Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablet
- 250mg
- 500mg
Alcoholism
Only administer after the patient has abstained from ethanol for at least 12 hr
Use ONLY as adjunct to supportive & psychotherapeutic treatment; in motivated patient
500 mg PO qDay initially for 1-2 weeks; not to exceed 500 mg/day
Maintenance: 250 mg PO qDay (125-500 mg range); continue therapy until a bases for self-control has been established; patient may continue to take drug therapy for months or even years
Glioblastoma Multiforme (Orphan)
Combination of disulfiram and copper gluconate
Orphan designation for treatment of glioblastoma multiforme
Sponsor
- Cantex Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 1792 Bell Tower Lane; Weston, Florida 33326
Safety and efficacy not established
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results

Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor

Contraindicated (5)
- benznidazole
benznidazole, disulfiram. Either increases toxicity of the other by aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibition. Contraindicated. Psychotic reactions have been reported in patients who were coadministered disulfiram and nitroimidazole agents (structurally related to benznidazole). Do not prescribe benznidazole to patients who have taken disulfiram within the last 2 weeks.
- dronabinol
disulfiram increases toxicity of dronabinol by aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibition. Contraindicated. Dronabinol oral solution (Syndros) contains 50% (w/w) dehydrated alcohol 5.5% (w/w) propylene glycol, which can produce disulfiramlike reactions if coadministered. Discontinue disulfiram at least 14 days before starting dronabinol solution and do not administer disulfiram within 7 days of completing treatment with dronabinol solution.
- eliglustat
disulfiram increases levels of eliglustat by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Contraindicated. If coadministered with strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors, reduce eliglustat dose from 84 mg BID to 84 mg once daily in extensive and intermediate metabolizers; eliglustat is contraindiated if strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors are given concomitantly with strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors.
- fezolinetant
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of fezolinetant by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Contraindicated. Fezolinetant AUC and peak plasma concentration are increased if coadministered with drugs that are weak, moderate, or strong CYP1A2 inhibitors
- ritonavir
disulfiram increases toxicity of ritonavir by aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibition. Contraindicated. Interaction only associated with oral solution, which contains 42% alcohol.
Serious - Use Alternative (8)
- carbamazepine
carbamazepine, disulfiram. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Pretomanid regimen associated with hepatotoxicity. Avoid alcohol and hepatotoxic agents, including herbal supplements and drugs other than bedaquiline and linezolid.
- ethanol
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of ethanol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2E1 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
disulfiram increases toxicity of ethanol by decreasing metabolism. Contraindicated. Enhanced CNS & cardiac toxicity. - lonafarnib
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of lonafarnib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of lonafarnib (a sensitive CYP3A substrate) with weak CYP3A inhibitors is unavoidable, reduce to, or continue lonafarnib at starting dose. Closely monitor for arrhythmias and events (eg, syncope, heart palpitations) since lonafarnib effect on QT interval is unknown.
- metronidazole
disulfiram increases toxicity of metronidazole by decreasing metabolism. Contraindicated. Enhanced CNS & cardiac toxicity.
- pexidartinib
disulfiram and pexidartinib both increase Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Pexidartinib can cause hepatotoxicity. Avoid coadministration of pexidartinib with other products know to cause hepatoxicity.
- selinexor
selinexor, disulfiram. unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Patients treated with selinexor may experience neurological toxicities. Avoid taking selinexor with other medications that may cause dizziness or confusion.
- tinidazole
tinidazole increases toxicity of disulfiram by aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibition. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Alcoholic beverages and preparations containing ethanol or propylene glycol should be avoided during tinidazole therapy and for 3 days afterward because abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, headaches, and flushing may occur. Tinidazole should not be given to patients who have taken disulfiram within the last two weeks. .
- tipranavir
disulfiram, tipranavir. Mechanism: decreasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of disulfiram reaction (tipranavir capsules contain alcohol).
Monitor Closely (30)
- alprazolam
disulfiram increases levels of alprazolam by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- atogepant
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of atogepant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- avapritinib
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of avapritinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- axitinib
disulfiram increases levels of axitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- brexpiprazole
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of brexpiprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administer a quarter of brexpiprazole dose if coadministered with a moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor PLUS a strong/moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor.
- cholic acid
disulfiram increases toxicity of cholic acid by decreasing elimination. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid concomitant use of inhibitors of the bile salt efflux pump (BSEP). May exacerbate accumulation of conjugated bile salts in the liver and result in clinical symptoms. If concomitant use is necessary, monitor serum transaminases and bilirubin.
- clonazepam
disulfiram increases levels of clonazepam by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clorazepate
disulfiram increases levels of clorazepate by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cocaine topical
disulfiram increases levels of cocaine topical by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diazepam
disulfiram increases levels of diazepam by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ethotoin
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of ethotoin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- etravirine
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of etravirine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- finerenone
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of finerenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor serum potassium during initiation and dosage adjustment of either finererone or weak CYP3A4 inhibitors. Adjust finererone dosage as needed.
- flibanserin
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of flibanserin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased flibanserin adverse effects may occur if coadministered with multiple weak CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- fosphenytoin
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of fosphenytoin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- green tea
disulfiram increases levels of green tea by decreasing elimination. Use Caution/Monitor. Combination may increase caffeine levels. Caution should be taken due to increased risk of adverse effects due to caffeine in green tea.
- isavuconazonium sulfate
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of isavuconazonium sulfate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- isoniazid
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of isoniazid by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2E1 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
isoniazid increases toxicity of disulfiram by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Enhanced CNS toxicity. - ivacaftor
disulfiram increases levels of ivacaftor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor when coadministered with weak CYP3A4 inhibitors .
- lemborexant
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of lemborexant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Lower nightly dose of lemborexant recommended if coadministered with weak CYP3A4 inhibitors. See drug monograph for specific dosage modification.
- lomitapide
disulfiram increases levels of lomitapide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Lomitapide dose should not exceed 30 mg/day.
- midazolam intranasal
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of midazolam intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of mild CYP3A4 inhibitors with midazolam intranasal may cause higher midazolam systemic exposure, which may prolong sedation.
- oliceridine
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of oliceridine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. If concomitant use is necessary, may require less frequent oliceridine dosing. Closely monitor for respiratory depression and sedation and titrate subsequent doses accordingly. If inhibitor is discontinued, consider increase oliceridine dosage until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal.
- phenytoin
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of phenytoin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- procarbazine
disulfiram, procarbazine. Mechanism: unknown. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of delirium (case report).
- tamsulosin
disulfiram increases levels of tamsulosin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tazemetostat
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of tazemetostat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tranylcypromine
disulfiram, tranylcypromine. Mechanism: unknown. Use Caution/Monitor. Possible CNS delirium including agitation, visual hallucinations, and disorientation may occur. .
- triazolam
disulfiram increases levels of triazolam by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- valoctocogene roxaparvovec
disulfiram and valoctocogene roxaparvovec both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Medications that may cause hepatotoxicity when combined with valoctogene roxaparvovec may potentiate the risk of elevated liver enzymes. Closely monitor these medications and consider alternative medications in case of potential drug interactions.
Minor (31)
- acetaminophen
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of acetaminophen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2E1 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- acetaminophen IV
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of acetaminophen IV by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2E1 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- acetaminophen rectal
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of acetaminophen rectal by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2E1 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- alosetron
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of alosetron by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- bosentan
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of bosentan by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- celecoxib
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of celecoxib by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- chlordiazepoxide
disulfiram increases levels of chlordiazepoxide by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- dapsone
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of dapsone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2E1 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- diclofenac
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of diclofenac by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ethotoin
disulfiram increases levels of ethotoin by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- flurbiprofen
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of flurbiprofen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fluvastatin
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of fluvastatin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fosphenytoin
disulfiram increases levels of fosphenytoin by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ibuprofen
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of ibuprofen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ibuprofen IV
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of ibuprofen IV by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- isocarboxazid
disulfiram, isocarboxazid. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of delirium (case report).
- linezolid
disulfiram, linezolid. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of delirium (case report).
- meloxicam
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of meloxicam by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- metronidazole topical
disulfiram increases toxicity of metronidazole topical by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Enhanced CNS & cardiac toxicity with oral metronidazole and disulfiram; less likely to occur with topical administration because of low absorption.
- metronidazole vaginal
disulfiram increases toxicity of metronidazole vaginal by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Enhanced CNS & cardiac toxicity with oral metronidazole and disulfiram; less likely to occur with vaginal administration because of low absorption.
- phenelzine
disulfiram, phenelzine. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of delirium (case report).
- phenytoin
disulfiram increases levels of phenytoin by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- piroxicam
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of piroxicam by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ramelteon
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of ramelteon by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ruxolitinib
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of ruxolitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ruxolitinib topical
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of ruxolitinib topical by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sevoflurane
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of sevoflurane by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2E1 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sulfamethoxazole
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of sulfamethoxazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- theophylline
disulfiram increases levels of theophylline by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- tolbutamide
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of tolbutamide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- voriconazole
disulfiram will increase the level or effect of voriconazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
Adverse Effects
Frequency Not Defined
Fatigue
Headache
Impotence
Metallic aftertaste
Acneiform eruptions
Polyneuritis
Rash
Hepatitis
Peripheral neuropathy
Optic neuritis
Psychotic disorder
Warnings
Black Box Warnings
Never administer to a patient in a state of alcohol intoxication or without patient's full knowledge
Instruct patient's relatives accordingly
Contraindications
Ethanol, metronidazole, paraldehyde, any alcohol-containing products (e.g., some mouthwashes)
Severe cardiac disease
Coronary occlusion
Psychosis
Hypersensitivity
Cautions
When EtOH ingested by patient taking disulfiram: flushing, throbbing HA, N/V, diaphoresis, thirst, SOB, syncope, vertigo, blurred vision, confusion; respiratory depression, cardiac arrhythmias, MI or liver failure may occur
Use caution in diabetes, hypothyroidism, seizures, nephritis, hepatic impairment
Severe hepatitis and/or hepatic failure has been associated with therapy even in patients without prior history of abnormal hepatic function
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy Category: C
Lactation: excretion in milk unknown/not recommended
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Produces sensitivity to EtOH via blocking its oxidation at acetaldehyde stage, resulting in unpleasant reactions including palpitations, hypotension, chest pain, nausea, vertigo, thirst, flushing, and nausea
Absorption
Peak plasma time: 4 hr
Peak plasma concentration: 2.4 mcg/mL
Duration: up to 2 wk
Onset: 2-12 hr
Metabolism
Hepatic 80-90%
Metabolites: Diethyldithiocarbamate
Enzymes inhibited: hepatic CYP2C9, CYP2E1
Elimination
Excretion: Feces and exhaled gases
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| disulfiram oral - | 250 mg tablet |  | |
| disulfiram oral - | 250 mg tablet |  | |
| disulfiram oral - | 500 mg tablet | 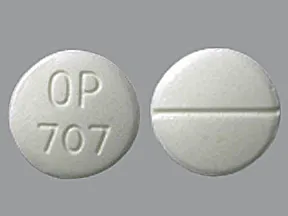 |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
disulfiram oral
DISULFIRAM - ORAL
(dye-SUL-fi-ram)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Antabuse
WARNING: This medication should not be given to a patient without their knowledge. Do not take this medication if you are under the influence of alcohol or have drunk alcohol in the last 12 hours.
USES: This medication is used along with counseling and support to treat alcoholism. Disulfiram works by blocking the processing of alcohol in the body. This causes you to have a bad reaction when you drink alcohol.
HOW TO USE: See also Precautions section.Take this medication by mouth with or without food as directed by your doctor, usually once daily in the morning. If this medication causes drowsiness, take it at bedtime.The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment.Use this medication regularly to get the most benefit from it. To help you remember, take it at the same time each day.
SIDE EFFECTS: Drowsiness, tiredness, headache, acne, and metallic/garlic-like taste in the mouth may occur as your body gets used to the medication. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: decreased sexual ability, vision changes, numbness/tingling of arms/legs, muscle weakness, mental/mood changes (such as agitation, confusion, extreme excitement), seizures.This drug may rarely cause serious (rarely fatal) liver disease. If you notice any of the following serious side effects, tell your doctor right away: nausea/vomiting that doesn't stop, severe stomach/abdominal pain, dark urine, yellowing eyes/skin.A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.Before taking disulfiram, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or to thiuram or thiuram-related chemicals (found in pesticides and rubber); or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: heart/blood vessel disease (such as coronary artery disease), mental/mood disorders, diabetes, underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), brain disorders (such as seizures, brain damage), kidney disease, liver disease, personal or family history of regular use/abuse of drugs.Avoid all alcoholic beverages or alcohol-containing products/foods (such as cough and cold syrups, mouthwash, aftershave, sauces, vinegars) while taking this medication and for 2 weeks after stopping the medication. Check all product labels carefully to make sure that there is no alcohol in the product. Using alcohol, even a small amount, while taking this medication can lead to a reaction that may include flushing, throbbing headache, breathing problems (such as shortness of breath, fast breathing), nausea, vomiting, dizziness, extreme tiredness, fainting, fast/irregular heartbeat, or blurred vision. These symptoms can last from 30 minutes to several hours. Tell your doctor right away if these symptoms occur, especially if they last or get worse.A more serious reaction with this medication and alcohol may include trouble breathing, seizures, loss of consciousness, chest/jaw/left arm pain. Get medical help right away if you have these symptoms.During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.It is unknown if this drug passes into breast milk. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.Some products that may interact with this drug are: alcohol-containing products (such as cough and cold syrups, aftershave), amitriptyline, benznidazole, "blood thinners" (such as warfarin), certain medications for seizures (including hydantoins such as phenytoin/fosphenytoin), fezolinetant, isoniazid, metronidazole, theophylline, tinidazole.This medication can increase the side effects of caffeine. Avoid drinking large amounts of beverages containing caffeine (coffee, tea, colas) or eating large amounts of chocolate.This medication may interfere with certain lab tests (such as urine VMA/HVA tests), possibly causing false test results. Make sure lab personnel and all your doctors know you use this drug.
OVERDOSE: If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center. Symptoms of overdose may include: vomiting, drowsiness, loss of coordination, loss of consciousness.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others.Lab and/or medical tests (such as liver function, complete blood count) should be done while you are taking this medication. Keep all medical and lab appointments. Consult your doctor for more details.It is recommended that you carry an identification card stating that you are taking this medication and describing the possible reaction that may occur if you consume alcohol.
MISSED DOSE: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose. Take your next dose at the regular time. Do not double the dose to catch up.
STORAGE: Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Information last revised March 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.




