.
- darunavir
darunavir will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. For HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors that are not contraindicated with cobicistat, dose should not exceed 20 mg/day.
- dasabuvir
dasabuvir increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- elagolix
elagolix decreases levels of rosuvastatin by unknown mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider increasing the dose of rosuvastatin.
- elbasvir/grazoprevir
elbasvir/grazoprevir increases levels of rosuvastatin by unknown mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. If coadministered, do not exceed rosuvastatin dose of 10 mg/day.
- eluxadoline
eluxadoline increases levels of rosuvastatin by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Eluxadoline may increase the systemic exposure of coadministered OATP1B1 or BCRP substrates. Potential for increased risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis with rosuvastatin. Decrease rosuvastatin to lowest effective dose.
- encorafenib
encorafenib will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Encorafenib (a OATP1B1, OATP1B3, and BCRP inhibitor) may increase the concentration and toxicities of OATP1B1, OATP1B3, and BCRP substrates. Closely monitor for signs and symptoms of increased exposure and consider adjusting the dose of these substrates. Screen reader support enabled.
- erythromycin base
erythromycin base increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- erythromycin ethylsuccinate
erythromycin ethylsuccinate increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- erythromycin lactobionate
erythromycin lactobionate increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- erythromycin stearate
erythromycin stearate increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- eslicarbazepine acetate
eslicarbazepine acetate will decrease the level or effect of rosuvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Dose adjustment of some statins may be needed if a clinically significant change in lipids is noted.
- fostamatinib
fostamatinib will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use of fostamatinib may increase concentrations of BCRP substrate drugs. Monitor for toxicities of BCRP substrate drug that may require dosage reduction when given concurrently with fostamatinib.
- fostemsavir
fostemsavir will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Fostemsavir inhibits OATP1B1/3 and BCRP transporters. If possible, avoid coadministration or modify dose of OATP1B1/3 or BCRP substrates coadministered with fostemsavir. Use lowest possible starting dose for statins and monitor for associated adverse events.
- glecaprevir/pibrentasvir
glecaprevir/pibrentasvir increases levels of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Increased statin concentrations resulting from OATP1B1 inhibition may increase risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis. If coadministered, do not exceed 10 mg/day of rosuvastatin.
- glyburide
glyburide increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Coadministration of rosuvastatin with OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase rosuvastatin levels and risk for myopathy.
- lanthanum carbonate
lanthanum carbonate decreases levels of rosuvastatin by cation binding in GI tract. Use Caution/Monitor. Administer statin at least 2 hr before or 2 hr after lanthanum. Monitor serum concentrations.
- ledipasvir/sofosbuvir
ledipasvir/sofosbuvir will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir with rosuvastatin may be associated withincreased risk of myopathy,including rhabdomyolysis. Monitor closely.
- letermovir
letermovir increases levels of rosuvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of letermovir with fluvastatin may require a dosage reduction. Closely monitor patients for myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. When letermovir is coadministered with cyclosporine, the dose of rosuvastatin should not exceed 5 mg PO qDay . .
- levonorgestrel oral/ethinylestradiol/ferrous bisglycinate
rosuvastatin increases levels of levonorgestrel oral/ethinylestradiol/ferrous bisglycinate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of rosuvastatin and certain combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) containing EE increase AUC values for EE by approximately 20-25%.
- mesterolone
mesterolone increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of rhabdomyolysis (theoretical interaction based on case reports of combination of danazol and >20 mg/day lovastatin).
- metyrapone
metyrapone increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
- mipomersen
mipomersen increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
- momelotinib
momelotinib increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. When coadministered with momelotinib (BCRP inhibitor), initiate rosuvastatin (BCRP substrate) at 5 mg and not to exceed 10 mg once daily.
- nirmatrelvir
nirmatrelvir will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider temporary discontinuation of rosuvastatin during treatment with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir.
- nirmatrelvir/ritonavir
nirmatrelvir/ritonavir will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider temporary discontinuation of rosuvastatin during treatment with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir.
- ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC)
ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC) will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by decreasing hepatic clearance. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Maximum daily dose of rosuvastatin should be limited to 10 mg/day
- paclitaxel
paclitaxel increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- pazopanib
pazopanib increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- pioglitazone
pioglitazone increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- ponatinib
ponatinib increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- pretomanid
pretomanid will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Increase monitoring for drug-related adverse effects if pretomanid is coadministered with sensitive OATP1B3 or BCRP substrates.
- ranolazine
ranolazine increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- regorafenib
regorafenib will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Regorafenib likely inhibits BCRP (ABCG2) transport. Coadministration with a BCRP substrate may increase systemic exposure to the substrate and related toxicity.
- repaglinide
repaglinide increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- resmetirom
resmetirom will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Resmetirom inhibits BCRP and OAT1B1/3 transporters. Monitor for statin-related adverse reactions, including but not limited to elevation of liver tests, myopathy, and rhabdomyolysis. Limit daily dosage of statin as recommended.
- rifampin
rifampin increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- ritonavir
ritonavir will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rolapitant
rolapitant will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for adverse reactions when unable to avoid rolapitant coadministration with narrow therapeutic index BCRP substrates. Use the lowest effective dose of rosuvastatin.
- rosiglitazone
rosiglitazone increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- safinamide
safinamide will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Safinamide and its major metabolite may inhibit intestinal BCRP. Monitor BCRP substrates for increased pharmacologic or adverse effects.
- sodium bicarbonate
sodium bicarbonate decreases levels of rosuvastatin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Separate by 2 hours.
- sodium citrate/citric acid
sodium citrate/citric acid decreases levels of rosuvastatin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Separate by 2 hours.
- sofosbuvir/velpatasvir
sofosbuvir/velpatasvir will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Velpatasvir is an inhibitor of the drug transporter BCRP. Coadministration may increase systemic exposure of drugs that are BCRP substrates. Coadministration may significantly increase rosuvastatin serum concentration, which is associated with increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis. If coadministered, do not exceed rosuvastatin dose of 10 mg/day.
sofosbuvir/velpatasvir will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir with rosuvastatin may significantly increase the concentration of rosuvastatin, which may increase risk of myopathy,including rhabdomyolysis. Rosuvastatin may beadministered with sofosbuvir/velpatasvir at a dose that does not exceed 10 mg. - stiripentol
stiripentol will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Stiripentol is a BCRP transport inhibitor. Consider dosage reduction for BCRP substrates if adverse effects are experienced when coadministered.
- tafamidis
tafamidis will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Tafamidis inhibits breast cancer resistant protein (BCRP) in vitro and may increase exposure of BCRP substrates following tafamidis or tafamidis meglumine administration. Dosage adjustment of these BCRP substrates may be necessary.
- tafamidis meglumine
tafamidis meglumine will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Tafamidis inhibits breast cancer resistant protein (BCRP) in vitro and may increase exposure of BCRP substrates following tafamidis or tafamidis meglumine administration. Dosage adjustment of these BCRP substrates may be necessary.
- tenapanor
tenapanor decreases levels of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Tenapanor (an inhibitor of intestinal uptake transporter, OATP2B1) may reduce the exposure of OATP2B1 substrates.
- tipranavir
tipranavir increases levels of rosuvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. This interaction is the net effect of tipranavir being coadministered with ritonavir (boosted therapy); increased risk of myopathy including rhabdomyolysis; do not exceed rosuvastatin dose of 10 mg/day.
- vadadustat
vadadustat will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Do not exceed maximum rosuvastatin dose of 5 mg/day.
- warfarin
rosuvastatin increases effects of warfarin by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
Minor (12)
- coenzyme Q10
rosuvastatin decreases levels of coenzyme Q10 by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- colestipol
colestipol decreases levels of rosuvastatin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- erythromycin base
erythromycin base decreases levels of rosuvastatin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- erythromycin ethylsuccinate
erythromycin ethylsuccinate decreases levels of rosuvastatin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- erythromycin lactobionate
erythromycin lactobionate decreases levels of rosuvastatin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- erythromycin stearate
erythromycin stearate decreases levels of rosuvastatin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ethinylestradiol
rosuvastatin increases levels of ethinylestradiol by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- isradipine
isradipine decreases levels of rosuvastatin by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- mestranol
rosuvastatin increases levels of mestranol by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- orlistat
orlistat increases effects of rosuvastatin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- trazodone
trazodone increases levels of rosuvastatin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- voclosporin
voclosporin will increase the level or effect of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Information suggests voclosporin (an OATP1B1 inhibitor) may increase in the concentration of OATP1B1 substrates is possible. Monitor for adverse reactions of OATP1B1 substrates when coadministered with voclosporin.
Adverse Effects
>10%
Myalgia (3-13%)
1-10%
Arthralgia (10%)
Pharyngitis (9%)
Headache (3.1-8.5%)
Myalgia (7.6%)
Nausea (2.4-6.3%)
Asthenia (0.9-6.3%)
Constipation (2.1-4.7%)
Dizziness (4%)
Arthralgia (3.8%)
CPK increased (3%)
Diabetes mellitus (2.8%)
Abdominal pain (2%)
ALT increased (2%)
Flulike illness (2%)
UTI (2%)
<1%
Jaundice
Myopathy
Rhabdomyolysis
Postmarketing Reports
Arthralgia
Peripheral neuropathy
Depression and sleep disorders (including insomnia and nightmares)
Fatal and nonfatal hepatic failure, hepatitis, jaundice
Thrombocytopenia
Gynecomastia
Interstitial lung disease
Immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy
Cognitive impairment (eg, memory loss, forgetfulness, amnesia, memory impairment, confusion)
New-onset or exacerbation of myasthenia gravis, including ocular myasthenia
Warnings
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to drug or excipients
Acute liver failure or decompensated cirrhosis (including unexplained persistent elevations of LFTs)
Cautions
Nonserious and reversible cognitive adverse effects may occur
Increased blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels reported with statin intake; in some instances, these increases may exceed the threshold for the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus; optimize lifestyle measures, including regular exercise, maintaining healthy body weight, and making healthy food choices
Use caution in patients who consume large amounts of ethanol or have a history of liver disease
Interrupt therapy if serious hepatotoxicity with clinical symptoms and/or hyperbilirubinemia or jaundice occurs during treatment
Increases in AST or ALT reported with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors; monitor liver enzymes before initiating and if signs or symptoms of liver injury occur
Cases of myopathy [muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness associated with elevated creatine kinase (CK)] and rhabdomyolysis and rhabdomyolysis with acute renal failure secondary to myoglobinuria reported with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors; may occur at any dose level, but are increased at the highest dose (40 mg); caution in patients with predisposing factors for myopathy (eg, age ≥65 years, inadequately treated hypothyroidism, renal impairment)
Discontinue treatment if markedly elevated creatine kinase levels occur or myopathy is diagnosed or suspected; temporarily withhold in any patient with an acute, serious condition suggestive of myopathy or predisposing to the development of renal failure secondary to rhabdomyolysis (eg, sepsis; hypotension; dehydration; major surgery; trauma; severe metabolic, endocrine, or electrolyte disorders; uncontrolled seizures)
Pharmacokinetic studies demonstrated an ~2-fold elevation in median exposure (AUC and peak plasma concentrations) in Asian subjects when compared with a white control group
Hematuria and proteinuria reported without decrease in renal function; consider dosage reduction if unexplained hematuria and proteinuria persists
Rule out secondary causes of hyperlipidemia prior to initiating therapy
Risk factors for myopathy
- Risk factors for myopathy include age 65 years or greater, uncontrolled hypothyroidism, renal impairment, concomitant use with certain other drugs (including other lipid-lowering therapies), and higher dosage; Asian patients may be at higher risk for myopathy; the myopathy risk is greater in patients taking 40 mg daily compared with lower dosages
Steps to prevent or reduce risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis
- Concomitant use of this medication with cyclosporine or gemfibrozil not recommended; dosage modifications are recommended for patients taking certain antiviral medications, darolutamide, and regorafenib; niacin, fibrates, and colchicine may also increase risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis
- Discontinue therapy if markedly elevated CK levels occur or if myopathy is either diagnosed or suspected; muscle symptoms and CK elevations may resolve if therapy is discontinued
- Temporarily discontinue therapy in patients experiencing an acute or serious condition at high risk of developing renal failure secondary to rhabdomyolysis (eg, sepsis; shock; severe hypovolemia; major surgery; trauma; severe metabolic, endocrine, or electrolyte disorders; or uncontrolled epilepsy)
- Inform patients of risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis when starting or increasing dosage; instruct patients to promptly report any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness, particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever
Immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy
- Immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), an autoimmune myopathy, reported with statin use
- IMNM is characterized by muscle biopsy showing necrotizing myopathy without significant inflammation improvement with immunosuppressive agents, proximal muscle weakness, and elevated serum creatine kinase, which persist despite discontinuation of statin treatment
- Treatment with immunosuppressive agents may be required
- Advice all patients starting therapy or whose dose is being increased, about the risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis
- Patients should report promptly any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever or if muscle signs and symptoms persist after discontinuing therapy; additional neuromuscular and serologic testing may be necessary
- Therapy should be discontinued immediately if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected
- Discontinue therapy if markedly elevated creatine kinase (CK) levels occur or if myopathy diagnosed or suspected
- Therapy should be temporarily withheld in any patient experiencing an acute or serious condition predisposing to development of renal failure secondary to rhabdomyolysis, eg, sepsis; hypotension; dehydration; major surgery; trauma; severe metabolic, endocrine, and electrolyte disorders; or uncontrolled epilepsy
- Consider risk of IMNM carefully prior to initiation of a different statin
- If therapy is initiated with a different statin, monitor for signs and symptoms of IMNM
- Additional neuromuscular and serologic testing may be necessary
- Treatment with immunosuppressive agents may be required
- Consider risk of IMNM carefully prior to initiation of a different statin
- If therapy is initiated with a different statin, monitor for signs and symptoms of IMNM
Drug interactions overview
- Exercise caution when anticoagulants coadministered with rosuvastatin because of its potentiation of effect of coumarin-type anticoagulants in prolonging the prothrombin time/INR; monitor INR at baseline and frequently during concomitant therapy
- Cyclosporine and gemfibrozil increased rosuvastatin exposure and may result in increased risk of myopathy
- Coadministration of rosuvastatin with certain protease inhibitors has differing effects on rosuvastatin exposure and may increase risk of myopathy
- Risk of skeletal muscle effects may be enhanced when used in combination with lipid-modifying doses (≥1 g/day) of niacin; use with caution when administered with rosuvastatin
- Because the risk of myopathy during treatment with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors is increased with concomitant use of fenofibrates, use with caution
- Cases of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, reported with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors when coadministered with colchicine
- Also see Dosage Modifications
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
Discontinue therapy when pregnancy is recognized; alternatively, consider ongoing therapeutic needs of individual patient
Therapy decreases synthesis of cholesterol and possibly other biologically active substances derived from cholesterol; therefore, therapy may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant patients based on the mechanism of action
In addition, treatment of hyperlipidemia is not generally necessary during pregnancy; atherosclerosis is a chronic process and discontinuation of lipid-lowering drugs during pregnancy should have little impact on outcome of long-term therapy of primary hyperlipidemia for most patients
Available data from case series and prospective and retrospective observational cohort studies over decades of use with statins in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major congenital malformations
Published data from prospective and retrospective observational cohort studies with rosuvastatin use in pregnant women are insufficient to determine if there is a drug-associated risk of miscarriage
Animal data
- In animal reproduction studies, no adverse developmental effects were observed in pregnant rats or rabbits orally administered rosuvastatin during period of organogenesis at doses that resulted in systemic exposures equivalent to human exposures at maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 40 mg/day, based on AUC and body surface area (mg/m2) respectively
Lactation
Limited data from case reports in published literature indicate that rosuvastatin is present in human milk
There is no available information on effects of drug on breastfed infant or effects on milk production; statins, decrease cholesterol synthesis and possibly synthesis of other biologically active substances derived from cholesterol and may cause harm to breastfed infant.
Because of potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infant; based on mechanism of action, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during therapy
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor; inhibits the rate-limiting step in cholesterol biosynthesis by competitively inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase
Absorption
Bioavailability: 20%
Peak plasma time: 3-5 hr
Distribution
Vd: 134 L
Protein bound: 88%
Metabolism
Metabolism: ~10% by hepatic CYP2C9
Metabolites: N-desmethyl, lactone
Elimination
Half-Life, Elimination: 19 hr
Excretion: Feces (90%)
Pharmacogenomics
Hepatic influx and efflux transporters (single-nucleotide polymorphisms [SNPs] within the solute carrier organic anion transporter 1B1 (SLCO1B1) gene, encoding the organic anion transporter polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1) influx transporter)
SLCO1B1 (OATP1B1) CC genotype significantly increases AUCs of parent drug and metabolites compared with the CT or TT genotypes
This polymorphism is proposed to reduced transport into the liver, the main site of statin metabolism and elimination, resulting in elevated plasma concentrations
SLCO1B1 polymorphism is thought to have a lesser effect on the more hydrophilic statins (eg, rosuvastatin, fluvastatin) compared with those that are more lipophilic (eg, atorvastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin)
Other genetic polymorphisms of elimination (eg, CYP450, P-glycoprotein) for each individual drug must also be considered, to explain variability for statin clearance among patients that exhibit SCLO1B1 polymorphism
SLCO1B1 CC genotype is most common in Caucasians and Asians (15%); decrease dose by 50% in people of Asian descent
Risk of myopathy is 2.6- to 4.3-fold higher if the C allele is present and 16.9-fold higher in CC homozygotes than in TT homozygotes
Genetic testing laboratories
- Optivia Biotechnology, Inc (http://optiviabio.com)
Administration
Oral Administration
Take with or without food
Tablets: Swallow whole
Capsules
- Swallow whole; do not crush or chew
For patients who have difficulty swallowing capsules
- May open capsule and carefully empty granules onto 1 tsp of applesauce; swallow immediately, without chewing
- Do not store mixture for future use
- If not used in its entirety, discard remaining contents immediately
Nasogastric Tube Administration
Open capsule and empty granules into a 60-mL catheter-tipped syringe and add 40 mL of water
Shake syringe vigorously for 15 seconds; granules may start dissolving which is acceptable
Attach syringe to a nasogastric tube (≥16-French) and deliver contents of syringe through nasogastric tube
After administering granules, flush nasogastric tube with 20 mL of additional water
Use immediately after preparation and do not store for future use
If not used in its entirety, discard remaining contents immediately
Use with any other liquids is not recommended
Storage
Capsules and tablets: Store at 20-25°C (68-77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F)
Protect from moisture
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crestor oral - | 20 mg tablet |  | |
| Crestor oral - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Crestor oral - | 40 mg tablet |  | |
| Crestor oral - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Crestor oral - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Crestor oral - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Crestor oral - | 40 mg tablet |  | |
| Crestor oral - | 20 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 40 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 20 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 40 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 20 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 20 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 20 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 40 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 40 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 40 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 40 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 20 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 20 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 40 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 20 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 20 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 40 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 40 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 20 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 40 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 40 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 20 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 10 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 40 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet |  | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 20 mg tablet | 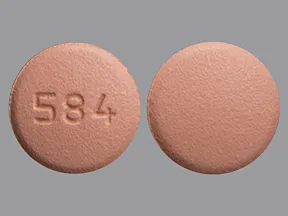 | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 10 mg tablet | 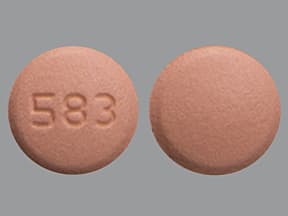 | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 5 mg tablet | 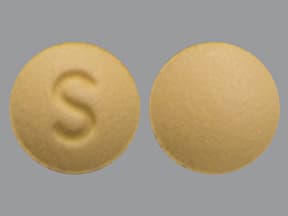 | |
| Rosuvastatin (Crestor) - | 40 mg tablet |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
Rosuvastatin (Crestor)
ROSUVASTATIN - ORAL
(roe-SUE-vuh-stah-tin)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Crestor, Ezallor Sprinkle
USES: Rosuvastatin is used along with a proper diet to help lower "bad" cholesterol and fats (such as LDL, triglycerides) and raise "good" cholesterol (HDL) in the blood. It belongs to a group of drugs known as "statins." It works by reducing the amount of cholesterol made by the liver. Lowering "bad" cholesterol and triglycerides and raising "good" cholesterol decreases the risk of heart disease and helps to prevent strokes and heart attacks.In addition to eating a proper diet (such as a low cholesterol/low-fat diet), other lifestyle changes that may help this medication work better include exercising, losing weight if overweight, and stopping smoking. Talk with your doctor for more details.
HOW TO USE: Read the Patient Information Leaflet if available from your pharmacist before you start taking rosuvastatin and each time you get a refill. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.Take this medication by mouth with or without food as directed by your doctor, usually once daily.If you are taking the capsule form of this medication, swallow the capsules whole. Do not crush or chew the capsules. If you have trouble swallowing the capsules, read and follow the manufacturer's Instructions for Use leaflet. You may carefully open the capsule and sprinkle the contents on 1 teaspoonful of soft food (such as applesauce, or chocolate- or vanilla-flavored pudding). Swallow all of the mixture without chewing. Use/discard the mixture within 60 minutes. Do not prepare a supply in advance.The dosage is based on your medical condition, response to treatment, age, race, and other medications you may be taking. Be sure to tell your doctor and pharmacist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products). If you are of Asian descent, your doctor may direct you to start with a lower dose because you may be more sensitive to its effects.Antacids containing aluminum or magnesium can reduce the absorption of this drug. If taking this type of antacid, take it at least 2 hours after this medication.Take this medication regularly in order to get the most benefit from it. Remember to take it at the same time each day. Keep taking this medication even if you feel well. Most people with high cholesterol or triglycerides do not feel sick.It is very important to continue to follow your doctor's advice about diet and exercise. It may take up to 4 weeks before you get the full benefit of this drug.
SIDE EFFECTS: Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.A very small number of people taking rosuvastatin may have mild memory problems or confusion. If these rare effects occur, talk to your doctor.Rarely, statins may cause or worsen diabetes. Talk to your doctor about the benefits and risks.Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: foamy urine.This drug may rarely cause muscle problems (which can rarely lead to very serious conditions called rhabdomyolysis and autoimmune myopathy). Tell your doctor right away if you develop any of these symptoms during treatment and if these symptoms last after your doctor stops this drug: muscle pain/tenderness/weakness (especially with fever or unusual tiredness), signs of kidney problems (such as change in the amount of urine).This medication may rarely cause liver problems. Tell your doctor right away if you develop symptoms of liver problems, including: nausea/vomiting that doesn't stop, yellowing eyes/skin, dark urine, stomach/abdominal pain.A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), dizziness, trouble breathing.This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: Before taking rosuvastatin, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: liver disease, kidney disease, alcohol use.Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).Limit alcoholic beverages. Daily use of alcohol may increase your risk for liver problems, especially when combined with rosuvastatin. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects of this drug, especially muscle problems.During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. It may harm an unborn baby. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.This medication passes into breast milk. Because of the possible risk to the infant, breastfeeding is not recommended while using this medication. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: See also How to Use section.Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.Some products that may interact with this drug include: daptomycin, gemfibrozil.Other medications can affect the removal of rosuvastatin from your body, which may affect how rosuvastatin works. Examples include ledipasvir, sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir, among others.Do not take any red yeast rice products while you are taking rosuvastatin because some red yeast rice products may also contain a statin called lovastatin. Taking rosuvastatin and red yeast rice products together can increase your risk of serious muscle and liver problems.
OVERDOSE: If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others.Lab and/or medical tests (such as blood cholesterol/triglyceride levels, liver function) should be done while you are taking this medication. Keep all medical and lab appointments. Consult your doctor for more details.
MISSED DOSE: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is within 12 hours of the next dose, skip the missed dose. Take your next dose at the regular time. Do not double the dose to catch up.
STORAGE: Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Information last revised February 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.







