Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
capsule, delayed-release
- 20mg (Cymbalta, Drizalma Sprinkle, generic)
- 30mg (Cymbalta, Drizalma Sprinkle, generic)
- 40mg (Drizalma Sprinkle, Irenka)
- 60mg (Cymbalta, Drizalma Sprinkle, generic)
Major Depressive Disorder
Indicated for major depressive disorder (MDD)
40-60 mg/day PO initially (in single daily dose or divided q12hr for 1 week if patient needs to adjust to therapy)
Consider starting at 30 mg qDay for 1 week to allow for therapy adjustment before increasing to 60 mg qDay
Target dosage: 60 mg/day PO; not to exceed 120 mg/day
There is no evidence that doses > 60 mg/day confer additional benefit
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain
Indicated for diabetic peripheral neuropathy/neuropathic pain
60 mg PO qDay initially (in single daily dose or divided q12hr); consider lowering initial dose if tolerability is a concern
Target dosage: 60 mg/day PO; not to exceed 60 mg/day
There is no evidence that doses >60 mg/day confer additional benefit
Consider a lower starting dosage and gradually increase dose for patients with renal impairment
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Indicated for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
Age <65 years: 60 mg PO qDay initially
Consider starting at 30 mg qDay for 1 week to allow for therapy adjustment before increasing to 60 mg qDay
Target dosage: 60 mg/day PO qDay
May increase dose in increments of 30 mg qDay; not to exceed 120 mg/day
No additional benefit shown with doses >60 mg/day
Fibromyalgia
Indicated for fibromyalgia
30 mg PO qDay initially for 1 week to allow for therapy adjustment before increasing to 60 mg qDay
Target dosage: 60 mg PO qDay; not to exceed 60 mg/day; no additional benefit shown with doses >60 mg
Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain
Indicated for chronic musculoskeletal pain, including discomfort from osteoarthritis and chronic lower back pain
30 mg PO qDay initially for 1 week to allow for therapy adjustment before increasing to 60 mg qDay
Target dosage: 60 mg/day PO; not to exceed 60 mg/day
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment
- Mild-to-moderate (CrCl 30-80 mL/min): Population PK analyses suggest that no significant effect on duloxetine apparent clearance
- Severe (CrCl <30 mL/min): Avoid use
- End-stage renal disease (ESRD): Limited data; peak plasma concentration and AUC were 100% greater for patients with ESRD receiving chronic hemodialysis
Hepatic impairment
- Avoid use with all degrees of hepatic impairment
Potent CYP1A2 inhibitors
- Avoid coadministration
Dosing Considerations
Uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma: Use not recommended due to increased risk of mydriasis
Monitoring parameters
- Before initiating treatment, screen for a personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania
-
GAD and MDD
- Periodically reassess to determine the continued need for maintenance treatment and appropriate dosage for such treatment
Discontinuation
- Gradually reduce dosage
- Abrupt discontinuance may result in symptoms (eg, dizziness, nausea, headache, paresthesia, fatigue, vomiting, irritability, insomnia, diarrhea, anxiety, hyperhidrosis)
Switching to and from a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI)
- Wait ≥14 days after discontinuing MAOI to initiate duloxetine therapy
- Wait ≥5 days after discontinuing duloxetine therapy to initiate MAOI therapy
Other MAO-Is (linezolid or methylene blue)
- Do not start duloxetine in a patients with linezolid or IV methylene blue due to the potential risk of serotonin syndrome
- Patients who requires more urgent treatment of a psychiatric condition: Consider other interventions, including hospitalization
- If linezolid or IV methylene blue must be administered, discontinue duloxetine immediately; monitor for symptoms of serotonin syndrome for 5 days or until 24 hr after the last dose of linezolid or IV methylene blue, whichever comes first
- Resume duloxetine 24 hr after the last dose of linezolid or IV methylene blue
- Risk of administering methylene blue by non-IV routes (eg, oral tablets, by local injection) or in IV doses <1 mg/kg with duloxetine is unclear; be aware of potential risk of serotonin syndrome with such use
Dosage Forms & Strengths
capsule, delayed-release
- 20mg (Cymbalta, Drizalma Sprinkle, generic)
- 30mg (Cymbalta, Drizalma Sprinkle, generic)
- 40mg (Drizalma Sprinkle, Irenka)
- 60mg (Cymbalta, Drizalma Sprinkle, generic)
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Indicated for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in adults and pediatric patients aged ≥7 years
7-17 years
- 30 mg/day PO qDay initially; after 2 weeks; recommended dose range 30-60 qDay
- May benefit from doses >60 mg/day; if increased >60 mg/day, use increments of 30 mg/day
- Maximum dose studied was 120 mg/day
Fibromyalgia
Cymbalta only
Indicated for fibromyalgia in adolescents aged 13-17 yr
<13 years: Safety and efficacy not established
13-17 years
- 30 mg PO qDay; may increase to 60 mg PO qDay based on response and tolerability
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment
- Mild-to-moderate (CrCl 30-80 mL/min): Population PK analyses suggest that no significant effect on duloxetine apparent clearance
- Severe (CrCl <30 mL/min): Avoid use
- End-stage renal disease (ESRD): Limited data; peak plasma concentration and AUC were 100% greater for patients with ESRD receiving chronic hemodialysis
Hepatic impairment
- Avoid use with all degrees of hepatic impairment
Dosing Considerations
Monitoring parameters
- Before initiating treatment, screen for a personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania
-
GAD and MDD
- Periodically reassess to determine the continued need for maintenance treatment and appropriate dosage for such treatment
Discontinuation
- Gradually reduce dosage
- Abrupt discontinuance may result in symptoms (eg, dizziness, nausea, headache, paresthesia, fatigue, vomiting, irritability, insomnia, diarrhea, anxiety, hyperhidrosis)
Switching to and from a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI)
- Wait ≥14 days after discontinuing MAOI to initiate duloxetine therapy
- Wait ≥5 days after discontinuing duloxetine therapy to initiate MAOI therapy
Other MAO-Is (linezolid or methylene blue)
- Do not start duloxetine in patients taking linezolid or IV methylene blue owing to potential risk of serotonin syndrome
- Patients who requires more urgent treatment of a psychiatric condition: Consider other interventions, including hospitalization
- If linezolid or IV methylene blue must be administered, discontinue duloxetine immediately; monitor for symptoms of serotonin syndrome for 5 days or until 24 hr after the last dose of linezolid or IV methylene blue, whichever comes first
- Resume duloxetine 24 hr after the last dose of linezolid or IV methylene blue
- Risk of administering methylene blue by non-IV routes (eg, oral tablets, by local injection) or in IV doses much <1 mg/kg with duloxetine is unclear; be aware of potential risk of serotonin syndrome with such use
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Indicated for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
≥65 years: 30 mg/day PO qDay initially; after 2 weeks, consider increasing to target dose of 60 mg/day
May benefit from doses >60 mg/day; if increased >60 mg/day, use increments of 30 mg/day
Maximum dose studied was 120 mg/day
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results

Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor

Contraindicated (8)
- eliglustat
duloxetine increases levels of eliglustat by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Contraindicated. If coadministered with strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors, reduce eliglustat dose from 84 mg BID to 84 mg once daily in extensive and intermediate metabolizers; eliglustat is contraindiated if strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors are given concomitantly with strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors.
- iobenguane I 123
duloxetine decreases effects of iobenguane I 123 by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. If clinically appropriate, discontinue drugs that decrease uptake of NE for at least 5 half-lives; may cause false-negative imaging results.
- isocarboxazid
isocarboxazid and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated.
- phenelzine
phenelzine and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated.
- procarbazine
procarbazine and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated. Combination is contraindicated within 2 weeks of MAOI use.
- safinamide
duloxetine, safinamide. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Contraindicated. Concomitant use could result in life-threatening serotonin syndrome.
- selegiline
selegiline and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated. At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of selegiline and initiation of treatment with a serotonergic drug.
- tranylcypromine
tranylcypromine and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated.
Serious - Use Alternative (81)
- amitriptyline
duloxetine and amitriptyline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- amobarbital
amobarbital will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- amoxapine
duloxetine and amoxapine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- apixaban
duloxetine and apixaban both increase anticoagulation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- armodafinil
armodafinil will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- artemether/lumefantrine
artemether/lumefantrine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- bupropion
duloxetine increases toxicity of bupropion by unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. May lower seizure threshold; keep bupropion dose as low as possible.
- buspirone
duloxetine and buspirone both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- butabarbital
butabarbital will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- butalbital
butalbital will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- carbamazepine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- cigarette smoking
cigarette smoking will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- cimetidine
cimetidine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- citalopram
citalopram and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Combination may increase risk of serotonin syndrome or neuroleptic malignant syndrome-like reactions.
- clomipramine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of clomipramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
duloxetine and clomipramine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - cyclobenzaprine
duloxetine and cyclobenzaprine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dacomitinib
dacomitinib will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid use with CYP2D6 substrates where minimal increases in concentration of the CYP2D6 substrate may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities.
- desipramine
duloxetine and desipramine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- desvenlafaxine
duloxetine and desvenlafaxine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dextromethorphan
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of dextromethorphan by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
duloxetine and dextromethorphan both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - dolasetron
dolasetron, duloxetine. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dosulepin
duloxetine and dosulepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- doxepin
duloxetine and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fluoxetine
fluoxetine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
duloxetine and fluoxetine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - fluvoxamine
fluvoxamine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
fluvoxamine and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - givosiran
givosiran will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of sensitive CYP1A2 substrates with givosiran. If unavoidable, decrease the CYP1A2 substrate dosage in accordance with approved product labeling.
givosiran will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of sensitive CYP2D6 substrates with givosiran. If unavoidable, decrease the CYP2D6 substrate dosage in accordance with approved product labeling. - granisetron
granisetron, duloxetine. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- imipramine
duloxetine and imipramine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- iobenguane I 131
duloxetine will decrease the level or effect of iobenguane I 131 by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Based on the mechanism of action of iobenguane, drugs that reduce catecholamine uptake or that deplete catecholamine stores may interfere with iobenguane uptake into cells, and thus, reduce iobenguane efficacy. Discontinue interfering drugs for at least 5 half-lives before administration of either the dosimetry or an iobenguane dose. Do not administer these drugs until at least 7 days after each iobenguane dose.
- leniolisib
leniolisib will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid leniolisib with CYP1A2 substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index
- levomilnacipran
duloxetine and levomilnacipran both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- linezolid
linezolid and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Linezolid may increase serotonin as a result of MAO-A inhibition. If linezolid must be administered, discontinue serotonergic drug immediately and monitor for CNS toxicity. Serotonergic therapy may be resumed 24 hours after last linezolid dose or after 2 weeks of monitoring, whichever comes first.
- lofepramine
duloxetine and lofepramine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lorcaserin
duloxetine and lorcaserin both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lumefantrine
lumefantrine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- maprotiline
duloxetine and maprotiline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- meperidine
duloxetine and meperidine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- methylene blue
methylene blue and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Methylene blue may increase serotonin as a result of MAO-A inhibition. If methylene blue must be administered, discontinue serotonergic drug immediately and monitor for CNS toxicity. Serotonergic therapy may be resumed 24 hours after last methylene blue dose or after 2 weeks of monitoring, whichever comes first.
- metoclopramide
metoclopramide and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Additive effects; increased risk for serotonin syndrome, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, dystonia, or other extrapyramidal reactions
- metoclopramide intranasal
duloxetine, metoclopramide intranasal. Either increases effects of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Avoid use of metoclopramide intranasal or interacting drug, depending on importance of drug to patient.
- mexiletine
mexiletine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- milnacipran
duloxetine and milnacipran both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nefazodone
duloxetine and nefazodone both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- netupitant/palonosetron
netupitant/palonosetron, duloxetine. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nortriptyline
duloxetine and nortriptyline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- olopatadine intranasal
duloxetine and olopatadine intranasal both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration increases risk of CNS depression, which can lead to additive impairment of psychomotor performance and cause daytime impairment.
- ondansetron
ondansetron, duloxetine. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ozanimod
ozanimod increases toxicity of duloxetine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Because the active metabolite of ozanimod inhibits MAO-B in vitro, there is a potential for serious adverse reactions, including hypertensive crisis. Therefore, coadministration of ozanimod with drugs that can increase norepinephrine or serotonin is not recommended. Monitor for hypertension with concomitant use.
- palonosetron
palonosetron, duloxetine. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- paroxetine
paroxetine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
duloxetine and paroxetine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - pefloxacin
pefloxacin will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- peginterferon alfa 2a
peginterferon alfa 2a will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pentobarbital
pentobarbital will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- phenobarbital
phenobarbital will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- phentermine
duloxetine, phentermine. Either increases toxicity of the other by Mechanism: unknown. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of serotonin syndrome.
- pipemidic acid
pipemidic acid will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- primidone
primidone will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- protriptyline
duloxetine and protriptyline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pseudoephedrine
duloxetine increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- quinidine
quinidine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- rasagiline
rasagiline and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Severe CNS toxicity associated with hyperpyrexia has been reported with the combined treatment of an antidepressant and rasagiline. Avoid combination within 14 days of MAOI use.
- rifampin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- ropeginterferon alfa 2b
ropeginterferon alfa 2b and duloxetine both increase Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Narcotics, hypnotics or sedatives can produce additive neuropsychiatric side effects. Avoid use and monitor patients receiving the combination for effects of excessive CNS toxicity.
- secobarbital
secobarbital will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- selegiline transdermal
selegiline transdermal and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- sertraline
sertraline will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
duloxetine and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - smoking
smoking will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- St John's Wort
duloxetine and St John's Wort both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tedizolid
tedizolid, duloxetine. Either increases effects of the other by Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. both increase serotonin levels; increased risk of serotonin syndrome.
- thioridazine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of thioridazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Contraindicated.
thioridazine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Contraindicated. - tipranavir
tipranavir will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tobacco use
tobacco use will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tramadol
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of tramadol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- trazodone
duloxetine and trazodone both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- trimipramine
duloxetine and trimipramine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- venlafaxine
duloxetine and venlafaxine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- verapamil
verapamil will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- vilazodone
duloxetine, vilazodone. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant therapy should be discontinued immediately if signs or symptoms of serotonin syndrome emerge and supportive symptomatic treatment should be initiated. .
- vortioxetine
duloxetine, vortioxetine. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- zileuton
zileuton will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- zuranolone
duloxetine, zuranolone. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of zuranolone with other CNS depressants may increase impairment of psychomotor performance or CNS depressant effects. If unavoidable, consider dose reduction. .
Monitor Closely (166)
- 5-HTP
duloxetine and 5-HTP both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- abiraterone
abiraterone increases levels of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid coadministration of abiraterone with substrates of CYP2D6. If alternative therapy cannot be used, exercise caution and consider a dose reduction of the CYP2D6 substrate.
- aceclofenac
duloxetine, aceclofenac. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- acemetacin
duloxetine, acemetacin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- almotriptan
almotriptan and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- amifostine
amifostine, duloxetine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of orthostatic hypotension.
- amiodarone
amiodarone will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- asenapine
asenapine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- aspirin
duloxetine, aspirin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- aspirin rectal
duloxetine, aspirin rectal. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate
duloxetine, aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- atomoxetine
duloxetine increases levels of atomoxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- benazepril
duloxetine, benazepril. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Enhanced hypotensive effects.
- benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hydromorphone (<3% of the circulating parent hydrocodone [benzhydrocodone is prodrug of hydrocodone]) is mainly formed by CYP2D6 mediated O-demethylation of hydrocodone. Hydromorphone may contribute to the total analgesic effect of hydrocodone.
benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen, duloxetine. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system may result in serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dose adjustment. - brexpiprazole
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of brexpiprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administer a quarter of brexpiprazole dose if coadministered with a moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor PLUS a strong/moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor.
- buprenorphine subdermal implant
duloxetine, buprenorphine subdermal implant. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use could result in life-threatening serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation, and during dose adjustment of the serotonergic drug. Discontinue buprenorphine if serotonin syndrome is suspected.
- buprenorphine, long-acting injection
duloxetine, buprenorphine, long-acting injection. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use could result in life-threatening serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation, and during dose adjustment of the serotonergic drug. Discontinue buprenorphine if serotonin syndrome is suspected.
- bupropion
bupropion will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cannabidiol
cannabidiol, duloxetine. affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Owing to the potential for both CYP1A2 induction and inhibition with the coadministration of CYP1A2 substrates and cannabidiol, consider reducing dosage adjustment of CYP1A2 substrates as clinically appropriate.
- captopril
captopril increases effects of duloxetine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Blood pressure lowering drugs may enhance the hypotensive effect of duloxetine. Monitor blood pressure.
- celecoxib
celecoxib will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
duloxetine, celecoxib. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets. - cenobamate
cenobamate, duloxetine. Either increases effects of the other by sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- choline magnesium trisalicylate
duloxetine, choline magnesium trisalicylate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- cimetidine
cimetidine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ciprofloxacin
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of CYP1A2 inhibiting quinolones with duloxetine may lead to significant increases in duloxetine levels, AUC, and half-life. Consider therapy modification if duloxetine is necessary.
- clobazam
clobazam will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Lower doses of drugs metabolized by CYP2D6 may be required when used concomitantly.
- clopidogrel
duloxetine increases effects of clopidogrel by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. SNRIs affect platelet activation; coadministration of SNRIs with clopidogrel may increase the risk of bleeding.
- cocaine topical
duloxetine and cocaine topical both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- codeine
duloxetine decreases effects of codeine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Prevents conversion of codeine to its active metabolite morphine.
- cyproheptadine
cyproheptadine decreases effects of duloxetine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Cyproheptadine may diminish the serotonergic effect of SNRIs.
- daridorexant
duloxetine and daridorexant both increase sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration increases risk of CNS depression, which can lead to additive impairment of psychomotor performance and cause daytime impairment.
- darifenacin
darifenacin will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- deferasirox
deferasirox increases levels of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- desipramine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of desipramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- desvenlafaxine
desvenlafaxine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Desvenlafaxine inhibits CYP2D6; with higher desvenlafaxine doses (ie, 400 mg) decrease the CYP2D6 substrate dose by up to 50%; no dosage adjustment needed with desvenlafaxine doses <100 mg
- dexfenfluramine
duloxetine and dexfenfluramine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dextroamphetamine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of dextroamphetamine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
duloxetine and dextroamphetamine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - dextroamphetamine transdermal
duloxetine, dextroamphetamine transdermal. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Initiate with lower doses and monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, particularly during initiation or dosage increase. If serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue dextroamphetamine transdermal and concomitant serotonergic drug(s).
- diazepam intranasal
diazepam intranasal, duloxetine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration may potentiate the CNS-depressant effects of each drug.
- dichlorphenamide
dichlorphenamide and duloxetine both decrease serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diclofenac
duloxetine, diclofenac. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- difelikefalin
difelikefalin and duloxetine both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diflunisal
duloxetine, diflunisal. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- dihydroergotamine
duloxetine and dihydroergotamine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dihydroergotamine intranasal
duloxetine and dihydroergotamine intranasal both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- diphenhydramine
diphenhydramine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dronedarone
dronedarone will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eletriptan
eletriptan and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- eliglustat
eliglustat increases levels of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor therapeutic drug concentrations, as indicated, or consider reducing the dosage of the concomitant drug and titrate to clinical effect.
- elranatamab
elranatamab will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Elranatamab causes cytokine release syndrome (CRS) that may suppress activity of CYP enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP substrates. This is more likely to occur from initiation of elranatamab step-up dosing up to 14 days after the first treatment dose and during and after CRS.
- eluxadoline
duloxetine increases levels of eluxadoline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. As a precautionary measure due to incomplete information on the metabolism of eluxadoline, use caution when coadministered with strong CYP1A2 inhibitors.
- elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF
elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF increases levels of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Cobicistat is a CYP2D6 inhibitor; caution with CYP2D6 substrates for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events.
- epcoritamab
epcoritamab, duloxetine. affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Epcoritamab causes release of cytokines that may suppress activity of CYP enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP substrates. For certain CYP substrates, minimal changes in their concentration may lead to serious adverse reactions. If needed, modify therapy as recommended in the substrate's prescribing information. .
- ergotamine
duloxetine and ergotamine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- escitalopram
duloxetine and escitalopram both increase serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor.
- esomeprazole
esomeprazole will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ethanol
ethanol, duloxetine. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hepatotoxicity.
- etodolac
duloxetine, etodolac. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- fedratinib
fedratinib will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Adjust dose of drugs that are CYP2D6 substrates as necessary.
- fenbufen
duloxetine, fenbufen. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- fenfluramine
duloxetine and fenfluramine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
fenfluramine, duloxetine. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with drugs that increase serotoninergic effects may increase the risk of serotonin syndrome. - fenoprofen
duloxetine, fenoprofen. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- fesoterodine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of fesoterodine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fexinidazole
fexinidazole will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fish oil triglycerides
fish oil triglycerides will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. Prolonged bleeding reported in patients taking antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants and oral omega-3 fatty acids. Periodically monitor bleeding time in patients receiving fish oil triglycerides and concomitant antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants.
- flurbiprofen
duloxetine, flurbiprofen. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- frovatriptan
frovatriptan and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- gabapentin
gabapentin, duloxetine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of CNS depressants can result in serious, life-threatening, and fatal respiratory depression. Use lowest dose possible and monitor for respiratory depression and sedation.
- gabapentin enacarbil
gabapentin enacarbil, duloxetine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of CNS depressants can result in serious, life-threatening, and fatal respiratory depression. Use lowest dose possible and monitor for respiratory depression and sedation.
- ganaxolone
duloxetine and ganaxolone both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- gepirone
gepirone and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for symptoms of serotonin syndrome when gepirone is used gepirone with other drugs that may affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter systems. If serotonin syndrome occurs, consider discontinue gepirone and/or concomitant serotonergic drug.
- glofitamab
glofitamab, duloxetine. affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Glofitamab causes release of cytokines that may suppress activity of CYP enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP substrates. For certain CYP substrates, minimal changes in their concentration may lead to serious adverse reactions. If needed, modify therapy as recommended in the substrate's prescribing information. .
- green tea
green tea, duloxetine. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Combination may increase risk of bleeding.
- hydrocodone
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of hydrocodone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hydromorphone (<3% of the circulating parent hydrocodone) is mainly formed by CYP2D6 mediated O-demethylation of hydrocodone. Hydromorphone may contribute to the total analgesic effect of hydrocodone.
hydrocodone, duloxetine. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system may result in serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dose adjustment. - hydromorphone
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of hydromorphone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ibrutinib
ibrutinib will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. Ibrutinib may increase the risk of hemorrhage in patients receiving antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapies and monitor for signs of bleeding.
- ibuprofen
duloxetine, ibuprofen. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- ibuprofen IV
duloxetine, ibuprofen IV. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- imatinib
imatinib will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- imipramine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of imipramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- indomethacin
duloxetine, indomethacin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- isoniazid
duloxetine and isoniazid both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ketoprofen
duloxetine, ketoprofen. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- ketorolac
duloxetine, ketorolac. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- ketorolac intranasal
duloxetine, ketorolac intranasal. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- L-tryptophan
duloxetine and L-tryptophan both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- lasmiditan
lasmiditan, duloxetine. Either increases effects of the other by sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of lasmiditan and other CNS depressant drugs, including alcohol have not been evaluated in clinical studies. Lasmiditan may cause sedation, as well as other cognitive and/or neuropsychiatric adverse reactions.
duloxetine increases effects of lasmiditan by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration may increase risk of serotonin syndrome. - lemborexant
lemborexant, duloxetine. Either increases effects of the other by sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Dosage adjustment may be necessary if lemborexant is coadministered with other CNS depressants because of potentially additive effects.
- lisdexamfetamine
duloxetine, lisdexamfetamine. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Initiate with lower doses and monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, particularly during initiation or dosage increase. If serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue along with concomitant serotonergic drug(s).
- lithium
duloxetine and lithium both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- lofepramine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of lofepramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lonapegsomatropin
lonapegsomatropin will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Limited published data indicate that growth hormone treatment increases cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-mediated antipyrine clearance. Caution with sensitive CYP substrates
- lorcaserin
lorcaserin will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lornoxicam
duloxetine, lornoxicam. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- lsd
duloxetine and lsd both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- lurasidone
lurasidone, duloxetine. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Potential for increased CNS depressant effects when used concurrently; monitor for increased adverse effects and toxicity.
- maraviroc
maraviroc will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- marijuana
marijuana will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- meclofenamate
duloxetine, meclofenamate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- mefenamic acid
duloxetine, mefenamic acid. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- meloxicam
duloxetine, meloxicam. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- methamphetamine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of methamphetamine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- metoprolol
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of metoprolol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mexiletine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of mexiletine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- midazolam intranasal
midazolam intranasal, duloxetine. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Concomitant use of barbiturates, alcohol, or other CNS depressants may increase risk of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, desaturation, or apnea and may contribute to profound and/or prolonged drug effect.
- mirabegron
mirabegron will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mirtazapine
duloxetine and mirtazapine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- morphine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of morphine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
duloxetine and morphine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - nabumetone
duloxetine, nabumetone. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- naproxen
duloxetine, naproxen. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- naratriptan
naratriptan and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- nebivolol
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of nebivolol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nilotinib
nilotinib will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nortriptyline
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of nortriptyline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- olanzapine/samidorphan
duloxetine, olanzapine/samidorphan. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of diazepam, alcohol, or other CNS acting drugs may potentiate orthostatic hypotension observed with olanzapine. Additive sedation may also occur.
- oliceridine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of oliceridine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. If concomitant use is necessary, may require less frequent oliceridine dosing. Closely monitor for respiratory depression and sedation and titrate subsequent doses accordingly. If inhibitor is discontinued, consider increase oliceridine dosage until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal.
duloxetine, oliceridine. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - oxaprozin
duloxetine, oxaprozin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- oxycodone
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of oxycodone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oxymorphone
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of oxymorphone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- parecoxib
parecoxib will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
duloxetine, parecoxib. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets. - peginterferon alfa 2b
peginterferon alfa 2b, duloxetine. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: When patients are administered peginterferon alpha-2b with CYP2D6 substrates, the therapeutic effect of these drugs may be altered. Peginterferon alpha-2b may increase or decrease levels of CYP2D6 substrate.
- pentazocine
duloxetine and pentazocine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- perphenazine
perphenazine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- piroxicam
duloxetine, piroxicam. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- pregabalin
pregabalin, duloxetine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of CNS depressants can result in serious, life-threatening, and fatal respiratory depression. Use lowest dose possible and monitor for respiratory depression and sedation.
- propafenone
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of propafenone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
propafenone will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - propranolol
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of propranolol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quinacrine
quinacrine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ranolazine
ranolazine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- remifentanil
remifentanil increases toxicity of duloxetine by serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Increases risk of serotonin syndrome.
- remimazolam
remimazolam, duloxetine. Either increases toxicity of the other by sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and/or death. Continuously monitor vital signs during sedation and recovery period if coadministered. Carefully titrate remimazolam dose if administered with opioid analgesics and/or sedative/hypnotics.
- risperidone
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of risperidone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ritlecitinib
ritlecitinib will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Ritlecitinib inhibits CYP1A2 substrates; coadministration increases AUC and peak plasma concentration sensitive substrates, which may increase risk of adverse reactions. Additional monitoring and dosage adjustment may be needed in accordance with product labeling of CYP1A2 substrates.
- ritonavir
ritonavir will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rivaroxaban
duloxetine increases toxicity of rivaroxaban by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. May enhance the antiplatelet effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents.
- rizatriptan
rizatriptan and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- rolapitant
rolapitant will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Rolapitant may increase plasma concentrations of CYP2D6 substrates for at least 28 days following rolapitant administration.
- rucaparib
rucaparib will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Adjust dosage of CYP1A2 substrates, if clinically indicated.
- salicylates (non-asa)
duloxetine, salicylates (non-asa). Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- salsalate
duloxetine, salsalate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- SAMe
duloxetine and SAMe both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- sodium sulfate/potassium chloride/magnesium sulfate/polyethylene glycol
duloxetine, sodium sulfate/potassium chloride/magnesium sulfate/polyethylene glycol. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Caution when bowel preps are used with drugs that cause SIADH or NSAIDs; increased risk for water retention or electrolyte imbalance.
- somapacitan
somapacitan will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Limited published data indicate that growth hormone treatment increases cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-mediated antipyrine clearance. Caution with sensitive CYP substrates
- somatrogon
somatrogon will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Limited published data indicate that growth hormone treatment increases cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-mediated antipyrine clearance. Caution with sensitive CYP substrates
- somatropin
somatropin will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Limited published data indicate that growth hormone treatment increases cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-mediated antipyrine clearance. Caution with sensitive CYP substrates
- stiripentol
stiripentol, duloxetine. affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Stiripentol is a CYP1A2 inhibitor and inducer. Monitor CYP1A2 substrates coadministered with stiripentol for increased or decreased effects. CYP1A2 substrates may require dosage adjustment.
- sufentanil SL
sufentanil SL, duloxetine. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system may result in serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dose adjustment.
- sulfasalazine
duloxetine, sulfasalazine. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- sulindac
duloxetine, sulindac. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- sumatriptan
sumatriptan and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- sumatriptan intranasal
sumatriptan intranasal and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- talquetamab
talquetamab will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Talquetamab causes cytokine release syndrome (CRS) that may suppress activity of CYP enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP substrates. This is more likely to occur from initiation of talquetamab step-up dosing up to 14 days after the first treatment dose and during and after CRS.
- tamoxifen
duloxetine decreases effects of tamoxifen by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Inhibition of CYP2D6 metabolism to tamoxifen's active metabolite, endoxifen.
- tamsulosin
duloxetine increases levels of tamsulosin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tapentadol
duloxetine and tapentadol both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- terbinafine
terbinafine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Assess need to reduce dose of CYP2D6-metabolized drug.
- teriflunomide
teriflunomide decreases levels of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- timolol
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of timolol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tolfenamic acid
duloxetine, tolfenamic acid. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- tolmetin
duloxetine, tolmetin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- tramadol
duloxetine and tramadol both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- valerian
valerian and duloxetine both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- venlafaxine
venlafaxine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vorapaxar
duloxetine, vorapaxar. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive antiplatelet effect may occur; SSRIs and SNRIs may cause platelet serotonin depletion .
- warfarin
duloxetine, warfarin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Serotonin release by platelets plays an important role in hemostasis. SSRIs and SNRIs may increase anticoagulation effect of warfarin. .
- zolmitriptan
zolmitriptan and duloxetine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
Minor (43)
- almotriptan
duloxetine, almotriptan. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
- aripiprazole
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of aripiprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- bumetanide
bumetanide, duloxetine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Possible additive hyponatremia.
- carvedilol
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of carvedilol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- celandine
celandine decreases effects of duloxetine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Based on animal studies.
- chloroquine
chloroquine will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- chlorpromazine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of chlorpromazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- dexfenfluramine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of dexfenfluramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- dexmethylphenidate
dexmethylphenidate increases effects of duloxetine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- donepezil
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of donepezil by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- doxepin
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- eletriptan
duloxetine, eletriptan. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
- encainide
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of encainide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ethacrynic acid
ethacrynic acid, duloxetine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Possible additive hyponatremia.
- ethinylestradiol
ethinylestradiol will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- flecainide
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of flecainide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fluoxetine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of fluoxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fluphenazine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of fluphenazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- frovatriptan
duloxetine, frovatriptan. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
- furosemide
furosemide, duloxetine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Possible additive hyponatremia.
- galantamine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of galantamine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- haloperidol
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of haloperidol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
haloperidol will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. - iloperidone
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of iloperidone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- lithium
duloxetine, lithium. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of neurotoxicity.
- loratadine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of loratadine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- naratriptan
duloxetine, naratriptan. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
- panax ginseng
panax ginseng increases effects of duloxetine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- paroxetine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of paroxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- perhexiline
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of perhexiline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- perphenazine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of perphenazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pleurisy root
pleurisy root decreases effects of duloxetine by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Theoretical interaction.
- prochlorperazine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of prochlorperazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- promazine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of promazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- promethazine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of promethazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- rizatriptan
duloxetine, rizatriptan. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
- serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate
serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate increases effects of duloxetine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sumatriptan
duloxetine, sumatriptan. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
- sumatriptan intranasal
duloxetine, sumatriptan intranasal. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
- tolterodine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of tolterodine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- torsemide
torsemide, duloxetine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Possible additive hyponatremia.
- trifluoperazine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of trifluoperazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- tropisetron
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of tropisetron by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- zolmitriptan
duloxetine, zolmitriptan. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
Adverse Effects
>10%
Nausea (23-25%)
Dry mouth (13-15%)
Headache (13-14%)
Somnolence (10-12%)
Fatigue (9-11%)
1-10%
Constipation (9-10%)
Dizziness (9-10%)
Insomnia (9-10%)
Diarrhea (9-10%)
Anorexia (8%)
Decreased appetite (7-8%)
Abdominal pain (4-6%)
Hyperhidrosis (6%)
Agitation (5%)
Nasopharyngitis (5%)
Vomiting (3-5%)
Male sexual dysfunction (2-5%)
Erectile dysfunction (4%)
Decreased libido (4%)
Musculoskeletal pain (4%)
Upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) (4%)
Decreased libido (3-4%)
Musculoskeletal pain (3-4%)
Abnormal orgasm (2-3%)
Agitation (3%)
Anxiety (3%)
Blurred vision (3%)
Cough (3%)
Influenza (3%)
Muscle spasms (2-3%)
Tremor (3%)
Abnormal dreams (2%)
Dyspepsia (2%)
Hot flushes (2%)
Oropharyngeal pain (2%)
Palpitations (2%)
Paresthesia (2%)
Weight loss (2%)
Yawning (2%)
Blood pressure increase (2%)
Ejaculation delayed (2%)
Dysuria (>1%)
Gastritis (>1%)
Rash (>1%)
Postmarketing Reports
General: Anaphylactic reaction, angioneurotic edema, hypersensitivity, chills/rigors, falls, feeling abnormal, feeling hot and/or cold, malaise, thirst
Cardiovascular: Hypertensive crisis, supraventricular arrhythmia, myocardial infarction, tachycardia, Takotsubo cardiomyopathy
Endocrine: Galactorrhea, gynecologic bleeding, hyperglycemia, hyperprolactinemia, hypothyroidism
Neurologic: Restless legs syndrome, seizures upon treatment discontinuance, extrapyramidal disorders, dysgeusia, lethargy, and paraesthesia/hypoesthesia, disturbance in attention, dyskinesia, myoclonus, poor quality sleep
Ophthalmic: Glaucoma, blurred vision, diplopia, dry eyes, visual impairment
Otic: Tinnitus (upon treatment discontinuance), ear pain, vertigo
Psychiatric: Aggression and anger (particularly early in treatment or after treatment discontinuance), hallucinations; abnormal dreams and sleep disorder; apathy, bruxism, disorientation/confusional state, irritability, mood swings, and suicide attempt; completed suicide (rare)
Musculoskeletal: Trismus, muscle spasm, muscle tightness, muscle twitching
Skin: Serious skin reactions (eg, erythema multiforme and Stevens-Johnson syndrome) necessitating drug discontinuance or hospitalization, urticaria, rash, pruritus, dermatitis, cold sweat, erythema, increased tendency to bruise, night sweats, photosensitivity reaction
Gastrointestinal: Colitis (microscopic or unspecified), cutaneous vasculitis (sometimes associated with systemic involvement), acute pancreatitis
Infection: Gastroenteritis, laryngitis
Investigations: Increased/decreased weight, increased blood cholesterol
Warnings
Black Box Warnings
Suicidal thoughts and behaviors
- Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies
- These studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior with antidepressant use in patients >24 yr
- There was a reduction in risk with antidepressant use in patients ≥65 yr
- In patients of all ages who are started on antidepressant therapy, monitor closely for worsening, and for emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors
- Advise families and caregivers of the need for close observation and communication with the prescriber
Contraindications
Concomitant use of duloxetine with MAOIs intended to treat psychiatric disorders
Use of duloxetine within 14 days of MAOI discontinuation
Initiating duloxetine in patients who are being treated with linezolid or IV methylene blue
Cautions
Prior to initiating treatment with, screen patients for any personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania
Suicidality; monitor for clinical worsening and suicide risk, especially in children, adolescents and young adults (18-24 years) during early phases of treatment and alterations in dosage (see Black Box Warnings)
Serotonin syndrome or neuroleptic malignant syndrome-like reactions may occur; discontinue and initiate supportive therapy; closely monitor patients concomitantly receiving triptans, antipsychotics and serotonin precursors
Neonates exposed to serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) late in 3rd trimester of pregnancy have developed complications necessitating prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding
Increased risk of hepatotoxicity, sometimes fatal; monitor for abdominal pain, hepatomegaly, elevated AST/ALT exceeding 20x ULN, and jaundice; cholestatic jaundice with minimal elevations of hepatic transaminases have also been reported; not recommended in patients with substantial alcohol use or chronic liver disease
SSRIs and SNRIs may impair platelet aggregation and increase the risk of bleeding events, ranging from ecchymoses, hematomas, epistaxis, petechiae, and GI hemorrhage to life-threatening hemorrhage; concomitant use of aspirin, NSAIDs, warfarin, other anticoagulants, or other drugs known to affect platelet function may add to this risk
Severe skin reactions (eg, erythema multiforme and Stevens-Johnson syndrome); discontinue at first appearance of blisters, peeling rash, mucosal erosions, or any other sign of hypersensitivity if no other etiology can be identified
Orthostatic hypotension and syncope, especially during week 1 of therapy; monitor patients taking drugs that increase risk of orthostatic hypotension; consider dose reduction or discontinue therapy in patients who experience symptomatic orthostatic hypotension, falls and/or syncope
Hyponatremia due to syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH); cases of serum sodium <110 mmol/L have been reported to be reversible upon discontinuance
Diabetes due to worsening of glycemic control in some patients; monitor increases in fasting blood glucose and hemoglobin A1c
Monitor weight and growth in adolescents and children; decrease in appetite and weight loss reported
Urinary hesitation and retention
Cognitive or motor function impairment; use with caution when operating heavy machinery
Bone fractures reported with antidepressant treatment; consider possibility of bone fracture if patient complains of unexplained bone pain or joint tenderness or experiences bruising or swelling
Use caution in gastroparesis, hypertension, controlled narrow-angle glaucoma, renal impairment, or seizure disorders
May lower seizure threshold when administered on currently with other drugs that lower seizure threshold
Risk of mydriasis; may trigger angle closure attack in patients with angle-closure glaucoma with anatomically narrow angles without a patent iridectomy
Headache, dizziness, nausea, diarrhea, paresthesia, vomiting, irritability, insomnia, hyperhidrosis, anxiety, and fatigue reported in patients following abrupt discontinuation of duloxetine
Therapy may increase blood pressure; measure blood prior to initiating treatment and periodically throughout treatment
Use with caution in patients with conditions that slow gastric emptying
Sexual dysfunction
- Use may cause symptoms of sexual dysfunction in both male and female patients; inform patients that they should discuss any changes in sexual function and potential management strategies with their healthcare provider
- Use of SSRIs, may cause symptoms of sexual dysfunction; in male patients, SSRI use may result in ejaculatory delay or failure, decreased libido, and erectile dysfunction
- Changes in sexual desire, sexual performance and sexual satisfaction often occur as manifestations of psychiatric disorders or diabetes, but may also be a consequence of pharmacologic treatment
- Use of SNRIs, may cause symptoms of sexual dysfunction; in male patients, SNRI use may result in ejaculatory delay or failure, decreased libido, and erectile dysfunction; in female patients, SNRI use may result in decreased libido and delayed or absent orgasm
- It is important for prescribers to inquire about sexual function prior to initiation of therapy and to inquire specifically about changes in sexual function during treatment; sexual function may not be spontaneously reported
- When evaluating changes in sexual function, obtaining a detailed history (including timing of symptom onset) is important because sexual symptoms may have other causes, including the underlying psychiatric disorder
- Discuss potential management strategies to support patients in making informed decisions about treatment
Increased risk of bleeding postpartum
- Drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake inhibition, may increase risk of bleeding; case reports and epidemiological studies (case-control and cohort design) have demonstrated an association between use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and occurrence of gastrointestinal bleeding
- A postmarketing study showed a higher incidence of postpartum hemorrhage in mothers receiving therapy;
- Other bleeding events related to SSRI and SNRI use have ranged from ecchymoses, hematomas, epistaxis, and petechiae to life-threatening hemorrhages; concomitant use of aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), warfarin, and other anticoagulants may add to this risk
- Inform about risk of bleeding associated with concomitant use of drug and NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation
Drug interaction overview
- Use caution when administering concomitantly with CNS depressants
- Duloxetine is CYP1A2 and CYP2D6 substrate; moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor
-
CYP2D6 Inhibitors
- Concomitant use of duloxetine with potent CYP2D6 inhibitors may result in higher concentrations (on average of 60%) of duloxetine
- Coadministration of duloxetine with drugs that are extensively metabolized by CYP2D6 with a narrow therapeutic index, including certain antidepressants (tricyclic antidepressants [TCAs]), phenothiazines and Type 1C antiarrhythmics (eg, propafenone, flecainide), should be used with caution
- Avoid coadministration with Drizalma Sprinkle and potent CYP2D6
-
Alcohol
- Cymbalta: Three treated patients had liver injury as manifested by ALT and total bilirubin elevations, with evidence of obstruction; substantial intercurrent ethanol use was present in each of these cases, and this may have contributed to the abnormalities seen
- Drizalma Sprinkle: An in vitro study showed significant increases of duloxetine hydrochloride release at 2 hr to ~86% and 56% of the drug release in the presence of 40% and 20% alcohol, respectively
-
Serotonergic drugs
- Development of a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with SNRIs and SSRIs, including duloxetine, when administered concomitantly with other serotonergic drugs (including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, meperidine, methadone, amphetamines, and St John’s Wort) and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (in particular, MAOIs, both those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue); serotonin syndrome can also occur when these drugs are used alone
- If concomitant use with other serotonergic drugs is clinically warranted, advise patients of potential risk for serotonin syndrome, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases; treatment with concomitant serotonergic agents, should be discontinued immediately if above events occur and initiate supportive symptomatic treatment
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
Data from a postmarketing retrospective cohort study indicate that use in the month before delivery may be associated with an increased risk of postpartum hemorrhage; data from published literature and from a postmarketing retrospective cohort study have not identified a clear drug-associated risk of major birth defects or other adverse developmental outcomes; there are risks associated with untreated depression in pregnancy and with exposure to SNRIs and SSRIs, during pregnancy
Women who discontinued antidepressants during pregnancy are more likely to experience a relapse of major depression than women who continued antidepressants; consider risk of untreated depression when discontinuing or changing treatment with antidepressant medication during pregnancy and postpartum
Pregnant women with fibromyalgia are at increased risk for adverse maternal and infant outcomes including preterm premature rupture of membranes, preterm birth, small for gestational age, intrauterine growth restriction, placental disruption, and venous thrombosis; not known if adverse maternal and fetal outcomes are a direct result of fibromyalgia or other comorbid factors
Animal data
-
Cymbalta
- In animal studies with duloxetine, fetal weights were decreased but there was no evidence of teratogenicity in pregnant rats and rabbits at oral doses administered during organogenesis up to 4 and 7 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 120 mg/day
- When duloxetine was administered orally to pregnant rats throughout gestation and lactation, pup weights at birth and pup survival to 1 day postpartum were decreased at a dose 2 times the MRHD
-
Drizalma Sprinkle
- In rats and rabbits treated with duloxetine during organogenesis, fetal weights decreased but there was no evidence of developmental effects at doses up to 3 and 6 times, respectively, the MRHD of 120 mg/day given to adolescents on a mg/m2 basis
- When oral duloxetine was administered to pregnant rats throughout gestation and lactation, pup weights at birth and pup survival to 1 day postpartum were decreased at a dose 2 times the MRHD given to adolescents on a mg/m2 basis
- For both formulations, pup behaviors consistent with increased reactivity, such as increased startle response to noise and decreased habituation of locomotor activity were observed
- Postweaning growth was not adversely affected
- Use in pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus
Pregnancy registry
- Pregnancy registry monitors the pregnancy outcomes in women exposed during pregnancy
- Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by contacting the National Pregnancy Registry for Antidepressants at 1-866-961-2388 or online at https://womensmentalhealth.org/research/pregnancyregistry/
- Drizalma Sprinkle: Contact the National Pregnancy Registry for Antidepressants at 1-844-405-6185 or visiting online at https://womensmentalhealth.org/clinical-and-research-programs/pregnancyregistry/antidepressants/
Clinical considerations
- Neonates exposed during pregnancy to serotonin - norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) have developed complications requiring prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding which can arise immediately upon delivery
- Reported clinical findings have included respiratory distress, cyanosis, apnea, seizures, temperature instability, feeding difficulty, vomiting, hypoglycemia, hypotonia, hypertonia, hyperreflexia, tremor, jitteriness, irritability, and constant crying
- These features are consistent with either a direct toxic effect of the SNRIs or SSRIs, or possibly, a drug discontinuation syndrome
- In some cases, the clinical picture is consistent with serotonin syndrome
Lactation
Cymbalta
- Drug present in human milk in a published study, lactating women who were weaning their infants were given duloxetine
- At steady state, duloxetine concentration in breast milk was ~25% that of maternal plasma
- Estimated daily infant dose was ~0.14% of the maternal dose
- Exercise caution when administering to a nursing woman
Drizalma Sprinkle
- Data from the published literature report the presence of duloxetine in human milk
- There are reports of sedation, poor feeding, and poor weight gain in infants exposed to duloxetine through breast milk
- There are no data on effect of duloxetine on milk production
- Developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with mother’s clinical need for therapy and any potential adverse effects on breastfed child from therapy or from underlying maternal condition
- Women given 40 mg of duloxetine PO BID for 3.5 days; peak concentration measured in breast milk occurred at a median of 3 hrs post-dose
- Amount of duloxetine in breast milk was ~7 mcg/day while on that dose; estimated daily infant dose was ~2 mcg/kg/day, which is <1% of the maternal dose
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Exact mechanism of action unknown; inhibits reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine; weakly inhibits reuptake of dopamine; has no MAOI activity; has no significant activity for histaminergic H1 receptor or alpha2-adrenergic receptor
Absorption
Well absorbed
Duloxetine steady-state plasma concentration was comparable in children (7-12 years), adolescents (13-17 years), and adults
Peak plasma time
- Cymbalta: 6 hr (empty stomach); 10 hr (with food)
- Drizalma Sprinkle: 5 hr; there is a 3 hr delay in absorption and a one-third increase in apparent duloxetine clearance after an evening dose as compared to a morning dose; ~1.7 hr delay when administered with a high-fat meal
Distribution
Vd: 1640 L
Protein bound: >90%
Metabolism
Metabolized in liver by CYP2D6 and CYP1A2
Metabolites: 4-hydroxy duloxetine glucuronide; 5-hydroxy, 6-methoxy duloxetine sulfate
Enzymes inhibited: CYP2D6
Elimination
Half-life: 12 hr
Excretion: Urine (70% as metabolites; <1% unchanged), feces (20%)
Administration
Oral Administration
Swallow capsule whole; do not chew or crush
May be administer without regard to meals
Cymbalta
- Do not open capsule and sprinkle its contents on food or mix with liquids
- All of these might affect the enteric coating
Drizalma Sprinkle
-
Patients with swallowing difficulty
- Open capsule and sprinkle contents over applesauce; swallow contents of the capsules along with a small amount (tablespoonful) of applesauce
- Swallow drug/food mixture immediately and do not store for future use
-
Nasogastric tube administration
- Open and add contents of capsule to an all plastic catheter tip syringe and add 50 mL of water
- Gently shake syringe for ~10 seconds
- Promptly deliver through a 12 French or larger nasogastric tube; ensure no pellets are left in the syringe
- Rinse with additional water (~15 mL) if needed
Missed dose
- If a dose is missed, take missed dose as soon as it is remembered
- If it is almost time for the next dose, skip missed dose and take the next dose at the regular time; do not take 2 doses at the same time
Storage
Cymbalta: Store at 25ºC (77ºF); excursions permitted to 15-30ºC (59-86ºF)
Drizalma Sprinkle: Store at 20-25ºC (68-77ºF); excursions permitted to 15-30ºC (59-86ºF)
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| duloxetine oral - | 60 mg capsule | 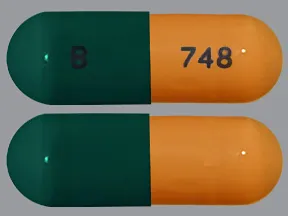 | |
| duloxetine oral - | 60 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 30 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 40 mg capsule | 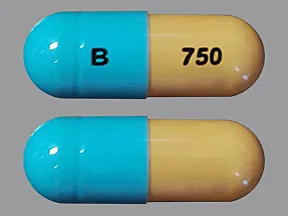 | |
| duloxetine oral - | 20 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 30 mg capsule | 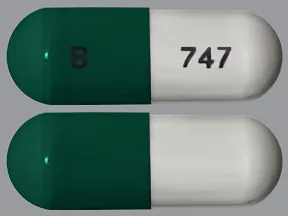 | |
| duloxetine oral - | 20 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 30 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 60 mg capsule | 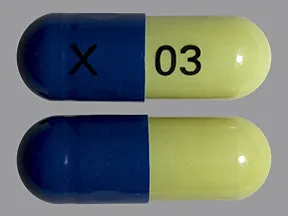 | |
| duloxetine oral - | 20 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 20 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 30 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 60 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 20 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 30 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 60 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 30 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 20 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 60 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 20 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 60 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 60 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 30 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 30 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 30 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 60 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 30 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 20 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 60 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 60 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 40 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 60 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 20 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 30 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 30 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 20 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 40 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 20 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 60 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 30 mg capsule |  | |
| duloxetine oral - | 30 mg capsule |  | |
| Cymbalta oral - | 30 mg capsule |  | |
| Cymbalta oral - | 60 mg capsule | 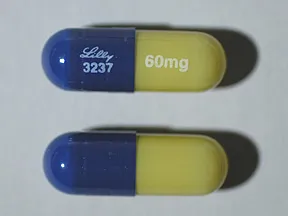 | |
| Cymbalta oral - | 60 mg capsule |  | |
| Cymbalta oral - | 20 mg capsule |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
duloxetine oral
DULOXETINE - ORAL
(doo-LOX-e-teen)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Cymbalta
WARNING: Antidepressant medications are used to treat a variety of conditions, including depression and other mental/mood disorders. These medications can help prevent suicidal thoughts/attempts and provide other important benefits. However, a small number of people (especially people younger than 25) who take antidepressants for any condition may experience worsening depression, other mental/mood symptoms, or suicidal thoughts/attempts. It is very important to talk with the doctor about the risks and benefits of antidepressant medication (especially for people younger than 25), even if treatment is not for a mental/mood condition.Tell the doctor right away if you notice worsening depression/other psychiatric conditions, unusual behavior changes (including possible suicidal thoughts/attempts), or other mental/mood changes (including new/worsening anxiety, panic attacks, trouble sleeping, irritability, hostile/angry feelings, impulsive actions, severe restlessness, very rapid speech). Be especially watchful for these symptoms when a new antidepressant is started or when the dose is changed.
USES: This medication is used to treat certain mental/mood disorders (such as depression, anxiety). It is also used to help relieve nerve pain (peripheral neuropathy) in people with diabetes or ongoing pain due to medical conditions such as arthritis, chronic back pain, or fibromyalgia (a condition that causes widespread pain). Duloxetine belongs to a class of drugs known as serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). It works by helping to restore the balance of certain natural substances (serotonin and norepinephrine) in the brain.
HOW TO USE: Read the Medication Guide and, if available, the Patient Information Leaflet provided by your pharmacist before you start using duloxetine and each time you get a refill. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.Take this medication by mouth as directed by your doctor, usually 1 or 2 times a day with or without food. If you have nausea, it may help to take this drug with food. Swallow the capsule whole. Do not crush or chew the capsule or mix the contents with food or liquid. Doing so can release all of the drug at once, increasing the risk of side effects.The dosage is based on your age, medical condition and response to treatment. To reduce your risk of side effects, your doctor may direct you to start this medication at a low dose and gradually increase your dose. Follow your doctor's instructions carefully. Take this medication regularly to get the most benefit from it. To help you remember, take it at the same time(s) each day.Keep taking this medication even if you feel well. Do not stop taking this medication without consulting your doctor. Some conditions may become worse when this drug is suddenly stopped. Also, you may experience symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, mood swings, headache, tiredness, diarrhea, sleep changes, and brief feelings similar to electric shock. Your dose may need to be gradually decreased to reduce side effects. Report any new or worsening symptoms right away.Tell your doctor if your condition lasts or gets worse.
SIDE EFFECTS: See also Warning section.Nausea, dry mouth, constipation, loss of appetite, tiredness, drowsiness, or increased sweating may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor promptly.Dizziness or lightheadedness may occur, especially when you first start or increase your dose of this drug. To reduce the risk of dizziness, lightheadedness, or falling, get up slowly when rising from a sitting or lying position.Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.This medication may raise your blood pressure. Check your blood pressure regularly and tell your doctor if the results are high.Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: confusion, easy bleeding/bruising, decreased interest in sex, changes in sexual ability, muscle cramps/weakness, shaking (tremor), difficulty urinating, signs of liver problems (such as nausea that doesn't stop, stomach/abdominal pain, vomiting, yellowing eyes/skin, dark urine).Get medical help right away if you have any very serious side effects, including: black stools, vomit that looks like coffee grounds, seizure, eye pain/swelling/redness, widened pupils, vision changes (such as seeing rainbows around lights at night, blurred vision).This medication may increase serotonin and rarely cause a very serious condition called serotonin syndrome/toxicity. The risk increases if you are also taking other drugs that increase serotonin, so tell your doctor or pharmacist of all the drugs you take (see Drug Interactions section). Get medical help right away if you develop some of the following symptoms: fast heartbeat, hallucinations, loss of coordination, severe dizziness, severe nausea/vomiting/diarrhea, twitching muscles, unexplained fever, unusual agitation/restlessness.A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing, skin blisters, mouth sores.This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: Before taking duloxetine, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: personal or family history of psychiatric disorders (such as bipolar/manic-depressive disorder), personal or family history of suicide attempts, bleeding problems, personal or family history of glaucoma (angle-closure type), high blood pressure, kidney disease, liver disease, seizure disorder, stomach problems (such as slow emptying of the stomach), use/abuse of alcohol.This drug may make you dizzy or drowsy. Alcohol or marijuana (cannabis) can make you more dizzy or drowsy. Do not drive, use machinery, or do anything that needs alertness until you can do it safely. Avoid alcoholic beverages. Talk to your doctor if you are using marijuana (cannabis).If you have diabetes, duloxetine may affect your blood sugar. Check your blood sugar regularly as directed and share the results with your doctor. Your doctor may need to adjust your diabetes medication, exercise program, or diet.Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects of this drug, especially bleeding, dizziness, lightheadedness, or loss of coordination. Older adults may also be more likely to develop a type of salt imbalance (hyponatremia), especially if they are taking "water pills" (diuretics). Dizziness, lightheadedness, or loss of coordination can increase the risk of falling.Children may be more sensitive to the side effects of this drug, especially loss of appetite and weight loss. Monitor weight and height in children who are taking this drug. See also Warning.During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. This medication may harm an unborn baby. Babies born to mothers who have used this drug during the last 3 months of pregnancy may rarely develop withdrawal symptoms such as feeding/breathing difficulties, seizures, muscle stiffness, or constant crying. If you notice any of these symptoms in your newborn, tell the doctor promptly.Since untreated mental/mood problems (such as depression, anxiety) can be a serious condition, do not stop taking this medication unless directed by your doctor. If you are planning pregnancy, become pregnant, or think you may be pregnant, immediately discuss the benefits and risks of using this medication during pregnancy with your doctor.This drug passes into breast milk and may have undesirable effects on a nursing infant. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.Some products that may interact with this drug are: other drugs that can cause bleeding/bruising (including antiplatelet drugs such as clopidogrel, NSAIDs such as ibuprofen/naproxen, "blood thinners" such as dabigatran/warfarin).Other medications can affect the removal of duloxetine from your body, which may affect how duloxetine works. Examples include cimetidine, viloxazine, certain quinolone antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin, enoxacin), among others.This medication can slow down the removal of other medications from your body, which may affect how they work. Examples of affected drugs include antiarrhythmic drugs (such as propafenone, flecainide, quinidine), antipsychotics (such as thioridazine), tricyclic antidepressants (such as desipramine, imipramine), among others.Taking MAO inhibitors with this medication may cause a serious (possibly fatal) drug interaction. Avoid taking MAO inhibitors (isocarboxazid, linezolid, metaxalone, methylene blue, moclobemide, phenelzine, procarbazine, rasagiline, safinamide, selegiline, tranylcypromine) during treatment with this medication. Most MAO inhibitors should also not be taken for two weeks before and at least 5 days after treatment with this medication. Ask your doctor when to start or stop taking this medication.The risk of serotonin syndrome/toxicity increases if you are also taking other drugs that increase serotonin. Examples include street drugs such as MDMA/"ecstasy," St. John's wort, certain antidepressants (including SSRIs such as fluoxetine/paroxetine, other SNRIs such as desvenlafaxine/venlafaxine), tryptophan, among others. The risk of serotonin syndrome/toxicity may be more likely when you start or increase the dose of these drugs.Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking other products that cause drowsiness including alcohol, marijuana (cannabis), antihistamines (such as cetirizine, diphenhydramine), drugs for sleep or anxiety (such as alprazolam, diazepam, zolpidem), muscle relaxants, and opioid pain relievers (such as codeine). Check the labels on all your medicines (such as allergy or cough-and-cold products) because they may contain ingredients that cause drowsiness. Ask your pharmacist about using those products safely.Aspirin can increase the risk of bleeding when used with this medication. However, if your doctor has told you to take low-dose aspirin to prevent heart attack or stroke (usually 81-162 milligrams a day), you should keep taking the aspirin unless your doctor tells you not to.
OVERDOSE: If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center. Symptoms of overdose may include: severe drowsiness, fainting.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others.Lab and/or medical tests (such as blood pressure, liver function) should be done while you are taking this medication. Keep all medical and lab appointments. Consult your doctor for more details
MISSED DOSE: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose. Take your next dose at the regular time. Do not double the dose to catch up.
STORAGE: Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Information last revised March 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.




