Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
capsule (generic)
- 10mg
- 25mg
- 50mg
- 75mg
- 100mg
- 150mg
tablet (Silenor)
- 3mg
- 6mg
oral concentrate (generic)
- 10mg/mL
Depression/Anxiety
Initiate at low dose (25 mg/day); gradually titrate upward every 5-7 days
Dosage range: 25-300 mg/day PO, up to 150 mg/day as single dose
If dose exceeds 150 mg/day, divide q12hr
Dosing considerations
- May give qHS to decrease daytime sedation
Insomnia (Silenor)
Sleep maintenance
3-6 mg PO within 30 minutes before bedtime; not to exceed 6 mg/day
Hepatic impairment/debilitated patients: 3 mg PO within 30 minutes before bedtime
Dosing considerations
- To minimize potential for next day drowsiness, do not take within 3 hr of a meal (AUC increased by 41% and Cmax by 15% when taken with high fat meal)
Dosing Modifications
Hepatic impairment: Use lower dose and adjust gradually for depression; initiate Silenor at 3 mg daily for insomnia
<12 years old: Not recommended
Insomnia (Silenor)
Sleep maintenance
Starting dose: 3 mg PO within 30 minutes before bedtime
May increase to 6 mg PO HS if clinically indicated
Depression/Anxiety
Lower initial dose (ie, 10 mg/day) and adjust gradually; 10-25 mg PO qHS
May increase by 10-25 mg increments q3Day for inpatients and weekly for outpatients if tolerated
Dosing considerations
Avoid; strong anticholinergic and sedative effects; may cause orthostatic hypotension (Beers criteria)
Consider alternatives; if must use, initiate with lower initial dose
May cause confusion and oversedation in elderly
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results

Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor

Contraindicated (17)
- disopyramide
doxepin and disopyramide both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- ibutilide
doxepin and ibutilide both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- indapamide
doxepin and indapamide both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- iobenguane I 123
doxepin decreases effects of iobenguane I 123 by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. If clinically appropriate, discontinue drugs that decrease uptake of NE for at least 5 half-lives; may cause false-negative imaging results.
- isocarboxazid
isocarboxazid and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated.
- lefamulin
lefamulin will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Lefamulin is contraindicated with CYP3A substrates know to prolong the QT interval.
- pentamidine
doxepin and pentamidine both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- phenelzine
phenelzine and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated.
- pimozide
doxepin and pimozide both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- procainamide
doxepin and procainamide both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- procarbazine
procarbazine and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated. Combination is contraindicated within 2 weeks of MAOI use.
- quinidine
quinidine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- safinamide
doxepin, safinamide. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Contraindicated. Concomitant use could result in life-threatening serotonin syndrome.
- selegiline
selegiline and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated. Concurrent use or use within 14 days of selegiline treatment is contraindicated
- sotalol
doxepin and sotalol both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- thioridazine
thioridazine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- tranylcypromine
tranylcypromine and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated.
Serious - Use Alternative (157)
- albuterol
doxepin, albuterol. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- amiodarone
doxepin and amiodarone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- amitriptyline
amitriptyline and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
amitriptyline and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - amoxapine
amoxapine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
amoxapine and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - arformoterol
doxepin, arformoterol. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- arsenic trioxide
doxepin and arsenic trioxide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- artemether
doxepin and artemether both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- artemether/lumefantrine
artemether/lumefantrine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin and artemether/lumefantrine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen
benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen and doxepin both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Limit use to patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate
- benzphetamine
doxepin, benzphetamine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- buprenorphine
doxepin and buprenorphine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine buccal
buprenorphine buccal and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine subdermal implant
buprenorphine subdermal implant and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
buprenorphine subdermal implant and doxepin both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Limit use to patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate - buprenorphine transdermal
buprenorphine transdermal and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
buprenorphine transdermal and doxepin both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Limit use to patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate - buprenorphine, long-acting injection
buprenorphine, long-acting injection and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
buprenorphine, long-acting injection and doxepin both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Limit use to patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate - buspirone
doxepin and buspirone both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- calcium/magnesium/potassium/sodium oxybates
doxepin, calcium/magnesium/potassium/sodium oxybates. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death may result if coadministered. Reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs in patients for whom other treatment options are inadequate. Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required. Monitor closely for signs of respiratory depression and sedation.
- chloroquine
doxepin and chloroquine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- chlorpromazine
chlorpromazine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- citalopram
citalopram and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Citalopram may increase TCA levels. Increased risk of serotonin syndrome or neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Potential risk for QT prolongation. ECG monitoring is recommended.
doxepin and citalopram both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - clarithromycin
doxepin and clarithromycin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- clomipramine
clomipramine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
clomipramine and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - clonidine
doxepin decreases effects of clonidine by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Inhibition of uptake by adrenergic neurons.
- cyclobenzaprine
doxepin and cyclobenzaprine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dacomitinib
dacomitinib will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid use with CYP2D6 substrates where minimal increases in concentration of the CYP2D6 substrate may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities.
- desipramine
desipramine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
desipramine and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - desvenlafaxine
doxepin and desvenlafaxine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dexfenfluramine
doxepin, dexfenfluramine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- dexmethylphenidate
doxepin, dexmethylphenidate. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- dextroamphetamine
doxepin, dextroamphetamine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- dextromethorphan
doxepin and dextromethorphan both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- diethylpropion
doxepin, diethylpropion. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- dobutamine
doxepin, dobutamine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- dofetilide
doxepin and dofetilide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dolasetron
dolasetron, doxepin. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dopamine
doxepin, dopamine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- dopexamine
doxepin, dopexamine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- dronedarone
doxepin and dronedarone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- droperidol
doxepin and droperidol both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- duloxetine
duloxetine and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- encorafenib
doxepin and encorafenib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ephedrine
doxepin, ephedrine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- epinephrine
epinephrine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin, epinephrine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron. - epinephrine racemic
epinephrine racemic and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin, epinephrine racemic. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron. - erythromycin base
doxepin and erythromycin base both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin ethylsuccinate
doxepin and erythromycin ethylsuccinate both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin lactobionate
doxepin and erythromycin lactobionate both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin stearate
doxepin and erythromycin stearate both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- escitalopram
escitalopram and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin and escitalopram both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - fenfluramine
doxepin, fenfluramine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- fentanyl
fentanyl and doxepin both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Limit use to patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate
- fentanyl intranasal
fentanyl intranasal and doxepin both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Limit use to patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate
- fentanyl iontophoretic transdermal system
fentanyl iontophoretic transdermal system and doxepin both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Limit use to patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate
- fentanyl transdermal
fentanyl transdermal and doxepin both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Limit use to patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate
- fentanyl transmucosal
fentanyl transmucosal and doxepin both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Limit use to patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate
- fexinidazole
fexinidazole and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of fexinidazole with drugs known to block potassium channels or prolong QT interval.
fexinidazole will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Fexinidazole inhibits CYP3A4. Coadministration may increase risk for adverse effects of CYP3A4 substrates. - fluconazole
doxepin and fluconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fluoxetine
fluoxetine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
fluoxetine and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - fluphenazine
fluphenazine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fluvoxamine
fluvoxamine and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- formoterol
doxepin and formoterol both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin, formoterol. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron. - fosamprenavir
fosamprenavir increases levels of doxepin by decreasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- givinostat
doxepin and givinostat both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid coadministration, obtain ECGs when initiating, during concomitant use, and as clinically indicated. Withhold if QTc interval >500 ms or a change from baseline >60 ms.
- givosiran
givosiran will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of sensitive CYP2D6 substrates with givosiran. If unavoidable, decrease the CYP2D6 substrate dosage in accordance with approved product labeling.
- glasdegib
doxepin and glasdegib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- granisetron
granisetron, doxepin. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- guanfacine
doxepin decreases effects of guanfacine by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Inhibition of uptake by adrenergic neurons.
- haloperidol
haloperidol will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin and haloperidol both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - hydroxychloroquine sulfate
doxepin and hydroxychloroquine sulfate both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- imipramine
doxepin and imipramine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin and imipramine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - inotuzumab
doxepin and inotuzumab both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- iobenguane I 131
doxepin will decrease the level or effect of iobenguane I 131 by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Based on the mechanism of action of iobenguane, drugs that reduce catecholamine uptake or that deplete catecholamine stores may interfere with iobenguane uptake into cells, and thus, reduce iobenguane efficacy. Discontinue interfering drugs for at least 5 half-lives before administration of either the dosimetry or an iobenguane dose. Do not administer these drugs until at least 7 days after each iobenguane dose.
- isoproterenol
doxepin, isoproterenol. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- ivosidenib
doxepin and ivosidenib both decrease QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ketoconazole
doxepin and ketoconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lenvatinib
doxepin and lenvatinib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- levalbuterol
doxepin, levalbuterol. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- levoketoconazole
doxepin and levoketoconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- levomilnacipran
levomilnacipran and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- linezolid
linezolid and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Linezolid may increase serotonin as a result of MAO-A inhibition. If linezolid must be administered, discontinue serotonergic drug immediately and monitor for CNS toxicity. Serotonergic therapy may be resumed 24 hours after last linezolid dose or after 2 weeks of monitoring, whichever comes first.
- lisdexamfetamine
doxepin, lisdexamfetamine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- lofepramine
doxepin and lofepramine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin and lofepramine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - lopinavir
doxepin and lopinavir both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lorcaserin
doxepin and lorcaserin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lumefantrine
lumefantrine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin and lumefantrine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - macimorelin
doxepin and macimorelin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- maprotiline
doxepin and maprotiline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin and maprotiline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - mefloquine
mefloquine increases toxicity of doxepin by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Mefloquine may enhance the QTc prolonging effect of high risk QTc prolonging agents.
- meperidine
doxepin and meperidine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- metaproterenol
doxepin, metaproterenol. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- methamphetamine
doxepin, methamphetamine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- methohexital
methohexital and doxepin both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Limit use to patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate
- methylene blue
methylene blue and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Methylene blue may increase serotonin as a result of MAO-A inhibition. If methylene blue must be administered, discontinue serotonergic drug immediately and monitor for CNS toxicity. Serotonergic therapy may be resumed 24 hours after last methylene blue dose or after 2 weeks of monitoring, whichever comes first.
- methylenedioxymethamphetamine
doxepin, methylenedioxymethamphetamine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- metoclopramide intranasal
doxepin, metoclopramide intranasal. Either increases effects of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Avoid use of metoclopramide intranasal or interacting drug, depending on importance of drug to patient.
- midodrine
doxepin, midodrine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- midostaurin
doxepin and midostaurin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- milnacipran
milnacipran and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- mirtazapine
doxepin and mirtazapine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- moxifloxacin
doxepin and moxifloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nefazodone
nefazodone and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- netupitant/palonosetron
netupitant/palonosetron, doxepin. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nilotinib
doxepin and nilotinib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- norepinephrine
doxepin, norepinephrine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- nortriptyline
doxepin and nortriptyline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin and nortriptyline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - octreotide
doxepin and octreotide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- octreotide (Antidote)
doxepin and octreotide (Antidote) both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- olopatadine intranasal
doxepin and olopatadine intranasal both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration increases risk of CNS depression, which can lead to additive impairment of psychomotor performance and cause daytime impairment.
- ondansetron
ondansetron, doxepin. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- osimertinib
doxepin and osimertinib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ozanimod
ozanimod increases toxicity of doxepin by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Because the active metabolite of ozanimod inhibits MAO-B in vitro, there is a potential for serious adverse reactions, including hypertensive crisis. Therefore, coadministration of ozanimod with drugs that can increase norepinephrine or serotonin is not recommended. Monitor for hypertension with concomitant use.
doxepin and ozanimod both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated. - palonosetron
palonosetron, doxepin. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- panobinostat
doxepin and panobinostat both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- paroxetine
paroxetine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
paroxetine and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - perphenazine
perphenazine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- phendimetrazine
doxepin, phendimetrazine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- phentermine
doxepin, phentermine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- phenylephrine
doxepin, phenylephrine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- phenylephrine PO
doxepin, phenylephrine PO. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- pirbuterol
doxepin, pirbuterol. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- pitolisant
doxepin decreases effects of pitolisant by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Pitolisant increases histamine levels in the brain; therefore, H1 receptor antagonists that cross the blood-brain barrier may reduce the efficacy of pitolisant.
doxepin and pitolisant both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - ponesimod
doxepin and ponesimod both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- primaquine
doxepin and primaquine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- promazine
promazine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- propylhexedrine
doxepin, propylhexedrine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- protriptyline
doxepin and protriptyline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin and protriptyline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - pseudoephedrine
doxepin increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- quinidine
quinidine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Both agents increase QTc interval.
- quinine
doxepin and quinine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- rasagiline
rasagiline and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Severe CNS toxicity associated with hyperpyrexia has been reported with the combined treatment of an antidepressant and rasagiline. Avoid combination within 14 days of MAOI use.
- ribociclib
ribociclib will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin and ribociclib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - salmeterol
doxepin, salmeterol. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- selegiline transdermal
selegiline transdermal and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- selinexor
selinexor, doxepin. unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Patients treated with selinexor may experience neurological toxicities. Avoid taking selinexor with other medications that may cause dizziness or confusion.
- serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate
doxepin, serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- sertraline
sertraline and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - sodium oxybate
doxepin, sodium oxybate. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death may result if coadministered. Reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs in patients for whom other treatment options are inadequate. Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required. Monitor closely for signs of respiratory depression and sedation.
- St John's Wort
doxepin and St John's Wort both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tedizolid
tedizolid, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. both increase serotonin levels; increased risk of serotonin syndrome.
- terbutaline
doxepin, terbutaline. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- thioridazine
thioridazine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- toremifene
doxepin and toremifene both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concurrent use of toremifene with agents causing QT prolongation should be avoided. If concomitant use is required it's recommended that toremifene be interrupted. If interruption not possible, patients requiring therapy with a drug that prolongs QT should be closely monitored. ECGs should be obtained for high risk patients.
- trazodone
doxepin and trazodone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
trazodone and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - trifluoperazine
trifluoperazine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- trimipramine
doxepin and trimipramine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin and trimipramine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - tucatinib
tucatinib will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid concomitant use of tucatinib with CYP3A substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities. If unavoidable, reduce CYP3A substrate dose according to product labeling.
- umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled
doxepin and umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Exercise extreme caution if vilanterol coadministered with MAOIs or TCAs, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of these drugs; adrenergic agonist effects on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated
- vandetanib
doxepin, vandetanib. Either increases toxicity of the other by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration with drugs known to prolong QT interval; if a drug known to prolong QT interval must be used, more frequent ECG monitoring is recommended.
- venlafaxine
venlafaxine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
venlafaxine and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - vilanterol/fluticasone furoate inhaled
doxepin and vilanterol/fluticasone furoate inhaled both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Exercise extreme caution if vilanterol coadministered with MAOIs or TCAs, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of these drugs; adrenergic agonist effects on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated
- vilazodone
doxepin, vilazodone. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant therapy should be discontinued immediately if signs or symptoms of serotonin syndrome emerge and supportive symptomatic treatment should be initiated. .
- vortioxetine
doxepin, vortioxetine. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- xylometazoline
doxepin, xylometazoline. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- yohimbe
yohimbe, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Contraindicated. May cause increase or decrease in blood pressure.
- yohimbine
doxepin, yohimbine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- ziprasidone
doxepin and ziprasidone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- zuranolone
doxepin, zuranolone. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of zuranolone with other CNS depressants may increase impairment of psychomotor performance or CNS depressant effects. If unavoidable, consider dose reduction. .
Monitor Closely (392)
- 5-HTP
doxepin and 5-HTP both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- abiraterone
abiraterone increases levels of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid coadministration of abiraterone with substrates of CYP2D6. If alternative therapy cannot be used, exercise caution and consider a dose reduction of the CYP2D6 substrate.
- abobotulinumtoxinA
doxepin increases effects of abobotulinumtoxinA by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs with anticholinergic effects may potentiate botulinum toxin effects, which may result in excessive neuromuscular weakness and heighten systemic anticholinergic effects.
- aclidinium
aclidinium and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- acrivastine
acrivastine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- albuterol
doxepin increases and albuterol decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and albuterol both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - alfentanil
alfentanil and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- alfuzosin
doxepin and alfuzosin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- almotriptan
almotriptan and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- alprazolam
alprazolam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amifampridine
doxepin increases toxicity of amifampridine by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Amifampridine can cause seizures. Coadministration with drugs that lower seizure threshold may increase this risk.
- amiodarone
amiodarone will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amisulpride
doxepin and amisulpride both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. ECG monitoring is recommended if coadministered.
- amitriptyline
amitriptyline and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
amitriptyline and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - amobarbital
amobarbital and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amoxapine
amoxapine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
amoxapine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - anagrelide
doxepin and anagrelide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- anticholinergic/sedative combos
anticholinergic/sedative combos and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- apomorphine
doxepin and apomorphine both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and apomorphine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - arformoterol
doxepin increases and arformoterol decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and arformoterol both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - aripiprazole
aripiprazole and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and aripiprazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - armodafinil
doxepin increases and armodafinil decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- asenapine
asenapine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and asenapine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
asenapine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - asenapine transdermal
asenapine transdermal and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
asenapine transdermal and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - atazanavir
atazanavir increases levels of doxepin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- atomoxetine
doxepin and atomoxetine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- atracurium
atracurium and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- atropine
atropine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- atropine IV/IM
atropine IV/IM and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- avapritinib
avapritinib and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- azelastine
azelastine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- azithromycin
doxepin and azithromycin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- baclofen
baclofen and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bedaquiline
doxepin and bedaquiline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- belladonna alkaloids
belladonna alkaloids and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- belladonna and opium
belladonna and opium and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
belladonna and opium and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - benperidol
benperidol and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen
benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system may result in serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dose adjustment.
- benzphetamine
doxepin increases and benzphetamine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- benztropine
benztropine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bethanechol
bethanechol increases and doxepin decreases cholinergic effects/transmission. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- brexpiprazole
brexpiprazole and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- brimonidine
brimonidine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- brivaracetam
brivaracetam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- brompheniramine
brompheniramine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- buprenorphine
buprenorphine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- buprenorphine buccal
buprenorphine buccal and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- buprenorphine subdermal implant
doxepin, buprenorphine subdermal implant. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use could result in life-threatening serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation, and during dose adjustment of the serotonergic drug. Discontinue buprenorphine if serotonin syndrome is suspected.
- buprenorphine, long-acting injection
doxepin, buprenorphine, long-acting injection. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use could result in life-threatening serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation, and during dose adjustment of the serotonergic drug. Discontinue buprenorphine if serotonin syndrome is suspected.
- bupropion
bupropion will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin increases toxicity of bupropion by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. May lower seizure threshold; keep bupropion dose as low as possible. - butabarbital
butabarbital and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- butalbital
butalbital and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- butorphanol
butorphanol and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- caffeine
doxepin increases and caffeine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- carbachol
carbachol increases and doxepin decreases cholinergic effects/transmission. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- carbinoxamine
carbinoxamine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cariprazine
cariprazine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- carisoprodol
carisoprodol and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- celecoxib
celecoxib will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cenobamate
cenobamate will decrease the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Increase dose of CYP3A4 substrate, as needed, when coadministered with cenobamate.
cenobamate, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - ceritinib
doxepin and ceritinib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cevimeline
cevimeline increases and doxepin decreases cholinergic effects/transmission. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chloral hydrate
chloral hydrate and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chlordiazepoxide
chlordiazepoxide and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chloroquine
chloroquine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chlorpheniramine
chlorpheniramine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chlorpromazine
chlorpromazine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chlorzoxazone
chlorzoxazone and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cimetidine
cimetidine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cinnarizine
cinnarizine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ciprofloxacin
doxepin and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cisatracurium
cisatracurium and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clemastine
clemastine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clobazam
clobazam will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Lower doses of drugs metabolized by CYP2D6 may be required when used concomitantly.
doxepin, clobazam. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Concomitant administration can increase the potential for CNS effects (e.g., increased sedation or respiratory depression). - clofazimine
doxepin and clofazimine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clomipramine
clomipramine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
clomipramine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - clonazepam
clonazepam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clorazepate
clorazepate and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clozapine
clozapine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and clozapine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - cobicistat
cobicistat will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Carefully titrate antidepressant to the desired effect, including using the lowest feasible initial or maintenance dose, and monitoring for antidepressant response
cobicistat will increase the level or effect of doxepin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Carefully titrate dose of the antidepressant to the desired effect, including using the lowest feasible initial or maintenance dose, and monitor its response during coadministration with TCAs and cobicistat. - cocaine topical
doxepin and cocaine topical both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- codeine
codeine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- crizotinib
doxepin and crizotinib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cyclizine
cyclizine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
cyclizine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - cyclobenzaprine
cyclobenzaprine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
cyclobenzaprine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - cyproheptadine
cyproheptadine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dabrafenib
dabrafenib will decrease the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dantrolene
dantrolene and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- daridorexant
doxepin and daridorexant both increase sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration increases risk of CNS depression, which can lead to additive impairment of psychomotor performance and cause daytime impairment.
- darifenacin
darifenacin will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
darifenacin and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor. - dasatinib
doxepin and dasatinib both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- daxibotulinumtoxinA
doxepin increases effects of daxibotulinumtoxinA by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs with anticholinergic effects may potentiate botulinum toxin effects, which may result in excessive neuromuscular weakness and heighten systemic anticholinergic effects.
- debrisoquine
doxepin decreases effects of debrisoquine by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Inhibition of uptake by adrenergic neurons.
- degarelix
degarelix and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- desflurane
desflurane and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
desflurane and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - desipramine
desipramine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
desipramine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - desvenlafaxine
desvenlafaxine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Desvenlafaxine inhibits CYP2D6; with higher desvenlafaxine doses (ie, 400 mg) decrease the CYP2D6 substrate dose by up to 50%; no dosage adjustment needed with desvenlafaxine doses <100 mg
- deutetrabenazine
doxepin and deutetrabenazine both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
deutetrabenazine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. At the maximum recommended dose, deutetrabenazine does not prolong QT interval to a clinically relevant extent. Certain circumstances may increase risk of torsade de pointes and/or sudden death in association with drugs that prolong the QTc interval (eg, bradycardia, hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, coadministration with other drugs that prolong QTc interval, presence of congenital QT prolongation). - dexchlorpheniramine
dexchlorpheniramine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dexfenfluramine
doxepin increases and dexfenfluramine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and dexfenfluramine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - dexmedetomidine
dexmedetomidine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dexmethylphenidate
doxepin increases and dexmethylphenidate decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dextroamphetamine
doxepin increases and dextroamphetamine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and dextroamphetamine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
doxepin increases effects of dextroamphetamine by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. - dextroamphetamine transdermal
doxepin will increase the level or effect of dextroamphetamine transdermal by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. May enhance the activity of tricyclic or sympathomimetic agents causing striking and sustained increases in dextroamphetamine levels in brain; May be potentiate cardiovascular effects. Monitor frequently and adjust or use an alternant based on clinical response.
- dextromoramide
dextromoramide and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diamorphine
diamorphine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diazepam
diazepam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diazepam intranasal
diazepam intranasal, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration may potentiate the CNS-depressant effects of each drug.
- dichlorphenamide
dichlorphenamide and doxepin both decrease serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dicyclomine
dicyclomine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diethylpropion
doxepin increases and diethylpropion decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- difelikefalin
difelikefalin and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- difenoxin hcl
difenoxin hcl and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dihydroergotamine
doxepin and dihydroergotamine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dihydroergotamine intranasal
doxepin and dihydroergotamine intranasal both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dimenhydrinate
dimenhydrinate and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diphenhydramine
diphenhydramine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
diphenhydramine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - diphenoxylate hcl
diphenoxylate hcl and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dipipanone
dipipanone and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dobutamine
doxepin increases and dobutamine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dolasetron
doxepin and dolasetron both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- donepezil
donepezil increases and doxepin decreases cholinergic effects/transmission. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
donepezil and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - dopamine
doxepin increases and dopamine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dopexamine
doxepin increases and dopexamine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- doxylamine
doxylamine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- droperidol
droperidol and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- echothiophate iodide
echothiophate iodide increases and doxepin decreases cholinergic effects/transmission. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- efavirenz
efavirenz and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eletriptan
eletriptan and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- eliglustat
eliglustat increases levels of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor therapeutic drug concentrations, as indicated, or consider reducing the dosage of the concomitant drug and titrate to clinical effect.
doxepin and eliglustat both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF
elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF increases levels of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Cobicistat is a CYP2D6 inhibitor; caution with CYP2D6 substrates for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events.
- entrectinib
doxepin and entrectinib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ephedrine
doxepin increases and ephedrine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin increases effects of ephedrine by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. - epinephrine
doxepin increases and epinephrine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin increases effects of epinephrine by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. - epinephrine inhaled
doxepin and epinephrine inhaled both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor. Tricyclic antidepressants may potentiate epinephrine effect on cardiovascular system.
- epinephrine racemic
doxepin increases and epinephrine racemic decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin increases effects of epinephrine racemic by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. - ergotamine
doxepin and ergotamine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- eribulin
doxepin and eribulin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- esketamine intranasal
esketamine intranasal, doxepin. Either increases toxicity of the other by sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- estazolam
estazolam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ethanol
doxepin and ethanol both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- etomidate
etomidate and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fedratinib
fedratinib will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Adjust dose of drugs that are CYP3A4 substrates as necessary.
fedratinib will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Adjust dose of drugs that are CYP2D6 substrates as necessary. - fenfluramine
doxepin increases and fenfluramine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and fenfluramine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
fenfluramine, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with drugs that increase serotoninergic effects may increase the risk of serotonin syndrome. - fesoterodine
fesoterodine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fingolimod
fingolimod and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- flavoxate
flavoxate and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- flecainide
doxepin and flecainide both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- fluoxetine
doxepin and fluoxetine both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- fluphenazine
fluphenazine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- flurazepam
flurazepam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- formoterol
doxepin increases and formoterol decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- foscarnet
doxepin and foscarnet both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- fostemsavir
doxepin and fostemsavir both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. QTc prolongation reported with higher than recommended doses of fostemsavir.
- frovatriptan
frovatriptan and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- gabapentin
gabapentin, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of CNS depressants can result in serious, life-threatening, and fatal respiratory depression. Use lowest dose possible and monitor for respiratory depression and sedation.
- gabapentin enacarbil
gabapentin enacarbil, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of CNS depressants can result in serious, life-threatening, and fatal respiratory depression. Use lowest dose possible and monitor for respiratory depression and sedation.
- gadobenate
gadobenate and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- galantamine
galantamine increases and doxepin decreases cholinergic effects/transmission. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ganaxolone
doxepin and ganaxolone both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- gemifloxacin
doxepin and gemifloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- gemtuzumab
doxepin and gemtuzumab both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- gepirone
gepirone and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for symptoms of serotonin syndrome when gepirone is used gepirone with other drugs that may affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter systems. If serotonin syndrome occurs, consider discontinue gepirone and/or concomitant serotonergic drug.
- gilteritinib
doxepin and gilteritinib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- glycopyrrolate
glycopyrrolate and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin increases levels of glycopyrrolate by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. - glycopyrrolate inhaled
glycopyrrolate inhaled and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin increases levels of glycopyrrolate inhaled by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. - glycopyrronium tosylate topical
glycopyrronium tosylate topical, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of glycopyrronium tosylate topical with other anticholinergic medications may result in additive anticholinergic adverse effects.
- goserelin
doxepin and goserelin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- granisetron
doxepin and granisetron both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- haloperidol
haloperidol and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- henbane
henbane and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- histrelin
doxepin and histrelin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- homatropine
homatropine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- huperzine A
huperzine A increases and doxepin decreases cholinergic effects/transmission. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- hydrocodone
hydrocodone, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system may result in serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dose adjustment.
- hydromorphone
hydromorphone and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- hydroxyzine
hydroxyzine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and hydroxyzine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - hyoscyamine
hyoscyamine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- hyoscyamine spray
hyoscyamine spray and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- icosapent
icosapent, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Icosapent may prolong bleeding time. Periodically monitor if coadministered with other drugs that affect bleeding.
- iloperidone
doxepin and iloperidone both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
iloperidone and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
iloperidone increases levels of doxepin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Iloperidone is a time-dependent CYP3A inhibitor and may lead to increased plasma levels of drugs predominantly eliminated by CYP3A4. - imatinib
imatinib will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- imipramine
doxepin and imipramine both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and imipramine both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - incobotulinumtoxinA
doxepin increases effects of incobotulinumtoxinA by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs with anticholinergic effects may potentiate botulinum toxin effects, which may result in excessive neuromuscular weakness and heighten systemic anticholinergic effects.
- indacaterol, inhaled
indacaterol, inhaled, doxepin. QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs that are known to prolong the QTc interval may have an increased the risk of ventricular arrhythmias.
- ipratropium
ipratropium and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor. Due to the poor systemic absorption of ipratropium, interaction unlikely at regularly recommended dosages.
- isoflurane
doxepin and isoflurane both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- isoniazid
doxepin and isoniazid both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- isoproterenol
doxepin increases and isoproterenol decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- istradefylline
istradefylline will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Istradefylline 40 mg/day increased peak levels and AUC of CYP3A4 substrates in clinical trials. This effect was not observed with istradefylline 20 mg/day. Consider dose reduction of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates.
- itraconazole
itraconazole and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ketamine
ketamine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ketotifen, ophthalmic
doxepin and ketotifen, ophthalmic both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- L-tryptophan
doxepin and L-tryptophan both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- lapatinib
doxepin and lapatinib both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- lasmiditan
lasmiditan, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of lasmiditan and other CNS depressant drugs, including alcohol have not been evaluated in clinical studies. Lasmiditan may cause sedation, as well as other cognitive and/or neuropsychiatric adverse reactions.
doxepin increases effects of lasmiditan by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration may increase risk of serotonin syndrome. - lefamulin
doxepin and lefamulin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lemborexant
lemborexant, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Dosage adjustment may be necessary if lemborexant is coadministered with other CNS depressants because of potentially additive effects.
- letibotulinumtoxinA
doxepin increases effects of letibotulinumtoxinA by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs with anticholinergic effects may potentiate botulinum toxin effects, which may result in excessive neuromuscular weakness and heighten systemic anticholinergic effects.
- leuprolide
doxepin and leuprolide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levalbuterol
doxepin increases and levalbuterol decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and levalbuterol both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - levetiracetam
levetiracetam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levofloxacin
doxepin and levofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- levorphanol
levorphanol and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levothyroxine
levothyroxine increases effects of doxepin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Increased catecholamine receptor sensitivity; may increase CNS and cardiovascular effects, including arrhythmias.
- liothyronine
liothyronine increases effects of doxepin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Increased catecholamine receptor sensitivity; may increase CNS and cardiovascular effects, including arrhythmias.
- liotrix
liotrix increases effects of doxepin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Increased catecholamine receptor sensitivity; may increase CNS and cardiovascular effects, including arrhythmias.
- lisdexamfetamine
doxepin increases and lisdexamfetamine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin, lisdexamfetamine. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Initiate with lower doses and monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, particularly during initiation or dosage increase. If serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue along with concomitant serotonergic drug(s). - lithium
doxepin and lithium both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
doxepin and lithium both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - lofepramine
doxepin and lofepramine both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and lofepramine both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - lofexidine
doxepin and lofexidine both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin decreases effects of lofexidine by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and lofexidine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - loperamide
doxepin and loperamide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- loprazolam
loprazolam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lorazepam
lorazepam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lorcaserin
lorcaserin will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lormetazepam
lormetazepam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- loxapine
loxapine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- loxapine inhaled
loxapine inhaled and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lsd
doxepin and lsd both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- lurasidone
lurasidone increases effects of doxepin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Potential for increased risk of hypotension with concurrent use. Monitor blood pressure and adjust dose of antihypertensive agent as needed.
- maprotiline
doxepin and maprotiline both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and maprotiline both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - marijuana
doxepin and marijuana both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- meclizine
meclizine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- melatonin
doxepin and melatonin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- meperidine
meperidine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- meprobamate
doxepin and meprobamate both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- metaproterenol
doxepin increases and metaproterenol decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- metaxalone
metaxalone and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methadone
doxepin and methadone both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
methadone and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - methamphetamine
doxepin increases and methamphetamine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methocarbamol
methocarbamol and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methscopolamine
methscopolamine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methylenedioxymethamphetamine
doxepin increases and methylenedioxymethamphetamine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methylphenidate
doxepin, methylphenidate. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- methylphenidate transdermal
methylphenidate transdermal will increase the level or effect of doxepin by decreasing elimination. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider decreasing the dose of these drugs when given coadministered with methylphenidate. Monitor for drug toxiticities when initiating or discontinuing methylphenidate.
- midazolam
midazolam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- midazolam intranasal
midazolam intranasal, doxepin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Concomitant use of barbiturates, alcohol, or other CNS depressants may increase risk of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, desaturation, or apnea and may contribute to profound and/or prolonged drug effect.
- midodrine
doxepin increases and midodrine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mifepristone
doxepin and mifepristone both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mirabegron
mirabegron will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mirtazapine
doxepin and mirtazapine both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and mirtazapine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - mitotane
mitotane decreases levels of doxepin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Mitotane is a strong inducer of cytochrome P-4503A4; monitor when coadministered with CYP3A4 substrates for possible dosage adjustments.
- mobocertinib
doxepin and mobocertinib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- modafinil
doxepin increases and modafinil decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- morphine
morphine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and morphine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - motherwort
doxepin and motherwort both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- moxonidine
doxepin and moxonidine both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nabilone
doxepin and nabilone both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nalbuphine
nalbuphine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- naratriptan
naratriptan and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- nefopam
nefopam, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Use combination with caution.
- neostigmine
neostigmine increases and doxepin decreases cholinergic effects/transmission. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nilotinib
nilotinib will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- norepinephrine
doxepin increases and norepinephrine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin increases effects of norepinephrine by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. - nortriptyline
doxepin and nortriptyline both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and nortriptyline both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - ofloxacin
doxepin and ofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- olanzapine
olanzapine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and olanzapine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Limited data, including some case reports, suggest that olanzapine may be associated with a significant prolongation of the QTc interval in rare instances - olanzapine/samidorphan
doxepin, olanzapine/samidorphan. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of diazepam, alcohol, or other CNS acting drugs may potentiate orthostatic hypotension observed with olanzapine. Additive sedation may also occur.
- oliceridine
doxepin, oliceridine. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
doxepin increases toxicity of oliceridine by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Anticholinergic drugs may increase risk of urinary retention and/or severe constipation, which may lead to paralytic ileus. Monitor for signs of urinary retention or reduced gastric motility if oliceridine is coadministered with anticholinergics. - olodaterol inhaled
doxepin and olodaterol inhaled both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs that prolong the QTc interval and may potentiate the effects of beta2 agonists on the cardiovascular system; increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
- onabotulinumtoxinA
doxepin increases effects of onabotulinumtoxinA by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs with anticholinergic effects may potentiate botulinum toxin effects, which may result in excessive neuromuscular weakness and heighten systemic anticholinergic effects.
- ondansetron
doxepin and ondansetron both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- opium tincture
opium tincture and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- orphenadrine
doxepin and orphenadrine both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
orphenadrine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - osilodrostat
osilodrostat and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oxaliplatin
doxepin and oxaliplatin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oxazepam
oxazepam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oxybutynin
oxybutynin and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oxybutynin topical
oxybutynin topical and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oxybutynin transdermal
oxybutynin transdermal and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oxycodone
oxycodone and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oxymetazoline intranasal
doxepin increases effects of oxymetazoline intranasal by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. TCAs inhibit norepinephrine uptake in adrenergic neurons, thereby increasing synaptic norepinephrine levels. Coadministration with alpha1 agonists may cause increased adrenergic receptor stimulation. When oxymetazoline is combined with intranasal tetracaine for dental anesthesia, avoid or use alternant anesthetic in patients taking TCAs.
- oxymorphone
oxymorphone and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- paliperidone
doxepin and paliperidone both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
paliperidone and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - pancuronium
pancuronium and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- papaveretum
papaveretum and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- papaverine
doxepin and papaverine both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- paroxetine
doxepin and paroxetine both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- pasireotide
doxepin and pasireotide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pazopanib
doxepin and pazopanib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- peginterferon alfa 2b
peginterferon alfa 2b, doxepin. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: When patients are administered peginterferon alpha-2b with CYP2D6 substrates, the therapeutic effect of these drugs may be altered. Peginterferon alpha-2b may increase or decrease levels of CYP2D6 substrate.
- pentazocine
pentazocine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and pentazocine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - pentobarbital
pentobarbital and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- perphenazine
perphenazine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phendimetrazine
doxepin increases and phendimetrazine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phenobarbital
phenobarbital and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phentermine
doxepin increases and phentermine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phenylephrine
doxepin increases and phenylephrine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phenylephrine ophthalmic
doxepin, phenylephrine ophthalmic. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
- phenylephrine PO
doxepin increases and phenylephrine PO decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor. .
- pholcodine
doxepin and pholcodine both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- physostigmine
physostigmine increases and doxepin decreases cholinergic effects/transmission. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pilocarpine
pilocarpine increases and doxepin decreases cholinergic effects/transmission. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pimavanserin
doxepin and pimavanserin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pimozide
pimozide and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pirbuterol
doxepin increases and pirbuterol decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- posaconazole
doxepin and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- prabotulinumtoxinA
doxepin increases effects of prabotulinumtoxinA by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs with anticholinergic effects may potentiate botulinum toxin effects, which may result in excessive neuromuscular weakness and heighten systemic anticholinergic effects.
- pralidoxime
pralidoxime and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pregabalin
pregabalin, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of CNS depressants can result in serious, life-threatening, and fatal respiratory depression. Use lowest dose possible and monitor for respiratory depression and sedation.
- primidone
primidone and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- prochlorperazine
prochlorperazine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
prochlorperazine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - promethazine
promethazine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
promethazine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - propafenone
propafenone will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and propafenone both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - propantheline
propantheline and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- propofol
propofol and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- propylhexedrine
doxepin increases and propylhexedrine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- protriptyline
doxepin and protriptyline both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and protriptyline both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - pyridostigmine
pyridostigmine increases and doxepin decreases cholinergic effects/transmission. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quazepam
quazepam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quetiapine
quetiapine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and quetiapine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - ramelteon
doxepin and ramelteon both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin will increase the level or effect of ramelteon by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. AUC and Cmax increased by 66% and 69% respectively. - ranolazine
doxepin and ranolazine both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- rapacuronium
rapacuronium and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- remifentanil
doxepin, remifentanil. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. May also increase risk of serotonin syndrome.
- remimazolam
remimazolam, doxepin. Either increases toxicity of the other by sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and/or death. Continuously monitor vital signs during sedation and recovery period if coadministered. Carefully titrate remimazolam dose if administered with opioid analgesics and/or sedative/hypnotics.
- rifabutin
rifabutin decreases levels of doxepin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rilpivirine
doxepin and rilpivirine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rimabotulinumtoxinB
doxepin increases effects of rimabotulinumtoxinB by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs with anticholinergic effects may potentiate botulinum toxin effects, which may result in excessive neuromuscular weakness and heighten systemic anticholinergic effects.
- risperidone
doxepin and risperidone both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
risperidone and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - ritonavir
ritonavir will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rivastigmine
rivastigmine increases and doxepin decreases cholinergic effects/transmission. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rizatriptan
rizatriptan and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- rocuronium
rocuronium and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rolapitant
rolapitant will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Rolapitant may increase plasma concentrations of CYP2D6 substrates for at least 28 days following rolapitant administration.
- romidepsin
doxepin and romidepsin both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- salmeterol
doxepin increases and salmeterol decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and salmeterol both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - SAMe
doxepin and SAMe both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- saquinavir
doxepin and saquinavir both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- scopolamine
scopolamine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- scullcap
doxepin and scullcap both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- secobarbital
secobarbital and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- selpercatinib
doxepin and selpercatinib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sevoflurane
sevoflurane and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and sevoflurane both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - shepherd's purse
doxepin and shepherd's purse both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- siponimod
doxepin and siponimod both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sodium sulfate/?magnesium sulfate/potassium chloride
sodium sulfate/?magnesium sulfate/potassium chloride increases effects of doxepin by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Closely monitor for evidence of seizures when using higher dose of magnesium sulfate together with drugs that lower the seizure threshold.
- sodium sulfate/potassium chloride/magnesium sulfate/polyethylene glycol
doxepin, sodium sulfate/potassium chloride/magnesium sulfate/polyethylene glycol. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Caution when bowel preps are used with drugs that cause SIADH or NSAIDs; increased risk for water retention or electrolyte imbalance.
- sodium sulfate/potassium sulfate/magnesium sulfate
sodium sulfate/potassium sulfate/magnesium sulfate increases effects of doxepin by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Closely monitor for evidence of seizures when using higher dose of magnesium sulfate together with drugs that lower the seizure threshold.
- solifenacin
solifenacin and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and solifenacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - sorafenib
doxepin and sorafenib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- stiripentol
stiripentol, doxepin. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Stiripentol is a CYP3A4 inhibitor and inducer. Monitor CYP3A4 substrates coadministered with stiripentol for increased or decreased effects. CYP3A4 substrates may require dosage adjustment.
stiripentol, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use stiripentol with other CNS depressants, including alcohol, may increase the risk of sedation and somnolence. - succinylcholine
succinylcholine increases and doxepin decreases cholinergic effects/transmission. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sufentanil
sufentanil and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sufentanil SL
sufentanil SL, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system may result in serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dose adjustment.
- sulfamethoxazole
doxepin and sulfamethoxazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- sumatriptan
sumatriptan and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- sumatriptan intranasal
sumatriptan intranasal and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- sunitinib
doxepin and sunitinib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- suvorexant
suvorexant and doxepin both increase sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Dosage adjustments of suvorexant and concomitant CNS depressants may be necessary
- tacrolimus
doxepin and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tapentadol
tapentadol and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and tapentadol both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - telavancin
doxepin and telavancin both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- temazepam
temazepam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- terbinafine
terbinafine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Assess need to reduce dose of CYP2D6-metabolized drug.
- terbutaline
doxepin increases and terbutaline decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- teriflunomide
teriflunomide decreases levels of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tetrabenazine
tetrabenazine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- thioridazine
thioridazine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- thiothixene
thiothixene and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and thiothixene both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - thyroid desiccated
thyroid desiccated increases effects of doxepin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Increased catecholamine receptor sensitivity; may increase CNS and cardiovascular effects, including arrhythmias.
- tiotropium
tiotropium and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tolterodine
tolterodine and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- topiramate
doxepin and topiramate both increase sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- tramadol
tramadol and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and tramadol both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - trazodone
doxepin and trazodone both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and trazodone both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - triazolam
triazolam and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- triclabendazole
doxepin and triclabendazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- triclofos
triclofos and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- trifluoperazine
trifluoperazine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- trihexyphenidyl
trihexyphenidyl and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor. Potential for additive anticholinergic effects.
- trimethoprim
doxepin and trimethoprim both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- trimipramine
doxepin and trimipramine both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
doxepin and trimipramine both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - triprolidine
triprolidine and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- triptorelin
doxepin and triptorelin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tropisetron
doxepin and tropisetron both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- trospium chloride
trospium chloride and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled
doxepin and umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled both decrease QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- valbenazine
valbenazine and doxepin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- valerian
valerian and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vardenafil
doxepin and vardenafil both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vecuronium
vecuronium and doxepin both decrease cholinergic effects/transmission. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vemurafenib
doxepin and vemurafenib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- venlafaxine
doxepin and venlafaxine both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- voclosporin
doxepin and voclosporin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- voriconazole
doxepin and voriconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- vorinostat
doxepin and vorinostat both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- xylometazoline
doxepin increases and xylometazoline decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- yohimbine
doxepin increases and yohimbine decreases sedation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ziconotide
doxepin and ziconotide both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ziprasidone
ziprasidone and doxepin both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- zolmitriptan
zolmitriptan and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
Minor (81)
- acarbose
doxepin increases effects of acarbose by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- amobarbital
amobarbital, doxepin. Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Comment: Barbiturates may increase adverse effects, including respiratory depression, produced by toxic doses of TCAs. With therapeutic doses of TCAs, barbiturates increase metabolism and decrease blood concentrations of TCAs.
- atropine
doxepin increases levels of atropine by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- atropine IV/IM
doxepin increases levels of atropine IV/IM by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens
bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Estrogens and progestins may decr tricyclic antidepressant effects, while increasing TCA plasma concentration and adverse effects.
- brimonidine
doxepin decreases effects of brimonidine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- butabarbital
butabarbital, doxepin. Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Comment: Barbiturates may increase adverse effects, including respiratory depression, produced by toxic doses of TCAs. With therapeutic doses of TCAs, barbiturates increase metabolism and decrease blood concentrations of TCAs.
- butalbital
butalbital, doxepin. Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Comment: Barbiturates may increase adverse effects, including respiratory depression, produced by toxic doses of TCAs. With therapeutic doses of TCAs, barbiturates increase metabolism and decrease blood concentrations of TCAs.
- carbamazepine
carbamazepine decreases levels of doxepin by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- chlorpromazine
doxepin, chlorpromazine. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects.
doxepin, chlorpromazine. Either increases levels of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects. - chlorpropamide
doxepin increases effects of chlorpropamide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- conjugated estrogens
conjugated estrogens, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Estrogens and progestins may decr tricyclic antidepressant effects, while increasing TCA plasma concentration and adverse effects.
- conjugated estrogens, vaginal
conjugated estrogens, vaginal, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Estrogens and progestins may decr tricyclic antidepressant effects, while increasing TCA plasma concentration and adverse effects.
- desflurane
desflurane, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of arrhythmias or hypotension.
- dexmethylphenidate
dexmethylphenidate increases effects of doxepin by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- diphenhydramine
diphenhydramine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- dronedarone
dronedarone will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- duloxetine
duloxetine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- estradiol
estradiol, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Estrogens and progestins may decr tricyclic antidepressant effects, while increasing TCA plasma concentration and adverse effects.
- estrogens conjugated synthetic
estrogens conjugated synthetic, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Estrogens and progestins may decr tricyclic antidepressant effects, while increasing TCA plasma concentration and adverse effects.
- estrogens esterified
estrogens esterified, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Estrogens may inhibit hepatic metabolism of tricyclic antidepressants. However, interactions are not common.
- estropipate
estropipate, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Estrogens and progestins may decr tricyclic antidepressant effects, while increasing TCA plasma concentration and adverse effects.
- ethanol
ethanol, doxepin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive impairment of motor skills.
- ethinylestradiol
ethinylestradiol, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Oxidative metabolism of TCAs may be decreased by ethinyl estradiol. Increased antidepressant serum concentrations may occur. Potential for increased TCA adverse effects.
- etomidate
etomidate, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of arrhythmias or hypotension.
- eucalyptus
doxepin and eucalyptus both increase sedation. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fluphenazine
doxepin, fluphenazine. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects.
doxepin, fluphenazine. Either increases levels of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects. - glimepiride
doxepin increases effects of glimepiride by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- glipizide
doxepin increases effects of glipizide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- glyburide
doxepin increases effects of glyburide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- hydroxyprogesterone caproate (DSC)
hydroxyprogesterone caproate (DSC), doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Estrogens and progestins may decr tricyclic antidepressant effects, while increasing TCA plasma concentration and adverse effects.
- insulin aspart
doxepin increases effects of insulin aspart by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- insulin detemir
doxepin increases effects of insulin detemir by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- insulin glargine
doxepin increases effects of insulin glargine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- insulin glulisine
doxepin increases effects of insulin glulisine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- insulin lispro
doxepin increases effects of insulin lispro by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- insulin NPH
doxepin increases effects of insulin NPH by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- insulin regular human
doxepin increases effects of insulin regular human by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- isoproterenol
isoproterenol, doxepin. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of cardiac arrhythmias.
- ketamine
ketamine, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of arrhythmias or hypotension.
- lithium
lithium, doxepin. Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Comment: Risk of neurotoxicity in geriatric pts. Multiple mechanisms involved.
- maraviroc
maraviroc will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- marijuana
marijuana will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- mestranol
mestranol, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Estrogens and progestins may decr tricyclic antidepressant effects, while increasing TCA plasma concentration and adverse effects.
- metformin
doxepin increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- miglitol
doxepin increases effects of miglitol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- nateglinide
doxepin increases effects of nateglinide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- panax ginseng
panax ginseng increases effects of doxepin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- parecoxib
parecoxib will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pentobarbital
pentobarbital, doxepin. Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Comment: Barbiturates may increase adverse effects, including respiratory depression, produced by toxic doses of TCAs. With therapeutic doses of TCAs, barbiturates increase metabolism and decrease blood concentrations of TCAs.
- perphenazine
perphenazine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
doxepin, perphenazine. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects.
doxepin, perphenazine. Either increases levels of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects. - phenobarbital
phenobarbital, doxepin. Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Comment: Barbiturates may increase adverse effects, including respiratory depression, produced by toxic doses of TCAs. With therapeutic doses of TCAs, barbiturates increase metabolism and decrease blood concentrations of TCAs.
- pioglitazone
doxepin increases effects of pioglitazone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pleurisy root
pleurisy root decreases effects of doxepin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Theoretical interaction.
- primidone
primidone, doxepin. Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Comment: Barbiturates may increase adverse effects, including respiratory depression, produced by toxic doses of TCAs. With therapeutic doses of TCAs, barbiturates increase metabolism and decrease blood concentrations of TCAs.
- prochlorperazine
doxepin, prochlorperazine. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects.
doxepin, prochlorperazine. Either increases levels of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects. - progesterone micronized
progesterone micronized, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Estrogens and progestins may decr tricyclic antidepressant effects, while increasing TCA plasma concentration and adverse effects.
- promazine
doxepin, promazine. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects.
doxepin, promazine. Either increases levels of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects. - promethazine
doxepin, promethazine. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects.
doxepin, promethazine. Either increases levels of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects. - propofol
propofol, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of arrhythmias or hypotension.
- quinacrine
quinacrine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ranolazine
ranolazine will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- repaglinide
doxepin increases effects of repaglinide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- rosiglitazone
doxepin increases effects of rosiglitazone by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sage
doxepin and sage both increase sedation. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- saxagliptin
doxepin increases effects of saxagliptin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- secobarbital
secobarbital, doxepin. Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Comment: Barbiturates may increase adverse effects, including respiratory depression, produced by toxic doses of TCAs. With therapeutic doses of TCAs, barbiturates increase metabolism and decrease blood concentrations of TCAs.
- serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate
serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate increases effects of doxepin by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sertraline
sertraline will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sevoflurane
sevoflurane, doxepin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of arrhythmias or hypotension.
- sitagliptin
doxepin increases effects of sitagliptin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sulfamethoxazole
sulfamethoxazole decreases levels of doxepin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- thioridazine
doxepin, thioridazine. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects.
doxepin, thioridazine. Either increases levels of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects. - tipranavir
tipranavir will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- tolazamide
doxepin increases effects of tolazamide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- tolbutamide
doxepin increases effects of tolbutamide by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- trifluoperazine
doxepin, trifluoperazine. Either increases levels of the other by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects.
doxepin, trifluoperazine. Either increases levels of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive anticholinergic effects. - vasopressin
doxepin increases effects of vasopressin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- verapamil
verapamil increases levels of doxepin by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- vildagliptin
doxepin increases effects of vildagliptin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- zolpidem
zolpidem, doxepin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive CNS depression.
Adverse Effects
Frequency Not Defined
Sedation, fatigue, weakness, lethargy
Dry mouth
Constipation
Blurred vision
Headache
Agitation
Insomnia
Anxiety
Nausea, vomiting
Sweating
Confusion, extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), dizziness, paresthesia
Orthostatic hypotension, ECG changes, tachycardia
Increased LFTs
Tinnitus
Sexual dysfunction
Rash
Seizure
Agranulocytosis
Thrombocytopenia
Eosinophilia
Leukopenia
SIADH
Warnings
Black Box Warnings
In short-term studies, antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents, and young adults (<24 years) taking antidepressants for major depressive disorders and other psychiatric illnesses
This increase was not seen in patients >24 years; a slight decrease in suicidal thinking was seen in adults >65 years
In children and young adults, risks must be weighed against the benefits of taking antidepressants
Patients should be monitored closely for changes in behavior, clinical worsening, and suicidal tendencies; this should be done during initial 1-2 months of therapy and dosage adjustments
The patient’s family should communicate any abrupt changes in behavior to the healthcare provider
Worsening behavior and suicidal tendencies that are not part of the presenting symptoms may require discontinuation of therapy
This drug is not approved for use in pediatric patients
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity
Untreated narrow-angle glaucoma
Severe urinary retention
Within 14 days of MAO inhibitors
Cautions
Use caution in BPH, urinary retention, decreased GI motility, hyperthyroidism, brain tumor, diabetes, hepatic impairment, cardiovascular disease, mania/hypomania, respiratory disease, and seizure disorders
Clinical worsening and suicidal ideation may occur despite medication in adolescents and young adults (aged 18-24 years)
Risk of anticholinergic side effects
Risk of mydriasis; may trigger angle closure attack in patients with angle closure glaucoma with anatomically narrow angles without a patent iridectomy
CNS depressant; can impair alertness and motor coordination; avoid use with other CNS depressants (eg, alcohol)
Overdose may cause EKG QRS widening and risk of dysrhythmias
Protect capsules and oral concentrate from direct sunlight
Prescriptions should be written for smallest quantity consistent with good patient care; patient's family or caregiver should alert healthcare professional about emergence of suicidality and related behaviors including agitation, panic attacks, irritability, impulsivity, mania, and insomnia or if worsening depression or psychosis occurs
Anticholinergic effects including blurred vision, urinary retention, xerostomia, and constipation may occur
Neuropsychiatric symptoms may occur unpredictably including anxiety and psychosis
Bone fracture reported with use of antidepressant therapy; consider possibility of fracture if patient presents with unexplained bone pain, joint tenderness, bruising or swelling
May cause orthostatic hypotension; use caution in patients at risk of this effect or that may not tolerate hypotensive episodes (eg, hypovolemia, cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease and others)
Sleep related activities including sleep driving, eating food, cooking, making phone calls reported; discontinue therapy if patient reports sleep-related episodes
Possibility of EPS and neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS)
May cause confusion in the elderly; avoid doses >6 mg/day
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
Available data from published epidemiologic studies and postmarketing reports have not established increased risk of major birth defects or miscarriage; there are risks of poor neonatal adaptation with exposure to drug during pregnancy
Neonatal adverse effects
- Neonates exposed to TCAs, including doxepin, late in third trimester have developed complications requiring prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding; such complications can arise immediately upon delivery
- Reported clinical findings have included respiratory distress, cyanosis, apnea, seizures, temperature instability, feeding difficulty, vomiting, hypoglycemia, hypotonia, hyperreflexia, tremor, jitteriness, irritability and constant crying. These findings are consistent with either direct toxic effects of TCAs or possibly a drug discontinuation syndrome
- Monitor neonates who were exposed to drug in third trimester of pregnancy for poor neonatal adaptation syndrome
Animal data
- Based on results from animal fertility studies conducted in rats, doxepin may reduce fertility in females and males of reproductive potential
- In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of doxepin to rats and rabbits during period of organogenesis caused adverse developmental effects at doses 65 and 23 times maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 6 mg/day based on AUC, respectively
- Oral administration to pregnant rats during pregnancy and lactation resulted in decreased pup survival and a delay in pup growth at doses 60 times MRHD based on AUC
Lactation
Data from published report presence of drug and metabolite in human milk; there are reports of excess sedation, respiratory depression, poor sucking and swallowing, and hypotonia in breastfed infants exposed to drug
There are no data on effects of drug on milk production; because of potential for serious adverse reactions, including excess sedation and respiratory depression in a breastfed infant, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during therapy
Infants exposed to drug through breast milk should be monitored for excess sedation, respiratory depression and hypotonia
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Exact mechanism for doxepin's sleep maintenance effect is unknown; however, doxepin's action is believed to result from antagonism of the histamine H1 receptor
Mechanism of action for depression is unknown; may increase CNS synaptic concentrations of serotonin and norepinephrine by inhibiting reuptake
Absorption
Peak plasma time: 2 hr
Onset: >2 weeks (depression)
Distribution
Protein bound: 80%
Metabolism
Hepatic CYP2D6, CYP2C19
Metabolites: N-demethyldoxepin
Elimination
Half-life: 6-8 hr
Excretion: Urine
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silenor oral - | 6 mg tablet | 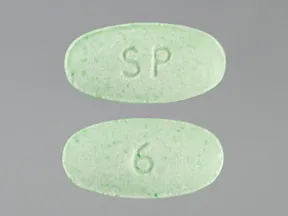 | |
| Silenor oral - | 3 mg tablet | 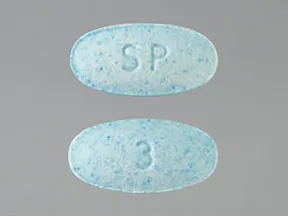 | |
| doxepin topical - | 5 % cream |  | |
| doxepin topical - | 5 % cream |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 10 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 50 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 10 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 100 mg capsule | 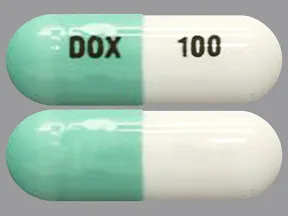 | |
| doxepin oral - | 75 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 50 mg capsule | 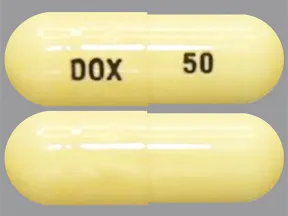 | |
| doxepin oral - | 25 mg capsule | 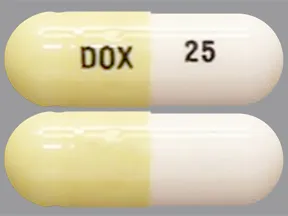 | |
| doxepin oral - | 10 mg capsule | 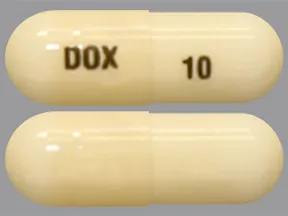 | |
| doxepin oral - | 10 mg/mL liquid |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 10 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 100 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 25 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 10 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 75 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 50 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 100 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 25 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 75 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 25 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 100 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 100 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 25 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 25 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 50 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 10 mg/mL liquid |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 75 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 150 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 75 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 100 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 50 mg capsule |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 3 mg tablet |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 6 mg tablet |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 6 mg tablet |  | |
| doxepin oral - | 3 mg tablet |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
doxepin topical
DOXEPIN CREAM - TOPICAL
(dox-EH-pin)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Zonalon
USES: This medication is used to relieve itching from certain skin conditions (such as atopic dermatitis, eczema, neurodermatitis). It should be used only for a short time (no more than 8 days). Doxepin is a tricyclic antidepressant. It is not known how this medication decreases itching. Some medication is absorbed into the body when the cream is applied. This medication may work by blocking a certain natural substance (histamine) that your body makes during an allergic reaction. The decrease in itching may be a result of drowsiness or some other effect in the brain that causes you not to notice or be bothered by the itching.
HOW TO USE: Before applying the medication, clean the affected area with mild soap and water, rinse well, and pat dry. Gently rub a small amount of the medication into the affected area in a thin layer as directed by your doctor, usually 4 times a day. Wait at least 3 to 4 hours between applications. How often the medication is applied and for how long depends on your condition and response to treatment. Usually, this medication is for short-term use only (up to 8 days).Wash hands immediately after use unless the area being treated includes the hands. This medication is for use on the skin only. Avoid getting the product in your eyes, nose, ears, mouth, or vaginal/anal area. If the medication gets in these areas, rinse immediately with clean water.Do not cover the area with plastic or waterproof bandages. Covering the treated area may increase the absorption of the medication through the skin and increase the risk of side effects.Do not use more of this product, use it more often, or keep using it longer than prescribed by your doctor. Your condition will not improve faster and the risk for side effects will increase. Side effects may increase when you use the cream on a larger area of skin (such as more than 10 percent of your body surface). Tell your doctor if you have severe drowsiness while using this product. It may be a sign that you are absorbing too much of the medication. Your doctor may tell you to decrease how often you apply the medication, the amount of medication used, or how much skin to spread the medication over. Follow your doctor's directions carefully.Tell your doctor if your condition does not improve or if it worsens.
SIDE EFFECTS: Burning/stinging at the application site, drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, blurred vision, or changes in taste may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.To reduce the risk of dizziness and lightheadedness, get up slowly when rising from a sitting or lying position.To relieve dry mouth, suck on (sugarless) hard candy or ice chips, chew (sugarless) gum, drink water, or use a saliva substitute.Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: heartburn that doesn't go away, mental/mood changes (such as agitation, confusion, depression), trouble urinating, swelling of the hands/feet.Get medical help right away if you have any very serious side effects, including: fast/irregular heartbeat, vision changes, fainting, seizures.A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: Before using doxepin, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it, or to other tricyclic antidepressants (such as amitriptyline); or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: problems urinating (such as due to enlarged prostate), breathing problems (such as bronchitis, emphysema), glaucoma, heart problems (such as irregular heartbeat), kidney problems, liver problems, overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism), personal or family history of mental/mood conditions (such as bipolar disorder, psychosis, suicide), seizures, conditions that may increase your risk of seizures (such as other brain disease, alcohol withdrawal).Doxepin may cause a condition that affects the heart rhythm (QT prolongation). QT prolongation can rarely cause serious (rarely fatal) fast/irregular heartbeat and other symptoms (such as severe dizziness, fainting) that need medical attention right away.The risk of QT prolongation may be increased if you have certain medical conditions or are taking other drugs that may cause QT prolongation. Before using doxepin, tell your doctor or pharmacist of all the drugs you take and if you have any of the following conditions: certain heart problems (heart failure, slow heartbeat, QT prolongation in the EKG), family history of certain heart problems (QT prolongation in the EKG, sudden cardiac death).Low levels of potassium or magnesium in the blood may also increase your risk of QT prolongation. This risk may increase if you use certain drugs (such as diuretics/"water pills") or if you have conditions such as severe sweating, diarrhea, or vomiting. Talk to your doctor about using doxepin safely.This drug may make you dizzy or drowsy or blur your vision. Alcohol or marijuana (cannabis) can make you more dizzy or drowsy. Do not drive, use machinery, or do anything that needs alertness or clear vision until you can do it safely. Limit alcoholic beverages. Talk to your doctor if you are using marijuana (cannabis).Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).If you have diabetes, this drug may affect your blood sugar. Check your blood sugar regularly as directed and share the results with your doctor. Tell your doctor right away if you have symptoms of high blood sugar such as increased thirst/urination or signs of low blood sugar such as sudden sweating, shaking, fast heartbeat, hunger, blurred vision, dizziness, or tingling hands/feet. Your doctor may need to adjust your diabetes medication, exercise program, or diet.Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects of this drug, especially dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, difficulty urinating, and QT prolongation (see above).During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.This medication passes into breast milk and could have undesirable effects on a nursing infant. Breastfeeding is not recommended while using this medication. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (such as prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.Some products that may interact with this drug are: certain drugs for high blood pressure (such as clonidine, guanadrel, guanethidine), thyroid medication.Taking MAO inhibitors with this medication may cause a serious (possibly fatal) drug interaction. Avoid taking MAO inhibitors (isocarboxazid, linezolid, metaxalone, methylene blue, moclobemide, phenelzine, procarbazine, rasagiline, safinamide, selegiline, tranylcypromine) during treatment with this medication. Most MAO inhibitors should also not be taken for two weeks before and after treatment with this medication. Ask your doctor when to start or stop taking this medication.Other medications can affect the removal of doxepin from your body, which may affect how doxepin works. Examples include cimetidine, St. John's Wort, drugs to treat irregular heart rate (such as propafenone, flecainide), antidepressants (such as SSRIs including paroxetine, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine), drugs used to treat seizures (such as phenobarbital, phenytoin), among others.Many drugs besides doxepin may affect the heart rhythm (QT prolongation), including amiodarone, dofetilide, halofantrine, pimozide, quinidine, procainamide, sotalol, macrolide antibiotics (such as erythromycin), sparfloxacin, among others. Before using doxepin, report all medications you are currently using to your doctor or pharmacist.Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking other products that cause drowsiness such as opioid pain or cough relievers (such as codeine, hydrocodone), alcohol, marijuana (cannabis), drugs for sleep or anxiety (such as alprazolam, lorazepam, zolpidem), muscle relaxants (such as carisoprodol, cyclobenzaprine), or antihistamines (such as cetirizine, diphenhydramine).Check the labels on all your medicines (such as allergy or cough-and-cold products) because they may contain ingredients that cause drowsiness. Ask your pharmacist about using those products safely.
OVERDOSE: This medicine may be harmful if swallowed. If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center. Symptoms of overdose or swallowing may include: confusion, hallucinations, big/wide pupils, fast/irregular heartbeat, severe dizziness, fainting, seizures, loss of consciousness.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others.Use this medication only for the condition for which it was prescribed. Tell all your doctors you use this medication.
MISSED DOSE: If you miss a dose, apply it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose. Use your next dose at the regular time. Do not apply more to catch up.
STORAGE: Store at room temperature. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Information last revised November 2023. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.



