Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
injectable solution
- 25mg/mL
powder for injection
- 1g/vial (25mg/mL when reconstituted)
SC autoinjector (Otrexup)
- 7.5 mg/0.4mL
- 10mg/0.4mL
- 12.5mg/0.4mL
- 15mg/0.4mL
- 17.5mg/0.4mL
- 20mg/0.4mL
- 22.5mg/0.4mL
- 25mg/0.4mL
SC autoinjector (Rasuvo)
- 2.5mg/0.05mL (delivers doses between 7.5 mg and 30 mg in 2.5 mg increments)
SC prefilled syringe (RediTrex)
- 7.5mg/0.3mL
- 10mg/0.4mL
- 12.5mg/0.5mL
- 15mg/0.6mL
- 17.5mg/0.7mL
- 20mg/0.8mL
- 22.5mg/0.9mL
- 25mg/mL
tablet
- 2.5mg
- 5mg
- 7.5mg
- 10mg
- 15mg
oral solution (Jylamvo)
- 2mg/mL
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Indicated for adult and pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) as part of a combination chemotherapy regimen
IV: Varies from 10-5,000 mg/m2; dose varies and depends disease state, patient risk category, concurrent drugs used, phase of treatment and response to treatment
Use leucovorin rescue in accordance with high-dose methotrexate IV regimen guidelines
Meningeal Leukemia
Indicated for prophylaxis and treatment of meningeal leukemia in adult and pediatric patients
Use preservative-free methotrexate for intrathecal (IT) injection
Treatment: 12 mg IT; not to exceed 15 mg/dose every 2-7 days; administer 1 additional dose after cell count on CSF returns to normal
Prophylaxis: 12-15 mg IT no more than once weekly
Patients with Down syndrome: Administer leucovorin rescue with methotrexate IT
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Indicated for treatment of adults and pediatric patients with Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)
Recommended dosage varies; refer to specific institutional protocol
See leucovorin rescue protocols for intermediate- and high-dose methotrexate regimens
Combination with other antineoplastics
- Range 10-8,000 mg/m2 IV
- Part of combination chemotherapy regimen: 1,000-3,000 mg/m2 IV infusion over 24 hr followed by leucovorin rescue in accordance with high-dose methotrexate regimen guidelines
Single agent
- Cutaneous forms of NHL: 5-75 mg IV
CNS-directed therapy
- Single agent: 8,000 mg/m2 IV infusion over 4 hr
- Combination with immunochemotherapy: 3,000-8,000 mg/m2 IV infusion followed by leucovorin rescue in accordance with high-dose methotrexate regimen guidelines
Osteosarcoma
Indicated for the treatment of adults and pediatric patients with osteosarcoma as part of a combination chemotherapy regimen
12 g/m2 IV over 4 hr on weeks 4, 5, 6, 7, 11, 12, 15, 16, 29, 30, 44, and 45 after surgery in combination with other chemotherapy
If peak serum methotrexate <454 mcg/mL at end of initial infusion, dose may be increased to 15 g/m2 in subsequent treatments
Not to exceed 20 g/dose
Administer leucovorin rescue in accordance with high-dose methotrexate regimen guidelines
Breast Cancer
Indicated for breast cancer as part of a combination chemotherapy regimen
40 mg/m2 IV as a component of a cyclophosphamide- and fluorouracil-based multidrug regimen
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
Indicated for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck as a single-agent
Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
Indicated for adults with gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN) as part of a combination chemotherapy regimen
30-200 mg/m2 or 0.4-1 mg/kg IV or IM
High-risk GTN: 300 mg/m2 IV infused over 12 hr as a component of a multidrug regimen
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Indicated for management of severe, active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in adults who have had an insufficient response or intolerance to an adequate trial of first-line therapy including full dose NSAIDs
Initial: 7.5 mg PO/IV/IM as a single weekly dose, OR
2.5 mg PO q12hr for 3 sequential doses per week
Increase dose to optimum response; single dose not to exceed 20 mg/week PO (increased risk of bone marrow suppression); reduce to lowest possible effective dose
Otrexup (SC): If used as initial therapy, start at lowest available dose (ie, 10 mg SC qWeek)
Rasuvo or RediTrex (SC), initial dose: 7.5 mg as a single SC dose once weekly; adjust autoinjector dose by 2.5 mg increments as clinically required
Administer folic acid or folinic acid to reduce the risk of methotrexate adverse reactions
Psoriasis
For symptomatic control of severe, recalcitrant, disabling psoriasis in adults not adequately responsive to other forms of therapy; use only with established diagnosis (by biopsy and/or after dermatologic consultation)
Initial: 10-25 mg weekly in single PO/SC/IM/IV dose; not to exceed 30 mg/wk
Gradually adjust dose to achieve to optimal clinical response; use lowest dose and longest rest period possible with return to conventional topical therapy encouraged
Trexall: May give weekly dose divided as 2.5 mg PO q12hr for 3 sequential doses
Otrexup (SC): If used as initial therapy, start a lowest available dose (ie, 10 mg SC qWeek)
Rasuvo or RediTrex (SC): 10-25 mg SC once weekly
Administer folic acid or folinic acid to reduce the risk of methotrexate adverse reactions
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment
- Methotrexate elimination reduced with CrCl <90 mL/min
- Patients with renal impairment are at increased risk for adverse effects; carefully monitor for toxicity
- Follow recommendations to promote methotrexate elimination and decrease risk of acute kidney injury and other methotrexate toxicities in patients who are receiving intermediate- or high-dose regimens
- Some patients may require dose reduction or, in some cases, discontinuation
Hepatic impairment
- Safety in patients with hepatic impairment is unknown
- Patients with hepatic impairment may be at increased risk for adverse reactions based on methotrexate elimination characteristics
- Consider dose reduction or discontinuing with hepatic impairment as appropriate
Dosing Considerations
Otrexup and Rasuvo (SC injections) are not indicated for neoplastic disease
If switching from PO to SC (Otrexup, Rasuvo), consider higher bioavailability with SC compared with PO (see Pharmacology Absorption section)
Ectopic Pregnancy (Off-label)
50 mg/m² IM; measure serum hCG levels on days 4 and 7; may repeat dose on day 7 if necessary
If hCG levels decrease <15% between days 4 and 7, administer methotrexate 50 mg/m² IM; if hCG ≥15% between days 4 and 7, discontinue treatment and measure hCG weekly until reaching nonpregnant levels
Myasthenia Gravis (Orphan)
Orphan designation for treatment of myasthenia gravis
Orphan Sponsor
- University of Kansas Medical Center; 3901 Rainbow Blvd, MSN 2012; Kansas City, KS 66160
Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy (Orphan)
Orphan designation for prevention of proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR)
Orphan Sponsor
- Helio Vision, Inc; 1000 Winter Street, 4th Floor; Waltham, Massachusetts 02451
Ectopic Pregnancy (Orphan)
Orphan designation for treatment of ectopic pregnancy
Orphan sponsor
- Antares Pharma, Inc; Princeton Crossroads Corporate Center; 100 Princeton South Suite 300; Ewing, New Jersey 08628
Dosage Forms & Strengths
injectable solution
- 25mg/mL
powder for injection
- 1g/vial (25mg/mL when reconstituted)
SC autoinjector (Otrexup)
- 7.5mg/0.4mL
- 10mg/0.4mL
- 12.5mg/0.4mL
- 15mg/0.4mL
- 17.5mg/0.4mL
- 20mg/0.4mL
- 22.5mg/0.4mL
- 25mg/0.4mL
SC autoinjector (Rasuvo)
- 2.5mg/0.05mL (delivers doses between 7.5 mg and 30 mg in 2.5 mg increments)
SC prefilled syringe (RediTrex)
- 7.5mg/0.3mL
- 10mg/0.4mL
- 12.5mg/0.5mL
- 15mg/0.6mL
- 17.5mg/0.7mL
- 20mg/0.8mL
- 22.5mg/0.9mL
- 25mg/mL
tablet
- 2.5mg
- 5mg
- 7.5mg
- 10mg
- 15mg
oral solution, ready-to-use (Xatmep)
- 2.5mg/mL
Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Management of active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA) in children who have had an insufficient response or intolerance to an adequate trial of first-line therapy including full dose NSAIDs
Initial: 10 mg/m² PO/IM/SC qWeek
If switching from PO to SC (Otrexup, Rasuvo, RediTrex), consider higher bioavailability with SC compared with PO (see Pharmacology Absorption section)
Dosing Considerations (PJIA)
- Data with doses up to 30 mg/m²/wk in children exist, although there are too few published studies to assess how doses >20 mg/m²/wk might affect the risk of serious toxicity in children, especially bone marrow suppression
- Experience does suggest, however, that children receiving 20 to 30 mg/m²/wk (0.65-1 mg/kg/wk) may have better absorption and fewer GI side effects if methotrexate is administered either IM or SC
- Administer folic acid or folinic acid to reduce the risk of methotrexate adverse reactions
Meningeal Leukemia
Indicated for prophylaxis and treatment of meningeal leukemia in adult and pediatric patients
Use preservative-free methotrexate for intrathecal (IT) injection
Treatment: Dose may be given at intervals of ≥2 days up to twice weekly; however, administration at intervals of <1 week may result in increased subacute toxicity
Prophylaxis: Administered no more than once weekly
Patients with Down syndrome: Administer leucovorin rescue with methotrexate IT
Age-based dosing
<1 year: 6 mg IT
1 to <2 years: 8 mg IT
2 to <3 years: 10 mg IT
3 to <9 years: 12 mg IT
≥9 years: 12-15 mg IT
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Indicated for treatment of pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) as part of a multi-phase, combination chemotherapy regimen
IV: Varies from 10-5,000 mg/m2; dose varies and depends disease state, patient risk category, concurrent drugs used, phase of treatment and response to treatment
Oral solution (Xatmep): 20 mg/m2 PO qWeek
Use leucovorin rescue in accordance with high-dose methotrexate IV regimen guidelines
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Indicated for treatment of adults and pediatric patients with Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)
Recommended dosage varies; refer to specific institutional protocol
See leucovorin rescue protocols for intermediate- and high-dose methotrexate regimens
Combination with other antineoplastics
- Range 10-8,000 mg/m2 IV
- Part of combination chemotherapy regimen: 1,000-3,000 mg/m2 IV infusion over 24 hr followed by leucovorin rescue in accordance with high-dose methotrexate regimen guidelines
Single agent
- Cutaneous forms of NHL: 5-75 mg IV
CNS-directed therapy
- Single agent: 8,000 mg/m2 IV infusion over 4 hr
- Combination with immunochemotherapy: 3,000-8,000 mg/m2 IV infusion followed by leucovorin rescue in accordance with high-dose methotrexate regimen guidelines
Osteosarcoma
- Indicated for adults and pediatric patients with osteosarcoma as part of a combination chemotherapy regimen
- 12 g/m2 IV over 4 hr on weeks 4, 5, 6, 7, 11, 12, 15, 16, 29, 30, 44, and 45 after surgery in combination with other chemotherapy
- Not to exceed 20 g/dose
- Administer leucovorin rescue in accordance with high-dose methotrexate regimen guidelines
- If peak serum methotrexate <454 mcg/mL at end of initial infusion, dose may be increased to 15 g/m2 in subsequent treatments
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment
- Methotrexate elimination reduced with CrCl <90 mL/min
- Patients with renal impairment are at increased risk for adverse effects; carefully monitor for toxicity
- Follow recommendations to promote methotrexate elimination and decrease risk of acute kidney injury and other methotrexate toxicities in patients who are receiving intermediate- or high-dose regimens
- Some patients may require dose reduction or, in some cases, discontinuation
Hepatic impairment
- Safety in patients with hepatic impairment is unknown
- Patients with hepatic impairment may be at increased risk for adverse reactions based on methotrexate elimination characteristics
- Consider dose reduction or discontinuing with hepatic impairment as appropriate
Dosing Considerations
May impair fertility, cause oligospermia, and menstrual dysfunction; exclude pregnancy before initiating treatment
Otrexup and Rasuvo (SC injections) are not indicated for neoplastic disease
If switching from PO to SC (Otrexup, Rasuvo), consider higher bioavailability with SC compared with PO (see Pharmacology Absorption section)
Use only preservative-free methotrexate injection for treatment of neonates or low-birth weight infants and for intrathecal use; do not use benzyl alcohol-containing formulations for high-dose regimens unless immediate treatment is required and preservative-free formulations are not available
Leucovorin rescue
- Administer leucovorin rescue doses ≥500 mg/m2 (ie, high-dose)
- Consider leucovorin rescue for doses 100 to <500 mg/m2 (ie, intermediate-dose)
Supportive care
- For high-dose regimens, the following are recommended; also consider for intermediate-dose regimens
- Monitor serum creatinine, electrolytes, at baseline and at least daily during therapy
- Administer IV fluids starting before first dose and continue throughout treatment to maintain hydration and urine output
- Alkalinize urine starting before first dose and continue throughout treatment to maintain urine pH ≥7
- Monitor methotrexate concentrations at least daily and adjust hydration and leucovorin dosing as needed
- Glucarpidase: Administer in patients with toxic plasma methotrexate concentrations (>1 micromole/L) and delayed methotrexate clearance owing to impaired renal function
Monitor closely for early signs of bone marrow suppression, and renal or hepatic toxicity
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results

Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor

Contraindicated (10)
- acitretin
acitretin, methotrexate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated. Risk of additive hepatotoxicity.
- influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, intranasal
methotrexate decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, intranasal by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunization with live virus vaccines is generally not recommended.
- measles mumps and rubella vaccine, live
methotrexate decreases effects of measles mumps and rubella vaccine, live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunization with live virus vaccines is generally not recommended.
- measles, mumps, rubella and varicella vaccine, live
methotrexate decreases effects of measles, mumps, rubella and varicella vaccine, live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunization with live virus vaccines is generally not recommended.
- rotavirus oral vaccine, live
methotrexate decreases effects of rotavirus oral vaccine, live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunization with live virus vaccines is generally not recommended.
- smallpox (vaccinia) vaccine, live
methotrexate decreases effects of smallpox (vaccinia) vaccine, live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunization with live virus vaccines is generally not recommended.
- typhoid vaccine live
methotrexate decreases effects of typhoid vaccine live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunization with live virus vaccines is generally not recommended.
- varicella virus vaccine live
methotrexate decreases effects of varicella virus vaccine live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunization with live virus vaccines is generally not recommended.
- yellow fever vaccine
methotrexate decreases effects of yellow fever vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunization with live virus vaccines is generally not recommended.
- zoster vaccine live
methotrexate decreases effects of zoster vaccine live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunization with live virus vaccines is generally not recommended.
Serious - Use Alternative (71)
- adenovirus types 4 and 7 live, oral
methotrexate decreases effects of adenovirus types 4 and 7 live, oral by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- anthrax vaccine
methotrexate decreases effects of anthrax vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- aspirin
aspirin increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Caution should be exercised when salicylates are given in combination with methotrexate. Risk for drug interactions with methotrexate is greatest during high-dose methotrexate therapy, it has been recommended that any of these drugs be used cautiously with methotrexate even when methotrexate is used in low doses.
- aspirin rectal
aspirin rectal increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. The relative risk of interaction of different NSAIDs w/methotrexate is not established. Selective COX 2 inhibitors are believed to have minimal interaction. Greater risk in pts. with renal impairment. Greater toxicity with high dose methotrexate (e.g., anti neoplastic regimen).
- aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate
aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Caution should be exercised when salicylates are given in combination with methotrexate. Risk for drug interactions with methotrexate is greatest during high-dose methotrexate therapy, it has been recommended that any of these drugs be used cautiously with methotrexate even when methotrexate is used in low doses.
- axicabtagene ciloleucel
methotrexate, axicabtagene ciloleucel. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- bacitracin
methotrexate and bacitracin both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid concurrent use of bacitracin with other nephrotoxic drugs
- BCG intravesical live
methotrexate decreases effects of BCG intravesical live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- bremelanotide
bremelanotide will decrease the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Bremelanotide may slow gastric emptying and potentially reduces the rate and extent of absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. Avoid use when taking any oral drug that is dependent on threshold concentrations for efficacy. Interactions listed are representative examples and do not include all possible clinical examples.
- brexucabtagene autoleucel
methotrexate, brexucabtagene autoleucel. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ceftobiprole medocaril sodium
ceftobiprole medocaril sodium will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Ceftobiprole (an OATP1B1/1B3 inhibitor) may increase plasma concentrations of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 substrates.
- celecoxib
celecoxib increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- choline magnesium trisalicylate
choline magnesium trisalicylate increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. The relative risk of interaction of different NSAIDs w/methotrexate is not established. Selective COX 2 inhibitors are believed to have minimal interaction. Greater risk in pts. with renal impairment. Greater toxicity with high dose methotrexate (e.g., anti neoplastic regimen).
- ciltacabtagene autoleucel
methotrexate, ciltacabtagene autoleucel. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- darolutamide
darolutamide will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Darolutamide is a BCRP inhibitor. Avoid coadministration with BCRP inhibitors. If use is unavoidable, closely monitor for adverse reactions and consider dose reduction of BCRP substrate drug (refer BCRP substrate prescribing information).
- deferiprone
deferiprone, methotrexate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid use of deferiprone with other drugs known to be associated with neutropenia or agranulocytosis; if an alternative is not possible, monitor absolute neutrophil count more frequently.
- diclofenac
diclofenac increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- diflunisal
diflunisal increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- divalproex sodium
methotrexate will decrease the level or effect of divalproex sodium by unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. may potentially result in increased frequency of seizures or bipolar symptoms; monitor serum valproate concentrations and clinical response when adding or discontinuing methotrexate and adjust valproate dosage
- erdafitinib
erdafitinib will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration unavoidable, separate administration by at least 6 hr before or after administration of P-gp substrates with narrow therapeutic index.
- ethanol
methotrexate, ethanol. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated. Ethanol (alcohol) may increase the risk for liver-related side effects of methotrexate. Patients should be advised to avoid intake of alcoholic beverages during methotrexate therapy. Patients who are noncompliant with alcohol restrictions (e.g., alcoholism) should not receive methotrexate.
- etodolac
etodolac increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- etrasimod
etrasimod, methotrexate. Either increases effects of the other by Mechanism: aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibition. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of additive immune system effects with etrasimod has not been studied in combination with antineoplastic, immune-modulating, or noncorticosteroid immunosuppressive therapies. Avoid coadministration during and in the weeks following administration of etrasimod.
- fenoprofen
fenoprofen increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- flurbiprofen
flurbiprofen increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- human papillomavirus vaccine, nonavalent
methotrexate decreases effects of human papillomavirus vaccine, nonavalent by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Immunosuppressive therapies, including irradiation, antimetabolites, alkylating agents, cytotoxic drugs, and corticosteroids (used in greater than physiologic doses), may reduce the immune responses to vaccines.
- human papillomavirus vaccine, quadrivalent
methotrexate decreases effects of human papillomavirus vaccine, quadrivalent by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Immunosuppressive therapies, including irradiation, antimetabolites, alkylating agents, cytotoxic drugs, and corticosteroids (used in greater than physiologic doses), may reduce the immune responses to vaccines.
- ibuprofen
ibuprofen increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- ibuprofen IV
ibuprofen IV increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- idecabtagene vicleucel
methotrexate, idecabtagene vicleucel. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- indomethacin
indomethacin increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, adjuvanted
methotrexate decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, adjuvanted by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Immunosuppressive drugs may reduce the immune response to influenza vaccine.
- influenza virus vaccine trivalent, adjuvanted
methotrexate decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine trivalent, adjuvanted by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Immunosuppressive drugs may reduce the immune response to influenza vaccine.
- ketoprofen
ketoprofen increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- ketorolac
ketorolac increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- ketorolac intranasal
ketorolac intranasal increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. The relative risk of interaction of different NSAIDs w/methotrexate is not established. Selective COX 2 inhibitors are believed to have minimal interaction. Greater risk in pts. with renal impairment. Greater toxicity with high dose methotrexate (e.g., anti neoplastic regimen).
- lasmiditan
lasmiditan increases levels of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Lasmiditan inhibits BCRP in vitro. Avoid coadministration of lasmiditan with BCRP substrates.
- leniolisib
leniolisib will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Leniolisib, a BCRP, OATP1B1, and OATP1B3 inhibitor, may increase systemic exposure of these substrates
- lisocabtagene maraleucel
methotrexate, lisocabtagene maraleucel. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- meclofenamate
meclofenamate increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- mefenamic acid
mefenamic acid increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- meloxicam
meloxicam increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- nabumetone
nabumetone increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- naproxen
naproxen increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity.
- oxaprozin
oxaprozin increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- pacritinib
pacritinib will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of pacritinib (BCRP inhibitor) with BCRP substrates may increase the plasma concentrations of these substrates.
- palifermin
palifermin increases toxicity of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Palifermin should not be administered within 24 hrbefore, during infusion of, or within 24 hr after administration of antineoplastic agents. Coadministration of palifermin within 24 hr of chemotherapy resulted in increased severity and duration of oral mucositis.
- pexidartinib
methotrexate and pexidartinib both increase inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Pexidartinib can cause hepatotoxicity. Avoid coadministration of pexidartinib with other products know to cause hepatoxicity.
- piroxicam
piroxicam increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- pneumococcal vaccine 13-valent
methotrexate decreases effects of pneumococcal vaccine 13-valent by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- pretomanid
methotrexate, pretomanid. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Pretomanid regimen associated with hepatotoxicity. Avoid alcohol and hepatotoxic agents, including herbal supplements and drugs other than bedaquiline and linezolid.
- probenecid
probenecid increases levels of methotrexate by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If combination must be used, decrease methotrexate dose; also, methotrexate increases uric acid production and risk for uric acid neuropathy.
- ropeginterferon alfa 2b
ropeginterferon alfa 2b, methotrexate. Either increases levels of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Myelosuppressive agents can produce additive myelosuppression. Avoid use and monitor patients receiving the combination for effects of excessive myelosuppression.
- salicylates (non-asa)
salicylates (non-asa) increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Caution should be exercised when salicylates are given in combination with methotrexate. Risk for drug interactions with methotrexate is greatest during high-dose methotrexate therapy, it has been recommended that any of these drugs be used cautiously with methotrexate even when methotrexate is used in low doses.
- salsalate
salsalate increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Caution should be exercised when salicylates are given in combination with methotrexate. Risk for drug interactions with methotrexate is greatest during high-dose methotrexate therapy, it has been recommended that any of these drugs be used cautiously with methotrexate even when methotrexate is used in low doses.
- sotorasib
sotorasib will decrease the level or effect of methotrexate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If use is unavoidable, refer to the prescribing information of the P-gp substrate for dosage modifications.
- sparsentan
sparsentan will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Sparsentan (a BCRP inhibitor) may increase exposure of sensitive BCRP substrates and the risk of these substrates toxicities.
- sulfadiazine
sulfadiazine increases toxicity of methotrexate by plasma protein binding competition. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- sulfamethoxazole
sulfamethoxazole increases toxicity of methotrexate by plasma protein binding competition. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Methotrexate concentrations may be elevated, increasing the risk of toxicity (eg, bone marrow suppression).
- sulfasalazine
sulfasalazine increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- sulfisoxazole
sulfisoxazole increases toxicity of methotrexate by plasma protein binding competition. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- sulindac
sulindac increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- tepotinib
tepotinib will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If concomitant use unavoidable, reduce the P-gp substrate dosage if recommended in its approved product labeling.
- tisagenlecleucel
methotrexate, tisagenlecleucel. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tocilizumab
tocilizumab and methotrexate both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tofacitinib
methotrexate, tofacitinib. Either increases toxicity of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tolmetin
tolmetin increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
- tongkat ali
methotrexate and tongkat ali both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tretinoin topical
methotrexate, tretinoin topical. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Additive hepatotoxicity.
- trimethoprim
trimethoprim, methotrexate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Due to an additive antifolate effect, trimethoprim has been shown to rarely increase bone marrow suppression in patients receiving methotrexate.
- trofinetide
trofinetide will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Trofinetide (an OATP131 and OATP13B inhibitor) may increase plasma levels of OATP131 or OATP13B substrates. Avoid coadministration with sensitive substrates.
Monitor Closely (152)
- acalabrutinib
acalabrutinib increases levels of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Acalabrutinib may increase exposure to coadministered BCRP substrates by inhibition of intestinal BCRP.
acalabrutinib, methotrexate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration may increase risk of myelosuppressive effects. - activated charcoal
activated charcoal will decrease the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Charcoal can reduce absorption of methotrexate and remove it from systemic circulation. Depending on the clinical situation, this will reduce the effectiveness or toxicity of methotrexate.
- aldesleukin
aldesleukin increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. May increase myelosupression and hepatotoxicity.
- allopurinol
allopurinol decreases effects of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Combination may increase risk of myelosuppression.
- aminohippurate sodium
aminohippurate sodium will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amoxicillin
amoxicillin increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased serum concentrations of methotrexate with concomitant hematologic and gastrointestinal toxicity have been observed with concurrent administration of high or low doses of methotrexate and penicillins.
- ampicillin
ampicillin increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased serum concentrations of methotrexate with concomitant hematologic and gastrointestinal toxicity have been observed with concurrent administration of high or low doses of methotrexate and penicillins.
- apalutamide
apalutamide will decrease the level or effect of methotrexate by increasing elimination. Use Caution/Monitor. Apalutamide weakly induces BCRP and OATP1B1 and may decrease systemic exposure of drugs that are substrates of both BCRP and OATP1B1.
- aspirin rectal
aspirin rectal will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate
aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- astragalus
methotrexate increases and astragalus decreases immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- belatacept
belatacept and methotrexate both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor.
- berotralstat
berotralstat will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor or titrate P-gp substrate dose if coadministered.
- bosutinib
bosutinib increases levels of methotrexate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- caffeine
caffeine decreases effects of methotrexate by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- carboplatin
carboplatin and methotrexate both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chlorpropamide
chlorpropamide will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Methotrexate is partially bound to plasma proteins, and drugs that can displace methotrexate from these proteins, such as oral sulfonylureas, could cause methotrexate-induced toxicity.
- cholera vaccine
methotrexate decreases effects of cholera vaccine by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Immunosuppressive therapies, including irradiation, antimetabolites, alkylating agents, cytotoxic drugs and corticosteroids (used in greater than physiologic doses), may reduce the immune response to cholera vaccine.
- cholestyramine
cholestyramine decreases levels of methotrexate by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. To minimize drug interactions, administer other drugs at least 1 hour before or at least 4-6 hours after the administration of cholestyramine.
- choline magnesium trisalicylate
choline magnesium trisalicylate will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cidofovir
cidofovir and methotrexate both decrease immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. May increase myelosupression.
- ciprofloxacin
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Renal tubular transport of methotrexate may be inhibited by coadministration of ciprofloxacin, potentially leading to increased methotrexate plasma levels and toxicity.
- cisplatin
cisplatin and methotrexate both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
- crofelemer
crofelemer increases levels of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Crofelemer has the potential to inhibit transporters MRP2 and OATP1A2 at concentrations expected in the gut; unlikely to inhibit systemically because minimally absorbed.
- cyclosporine
cyclosporine, methotrexate. Either increases levels of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Close monitoring of cyclosporine and methotrexate concentrations, renal function, and liver enzymes is recommended during concurrent therapy. .
- danicopan
danicopan will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Danicopan increases plasma concentrations of BCRP substrates; consider dose reduction of BCRP substrate according to its prescribing information.
danicopan will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Danicopan increases plasma concentrations of P-gp substrates; consider dose reduction of P-gp substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions. - dapsone
dapsone, methotrexate. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Combination may increase risk of hematologic toxicity.
- demeclocycline
demeclocycline increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing elimination. Use Caution/Monitor. Tetracyclines may decrease intestinal absorption of methotrexate or interfere with the enterohepatic circulation by inhibiting bowel flora and suppressing metabolism of the drug by bacteria.
- dengue vaccine
methotrexate decreases effects of dengue vaccine by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Immunosuppressive therapies (eg, irradiation, antimetabolites, alkylating agents, cytotoxic drugs, corticosteroids [greater than physiologic doses]) may reduce immune response to dengue vaccine.
- denosumab
methotrexate, denosumab. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Caution should be taken in patients on concomitant immunosuppressants or with impaired immune systems because of increased risk for serious infections.
- dexlansoprazole
dexlansoprazole increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of toxicity with higher doses.
- dicloxacillin
dicloxacillin increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased serum concentrations of methotrexate with concomitant hematologic and gastrointestinal toxicity have been observed with concurrent administration of high or low doses of methotrexate and penicillins.
- digoxin
methotrexate decreases levels of digoxin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Serum levels of digoxin may be reduced and actions may be decreased. Monitor patient for signs of reduction in pharmacologic effect of digoxin and increase digoxin dose if necessary. Serum level monitoring may facilitate tailoring dosage.
- diphtheria & tetanus toxoids
methotrexate decreases effects of diphtheria & tetanus toxoids by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration of methotrexate can decrease the immunological response of vaccines.
- diphtheria & tetanus toxoids/ acellular pertussis vaccine
methotrexate decreases effects of diphtheria & tetanus toxoids/ acellular pertussis vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration of methotrexate can decrease the immunological response of vaccines.
- diphtheria & tetanus toxoids/acellular pertussis/poliovirus, inactivated vaccine
methotrexate decreases effects of diphtheria & tetanus toxoids/acellular pertussis/poliovirus, inactivated vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Immunosuppressants also increase risk of infection with concomitant live vaccines.
- doxycycline
doxycycline increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing elimination. Use Caution/Monitor. Tetracyclines may decrease intestinal absorption of methotrexate or interfere with the enterohepatic circulation by inhibiting bowel flora and suppressing metabolism of the drug by bacteria.
- echinacea
methotrexate increases and echinacea decreases immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- elacestrant
elacestrant will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Elacestrant (a BCRP inhibitor) may increase plasma concentrations of sensitive BCRP substrates, which may increase risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates. Refer to prescribing information for sensitive BCRP substrates for dosing recommendations.
- elagolix
elagolix will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eliglustat
eliglustat increases levels of methotrexate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor therapeutic drug concentrations, as indicated, or consider reducing the dosage of the P-gp substrate and titrate to clinical effect.
- eltrombopag
eltrombopag increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. OATP transporter protein inhibition.
- eluxadoline
eluxadoline increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Eluxadoline may increase the systemic exposure of coadministered BCRP substrates.
- elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF
methotrexate and elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
- encorafenib
encorafenib will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Encorafenib (a OATP1B1, OATP1B3, and BCRP inhibitor) may increase the concentration and toxicities of OATP1B1, OATP1B3, and BCRP substrates. Closely monitor for signs and symptoms of increased exposure and consider adjusting the dose of these substrates. Screen reader support enabled.
- esomeprazole
esomeprazole increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of toxicity with higher doses.
- ferric maltol
ferric maltol, methotrexate. Either increases levels of the other by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of ferric maltol with certain oral medications may decrease the bioavailability of either ferric maltol and some oral drugs. For oral drugs where reductions in bioavailability may cause clinically significant effects on its safety or efficacy, separate administration of ferric maltol from these drugs. Duration of separation may depend on the absorption of the medication concomitantly administered (eg, time to peak concentration, whether the drug is an immediate or extended release product).
- fingolimod
methotrexate increases effects of fingolimod by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Concomitant therapy is expected to increase the risk of immunosuppression. Use caution when switching patients from long-acting therapies with immune effects. .
- food
food decreases levels of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Food may delay the absorption and reduce the peak concentration of methotrexate.
- fosphenytoin
fosphenytoin increases toxicity of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Methotrexate is partially bound to serum albumin, and toxicity may be increased because of displacement by certain drugs.
- fostamatinib
fostamatinib will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use of fostamatinib may increase concentrations of P-gp/BCRP substrate drugs. Monitor for toxicities of P-gp/BCRP substrate drug that may require dosage reduction when given concurrently with fostamatinib.
- fostemsavir
fostemsavir will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Fostemsavir inhibits OATP1B1/3 and BCRP transporters. If possible, avoid coadministration or modify dose of OATP1B1/3 or BCRP substrates coadministered with fostemsavir.
- glecaprevir/pibrentasvir
glecaprevir/pibrentasvir will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir may increase plasma concentration of OATP1B1/OATP1B3, P-gp and BCRP substrates.
- haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine
methotrexate decreases effects of haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid vaccination during chemotherapy or radiation therapy if possible because antibody response might be suboptimal. Patients vaccinated within a 14-day period before starting or during immunosuppressive therapy should be revaccinated =3 months after therapy is discontinued if immune competence has been restored. .
- hepatitis A vaccine inactivated
methotrexate decreases effects of hepatitis A vaccine inactivated by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration of methotrexate can decrease the immunological response of vaccines.
- hepatitis a/b vaccine
methotrexate decreases effects of hepatitis a/b vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration of methotrexate can decrease the immunological response of vaccines.
- hepatitis b vaccine
methotrexate decreases effects of hepatitis b vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration of methotrexate can decrease the immunological response of vaccines.
- hydroxychloroquine sulfate
hydroxychloroquine sulfate decreases levels of methotrexate by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hydroxychloroquine may reduce the renal clearance of methotrexate; the exact mechanism of this interaction is unknown. .
- hydroxyurea
methotrexate, hydroxyurea. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Combination may increase risk of myelosuppression.
- ibuprofen IV
ibuprofen IV will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ifosfamide
ifosfamide, methotrexate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with ifosfamide may increase the risk of immunosuppression and myelosuppression.
- influenza A (H5N1) vaccine
methotrexate decreases effects of influenza A (H5N1) vaccine by Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Immunosuppressive therapies may reduce immune response to H5N1 vaccine.
- influenza virus vaccine (H5N1), adjuvanted
methotrexate decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine (H5N1), adjuvanted by Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Immunosuppressive therapies may reduce immune response to H5N1 vaccine.
- influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent
methotrexate decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration of methotrexate can decrease the immunological response of vaccines.
- influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, cell-cultured
methotrexate decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, cell-cultured by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration of methotrexate can decrease the immunological response of vaccines.
- influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, recombinant
methotrexate decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine quadrivalent, recombinant by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Immune response to vaccine may be decreased in immunocompromised individuals.
- influenza virus vaccine trivalent
methotrexate decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine trivalent by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration of methotrexate can decrease the immunological response of vaccines.
- influenza virus vaccine trivalent, recombinant
methotrexate decreases effects of influenza virus vaccine trivalent, recombinant by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Immune response to vaccine may be decreased in immunocompromised individuals.
- ioversol
ioversol and methotrexate both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
- isavuconazonium sulfate
methotrexate and isavuconazonium sulfate both decrease immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor.
- isotretinoin
methotrexate, isotretinoin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patients receiving other agents that may cause hepatotoxicity, including systemic retinoids, could be at increased risk of liver-related side effects of methotrexate and such patients should be monitored closely during methotrexate therapy.
- istradefylline
istradefylline will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Istradefylline 40 mg/day increased peak levels and AUC of P-gp substrates in clinical trials. Consider dose reduction of sensitive P-gp substrates.
- Japanese encephalitis virus vaccine
methotrexate decreases effects of Japanese encephalitis virus vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration of methotrexate can decrease the immunological response of vaccines.
- ketorolac intranasal
ketorolac intranasal will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- L-methylfolate
methotrexate decreases effects of L-methylfolate by Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Folic acid antagonists may interfere with folic acid utilization.
- lansoprazole
lansoprazole increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of toxicity with higher doses.
- leflunomide
leflunomide increases levels of methotrexate by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Additive hepatotoxicity, pancytopenia. If leflunomide and methotrexate are given concomitantly, monitor liver toxicity with ALT, AST, and serum albumin testing. Also, monitor platelets, WBC count, hemoglobin, or hematocrit at baseline and monthly for 6 months following initiation and every 6-8 weeks thereafter.
- letermovir
letermovir increases levels of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Letermovir, an OATP1B1/3 inhibitor may increase plasma concentrations of coadministered OATP1B1/3 substrates.
- lomitapide
lomitapide increases levels of methotrexate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing dose when used concomitantly with lomitapide.
- lomustine
lomustine, methotrexate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with lomustine may increase the risk of immunosuppression and myelosuppression.
- lonafarnib
lonafarnib will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Lonafarnib is a weak P-gp inhibitor. Monitor for adverse reactions if coadministered with P-gp substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities. Reduce P-gp substrate dose if needed.
- maitake
methotrexate increases and maitake decreases immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
- meclofenamate
meclofenamate will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- meningococcal A C Y and W-135 polysaccharide vaccine combined
methotrexate decreases effects of meningococcal A C Y and W-135 polysaccharide vaccine combined by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration of methotrexate can decrease the immunological response of vaccines.
- meningococcal group B vaccine
methotrexate decreases effects of meningococcal group B vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Individuals with altered immunocompetence may have reduced immune responses to the vaccine.
- methyclothiazide
methyclothiazide will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- minocycline
minocycline increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing elimination. Use Caution/Monitor. If tetracyclines cannot be avoided in patients receiving high-dose methotrexate, closely monitor methotrexate plasma concentrations and patients for signs and symptoms of toxicity.
- mipomersen
mipomersen, methotrexate. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Both drugs have potential to increase hepatic enzymes; monitor LFTs.
- momelotinib
momelotinib increases toxicity of methotrexate by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Momelotinib (BCRP inhibitor) may increase exposure of BCRP substrates, which may increase the risk of BCRP substrate adverse reactions. Dose adjustment of other BCRP substrates may necessary.
- muromonab CD3
methotrexate and muromonab CD3 both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Combination may increase risk of myelosuppression.
- mycophenolate
mycophenolate, methotrexate. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Infections may occur.
- nafcillin
nafcillin increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased serum concentrations of methotrexate with concomitant hematologic and gastrointestinal toxicity have been observed with concurrent administration of high or low doses of methotrexate and penicillins.
- neomycin PO
neomycin PO decreases levels of methotrexate by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Neomycin may decrease intestinal absorption of methotrexate or interfere with enterohepatic circulation by inhibiting bowel flora and suppressing metabolism of the drug by bacteria.
- ocrelizumab
methotrexate and ocrelizumab both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ocrelizumab with immunosuppessants is expected to increase the risk of immunosuppression.
- ofatumumab SC
ofatumumab SC, methotrexate. Either decreases toxicity of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider the risk of additive immune system effects when coadministering immunosuppressive therapies with coadministration. When switching from therapies with immune effects, take into account the duration and mechanism of action of these therapies when initiating ofatumumab SC.
- olaparib
methotrexate and olaparib both increase pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with other other myelosuppressive anticancer agents, including DNA damaging agents, may potentiate and prolongate the myelosuppressive toxicity.
- omeprazole
omeprazole increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Temporary withdrawal of PPI may be considered in some patients.
- osimertinib
osimertinib will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Osimertinib is an inhibitor of BCRP transport. Caution if coadministered with sensitive BCRP substrates.
- oteseconazole
oteseconazole will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Otesezonale, a BCRP inhibitor, may increase the effects and risk of toxicities of BCRP substrates. Use lowest starting dose of BCRP substrate, or consider reducing BCRP substrate dose.
- oxaliplatin
methotrexate and oxaliplatin both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
oxaliplatin, methotrexate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Combination may increase risk of myelosuppression. - ozanimod
ozanimod, methotrexate. Either increases effects of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with immunosuppressive therapies may increase the risk of additive immune effects during therapy and in the weeks following administration. When switching from drugs with prolonged immune effects, consider the half-life and mode of action of these drugs in order to avoid unintended additive immunosuppressive effects.
- pantoprazole
pantoprazole increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of toxicity with higher doses.
- paromomycin
paromomycin decreases levels of methotrexate by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Paromomycin may decrease intestinal absorption of methotrexate or interfere with enterohepatic circulation by inhibiting bowel flora and suppressing metabolism of the drug by bacteria.
- pegaspargase
pegaspargase decreases effects of methotrexate by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. It is recommended to give pegaspargase at least 10-14 days prior to methotrexate or shortly after methotrexate administration.
- phenytoin
phenytoin increases toxicity of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Methotrexate is partially bound to serum albumin, and toxicity may be increased because of displacement by certain drugs, such as phenytoin.
- pirtobrutinib
pirtobrutinib will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Pirtobrutinib (a BCRP inhibitor) may increase plasma concentrations of sensitive BCRP substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates. Refer to prescribing information for sensitive BCRP substrates for dosing recommendations.
- pneumococcal vaccine polyvalent
methotrexate decreases effects of pneumococcal vaccine polyvalent by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration of methotrexate can decrease the immunological response of vaccines.
- poliovirus vaccine inactivated
methotrexate decreases effects of poliovirus vaccine inactivated by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid vaccination during chemotherapy or radiation therapy if possible because antibody response might be suboptimal. Patients vaccinated within a 14-day period before starting or during immunosuppressive therapy should be revaccinated =3 months after therapy is discontinued if immune competence has been restored. .
- ponatinib
ponatinib increases levels of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
- ponesimod
ponesimod and methotrexate both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution if coadministered because of additive immunosuppressive effects during such therapy and in the weeks following administration. When switching from drugs with prolonged immune effects, consider the half-life and mode of action of these drugs to avoid unintended additive immunosuppressive effects.
- pretomanid
pretomanid will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. In vitro studies demonstrated that pretomanid significantly inhibits OAT3; monitor for increased adverse effects and consider dosage reduction for OAT3 substrates.
- probenecid
probenecid will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Methotrexate plasma levels, therapeutic effects, and toxicity may be enhanced. Monitor methotrexate concentrations and adjust dose accordingly.
- procarbazine
procarbazine, methotrexate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of immunosupression.
- rabeprazole
rabeprazole increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of toxicity with higher doses.
- rabies vaccine
methotrexate decreases effects of rabies vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration of methotrexate can decrease the immunological response of vaccines.
- regorafenib
regorafenib will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Regorafenib likely inhibits BCRP (ABCG2) transport. Coadministration with a BCRP substrate may increase systemic exposure to the substrate and related toxicity.
- rilonacept
methotrexate and rilonacept both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Combination may increase risk of myelosuppression.
- rolapitant
rolapitant will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Oral rolapitant (BCRP inhibitor) may increase plasma concentrations of BCRP substrates and may result in potential adverse reactions. Monitor possible adverse reactions if concomitant use of BCRP substrates and rolapitant can not be avoided.
- rose hips
rose hips will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- safinamide
safinamide will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Safinamide and its major metabolite may inhibit intestinal BCRP. Monitor BCRP substrates for increased pharmacologic or adverse effects.
- sapropterin
methotrexate decreases levels of sapropterin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Mechanism: Inhibition of dihydropteridine reductase (DHPR).
- sarecycline
sarecycline will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for toxicities of P-gp substrates that may require dosage reduction when coadministered with P-gp inhibitors.
- siponimod
siponimod and methotrexate both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution if coadministered because of additive immunosuppressive effects during such therapy and in the weeks following administration. When switching from drugs with prolonged immune effects, consider the half-life and mode of action of these drugs to avoid unintended additive immunosuppressive effects.
- sipuleucel-T
methotrexate decreases effects of sipuleucel-T by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- sirolimus
methotrexate and sirolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Combination may increase risk of myelosuppression.
- sofosbuvir/velpatasvir
sofosbuvir/velpatasvir will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Velpatasvir is an inhibitor of the drug transporter BCRP. Coadministration may increase systemic exposure of drugs that are BCRP substrates.
- stiripentol
stiripentol will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing the dose of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrates, if adverse reactions are experienced when administered concomitantly with stiripentol.
stiripentol will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Stiripentol is a BCRP transport inhibitor. Consider dosage reduction for BCRP substrates if adverse effects are experienced when coadministered. - streptozocin
methotrexate and streptozocin both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tacrolimus
methotrexate and tacrolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Combination may increase risk of myelosuppression.
- tafamidis
tafamidis will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Tafamidis inhibits breast cancer resistant protein (BCRP) in vitro and may increase exposure of BCRP substrates following tafamidis or tafamidis meglumine administration. Dosage adjustment of these BCRP substrates may be necessary.
- tafamidis meglumine
tafamidis meglumine will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Tafamidis inhibits breast cancer resistant protein (BCRP) in vitro and may increase exposure of BCRP substrates following tafamidis or tafamidis meglumine administration. Dosage adjustment of these BCRP substrates may be necessary.
- temsirolimus
methotrexate and temsirolimus both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Combination may increase risk of myelosuppression.
- tetanus toxoid adsorbed or fluid
methotrexate decreases effects of tetanus toxoid adsorbed or fluid by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration of methotrexate can decrease the immunological response of vaccines.
- tetracycline
tetracycline increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing elimination. Use Caution/Monitor. If tetracyclines cannot be avoided in patients receiving high-dose methotrexate, closely monitor methotrexate plasma concentrations and patients for signs and symptoms of toxicity.
- theophylline
methotrexate increases levels of theophylline by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Methotrexate may decrease the clearance of theophylline. Theophylline levels should be monitored when used concomitantly with methotrexate.
- ticarcillin
ticarcillin increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased serum concentrations of methotrexate with concomitant hematologic and gastrointestinal toxicity have been observed with concurrent administration of high or low doses of methotrexate and penicillins.
- trastuzumab
trastuzumab, methotrexate. Either increases toxicity of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Neutropenia or febrile neutropenia incidence were increased when trastuzumab was coadministered with myelosuppressive chemotherapy. .
- trastuzumab deruxtecan
trastuzumab deruxtecan, methotrexate. Either increases toxicity of the other by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Neutropenia or febrile neutropenia incidence were increased when trastuzumab was coadministered with myelosuppressive chemotherapy. .
- tretinoin
methotrexate, tretinoin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Patients receiving other agents that may cause hepatotoxicity, including systemic retinoids, could be at increased risk of liver-related side effects of methotrexate and such patients should be monitored closely during methotrexate therapy.
- trimethoprim
trimethoprim increases toxicity of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Trimethoprim may increase risk of methotrexate-induced bone marrow suppression and megaloblastic anemia. If this drug combination cannot be avoided, closely monitor for signs of hematologic toxicity.
- tucatinib
tucatinib will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider reducing the dosage of P-gp substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities.
- typhoid polysaccharide vaccine
methotrexate decreases effects of typhoid polysaccharide vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant administration of methotrexate can decrease the immunological response of vaccines.
- ublituximab
ublituximab and methotrexate both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Owing to potential additive immunosuppressive effects, consider duration of effect and mechanism of action of these therapies if coadministered
- ustekinumab
methotrexate and ustekinumab both increase immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Use Caution/Monitor. Combination may increase risk of myelosuppression.
ustekinumab, methotrexate. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines during chronic inflammation; thus, normalizing the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of ustekinumab in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect. - vadadustat
vadadustat will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Vadadustat may increase exposure of BCRP and OAT3 substrates. Monitor for signs of adverse effect of BCRP and OAT3 substrates and reduce substrate dose in accordance with their product labeling.
- valoctocogene roxaparvovec
methotrexate and valoctocogene roxaparvovec both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Medications that may cause hepatotoxicity when combined with valoctogene roxaparvovec may potentiate the risk of elevated liver enzymes. Closely monitor these medications and consider alternative medications in case of potential drug interactions.
- vancomycin
vancomycin decreases levels of methotrexate by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Recent exposure to vancomycin, in the absence of overt renal impairment, may adversely affect methotrexate excretion and increase risk of toxicity. Assess renal function, so appropriate methotrexate dose modifications can be made. .
- voclosporin
voclosporin, methotrexate. Either increases toxicity of the other by nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration with drugs associated with nephrotoxicity may increase the risk for acute and/or chronic nephrotoxicity.
- warfarin
methotrexate increases effects of warfarin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- willow bark
willow bark will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- zidovudine
methotrexate, zidovudine. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of myelosuppression.
- zoster vaccine recombinant
methotrexate decreases effects of zoster vaccine recombinant by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Immunosuppressive therapies may reduce the effectiveness of zoster vaccine recombinant.
Minor (10)
- adalimumab
methotrexate decreases levels of adalimumab by decreasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown. Methotrexate reduced adalimumab apparent clearance after single and multiple dosing by 29% and 44%, respectively. Dosage adjustment is not needed.
- colestipol
colestipol decreases levels of methotrexate by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown. Patients should take other drugs at least 1 hour before or 4 hours after colestipol to avoid impeding their absorption.
- folic acid
folic acid decreases effects of methotrexate by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Vitamin preparations containing folic acid or its derivatives may decrease responses to systemically administered methotrexate.
- golimumab
golimumab, methotrexate. Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Comment: Patients receiving immunosuppressives along with golimumab may be at a greater risk of developing an infection.
- hydrochlorothiazide
hydrochlorothiazide increases toxicity of methotrexate by decreasing elimination. Minor/Significance Unknown. Increased myelosuppression.
- L-methylfolate
L-methylfolate decreases levels of methotrexate by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Folic acid antagonists may interfere with folic acid utilization.
L-methylfolate decreases levels of methotrexate by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
methotrexate decreases levels of L-methylfolate by altering metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. - maitake
maitake increases effects of methotrexate by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Maitake mushroom has anti-tumor effects (animal/in vitro research).
- methyclothiazide
methyclothiazide increases toxicity of methotrexate by decreasing elimination. Minor/Significance Unknown. Increased myelosuppression.
- rituximab-hyaluronidase
methotrexate and rituximab-hyaluronidase both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- voclosporin
voclosporin will increase the level or effect of methotrexate by Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Information suggests voclosporin (an OATP1B1 inhibitor) may increase in the concentration of OATP1B1 substrates is possible. Monitor for adverse reactions of OATP1B1 substrates when coadministered with voclosporin.
Adverse Effects
>10%
Arachnoiditis with intrathecal administration
Subacute toxicity with intrathecal administration (paralysis of extremities, cranial nerve palsy, seizure or coma)
Demyelinating encephalopathy with cranial irradiation or other systemic chemotherapy
Reddening of skin
Hyperuricemia
Ulcerative stomatitis
Glossitis
Gingivitis
Nausea and vomiting
Diarrhea
Anorexia
Intestinal perforation
Mucositis (dose-dependent)
Leukopenia
Thrombocytopenia
Renal failure
Azotemia
Nephropathy
Pharyngitis
1-10%
Alopecia
Photosensitivity
Rash
Abdominal distress
Malaise
Fatigue
Chills, fever
Decreased resistance to infection
Gastrointestinal hemorrhage
Myelosuppression
Disorders of lung, interstitial pneumonia (acute, chronic)
Atrophy of liver, cirrhosis, hepatic fibrosis or necrosis, elevated liver function tests, hepatic failure
Postmarketing Reports
Injection site necrosis, injection site reaction
Warnings
Black Box Warnings
Severe hypersensitivity
- Contraindicated with history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to methotrexate, including anaphylaxis
Embryofetal toxicity
- Can cause embryofetal toxicity, including fetal death
- Contraindicated in non-neoplastic diseases during pregnancy
- Advise females and males of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during and after treatment
Benzyl alcohol-containing products
- Formulations with benzyl alcohol can cause severe central nervous toxicity or metabolic acidosis; use only preservative-free methotrexate Injection for treatment of neonates or low-birth weight infants and for intrathecal use
- Do not use benzyl alcohol-containing formulations for high-dose regimens unless immediate treatment is required and preservative-free formulations are not available
Serious adverse effects
- Serious adverse reactions, including death, reported with methotrexate
- Closely monitor for infections and adverse reactions of bone marrow, kidneys, liver, nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and skin
- Withhold or discontinue methotrexate as appropriate
Contraindications
Pregnant women with nonmalignant disease
Known hypersensitivity; severe reactions observed
Cautions
Based on published reports and its mechanism of action, can cause embryofetal toxicity, including fetal death; contraindicated in females with nonmalignant disease
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, reported; if hypersensitivity occurs, immediately discontinue and institute appropriate therapy
Myelosuppression reported, including severe and life-threatening pancytopenia, anemia, aplastic anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia; obtain blood counts at baseline and periodically; provide supportive care and withhold, reduce dose, or discontinue methotrexate if needed
GI toxicity may occur, including diarrhea, vomiting, stomatitis, hemorrhagic enteritis, and fatal intestinal perforation; patients with peptic ulcer disease or ulcerative colitis at greater risk; withhold or discontinued for severe GI toxicity and institute supportive care
Pulmonary toxicity reported, including acute or chronic interstitial pneumonitis and irreversible or fatal cases can occur at all dose levels; pulmonary symptoms (especially a dry, non-productive cough) may require interruption of therapy and careful investigation
Pulmonary toxicity reported, including acute or chronic interstitial pneumonitis and irreversible or fatal cases can occur at all dose levels
Secondary malignancies can occur at all dose levels; in some cases, lymphoproliferative disease that occurred during therapy with low-dose methotrexate regressed completely following withdrawal of methotrexate; if lymphoproliferative disease occurs, discontinue and institute appropriate treatment if lymphoma does not regress
Can induce tumor lysis syndrome with rapidly growing tumors; institute appropriate treatment for prevention and management
Can cause impairment of fertility, oligospermia, and menstrual dysfunction; unknown if infertility is reversible; discuss reproduction risks with female and male patients of reproductive potential
Methotrexate can exit slowly from third space accumulations resulting in prolonged terminal plasma half-life and toxicity; evacuate significant third-space accumulations prior injection Concomitant radiation therapy increases risk of soft tissue necrosis and osteonecrosis associated with methotrexate
Serious adverse reactions, including death, have occurred due to medication errors; most commonly, these errors occurred in patients who were taking methotrexate daily when a weekly dosing regimen was prescribed; ensure that patients receive the recommended dosage
Risk associated with benzyl alcohol preservative
- Formulations with benzyl alcohol can cause severe CNS toxicity or metabolic acidosis, if used in neonates or low-birth weight infants, IT, or in high-dose regimens
- Use only preservative-free injection for treatment of neonates or low-birth weight infants and for intrathecal use
- Do not use benzyl alcohol-containing formulations for high-dose regimens unless immediate treatment is required, and preservative-free formulations are not available
- Benzyl alcohol can cross the placenta; when possible, use the preservative-free formulation when injection required during pregnancy to treat neoplastic disease
-
Gasping syndrome
- Serious and fatal adverse reactions including “gasping syndrome” can occur in neonates and low birth weight infants treated with drugs containing benzyl alcohol
- Gasping syndrome characterized by CNS depression, metabolic acidosis, and gasping respirations
- When prescribing in infants (non-neonate, non-low-birth weight), if preservative-free formulation unavailable and use of a benzyl alcohol-containing formulation is necessary, consider combined daily metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from all sources
Neurotoxicity
- Serious neurotoxicity, including generalized and focal seizures, reported in pediatric patients
- Leukoencephalopathy can occur with intermediate and high-dose IV regimens, IT administration, and low-dose methotrexate therapy; risk increased with prior cranial radiation
- Transient acute stroke-like syndrome can occur with high-dose regimens; clinical manifestations include confusion, hemiparesis, transient blindness, seizures, and coma
-
Intrathecal (IT) administration
- IT administration can cause acute chemical arachnoiditis manifested by symptoms such as headache, back pain, nuchal rigidity, and fever
- May also cause subacute myelopathy characterized by paraparesis or paraplegia Avoid IT use of methotrexate injection that contains the preservative benzyl alcohol because of risk of serious neurotoxicity
Infections
- Increased risk for developing life-threatening or fatal bacterial, fungal, or viral infections including opportunistic infections (eg, Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, invasive fungal infections, hepatitis B reactivation, tuberculosis primary infection or reactivation, disseminated Herpes zoster and cytomegalovirus infections)
- Closely monitor patients for development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment; withhold or discontinue in patients who develop serious infections
Renal Toxicity
- Can cause renal toxicity including irreversible acute renal failure
- Monitor renal function and withhold or discontinue as needed for severe renal toxicity
- For high-dose regimens, follow recommendations to decrease renal injury and mitigate renal toxicity (eg, hydration, alkalinize urine, leucovorin rescue)
- Patients with impaired renal function have increased risk for toxicity
- Consider administration of glucarpidase in patients with toxic plasma methotrexate concentrations (>1 micromole per liter) and delayed clearance due to impaired renal function
Hepatotoxicity
- Can cause severe and potentially irreversible hepatotoxicity including fibrosis, cirrhosis, and fatal liver
- Avoid use in patients with chronic liver disease, unless benefits clearly outweigh risks; risk increased with heavy alcohol consumption
- In patients with psoriasis, fibrosis or cirrhosis may occur in the absence of symptoms or abnormal liver function tests; risk of hepatotoxicity appears to increase with total cumulative dose ≥1.5 g
- Assess liver function before initiating and monitor liver function tests during treatment; withhold or discontinue methotrexate Injection as appropriate
Dermatologic reactions
- Severe, including fatal, dermatologic reactions reported (eg, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, exfoliative dermatitis, skin necrosis, erythema multiforme)
- Psoriasis may be aggravated by concomitant exposure to UV radiation
- Can cause radiation recall dermatitis and photodermatitis (sunburn) reactivation
- Monitor for signs of dermatologic toxicity and withhold or permanently discontinue for severe dermatologic adverse reactions
- Counsel patients to avoid excessive sun exposure and use sun protection measures
Folic acid supplementation
- Neoplastic diseases: Products containing folic acid or its derivatives may decrease the clinical effectiveness of methotrexate; avoid products containing folic acid or folinic acid unless clinically indicated
- Non-neoplastic diseases: Folate deficiency may increase methotrexate adverse reactions; administer folic acid or folinic acid to patients with rheumatoid arthritis, pJIA, and psoriasis
Drug interaction overview
-
Drugs that increase methotrexate systemic exposure or adverse effects
- If unable to avoid coadministration, monitor closely for methotrexate adverse effects
- Penicillin or sulfonamide antibiotics
- Highly protein-bound drugs (eg, oral anticoagulants, phenytoin, salicylates, sulfonamides, sulfonylureas, tetracyclines)
- Proton pump inhibitors
- Probenecid
- Antifolate drugs (eg, dapsone, pemetrexed, pyrimethamine, sulfonamides)
- Aspirin and other NSAIDs; unexpectedly severe and fatal GI toxicity can occur with concomitant administration of methotrexate (primarily at high dose)
- Mercaptopurine
- Hepatotoxic products
- Weak acids (eg, salicylates)
- Nephrotoxic products
-
Nitrous oxide
- Avoid nitrous oxide anesthesia; consider alternative therapies in patients who have received prior nitrous oxide anesthesia
- Coadministration with nitrous oxide anesthesia potentiates methotrexate’s effect on folate-dependent metabolic pathways, which may increase risk of severe methotrexate adverse reactions
- Folic acid H5Avoid coadministration of folic/folinic acid supplements unless specifically prescribed (eg, for use with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, or pJIA)
- Coadministration with folic acid or its derivatives decreases clinical effectiveness of methotrexate in patients with neoplastic diseases
- Methotrexate competes with reduced folates for active transport across cell membranes
-
Theophylline
- Monitor theophylline levels and adjust theophylline dosage accordingly
- Methotrexate may increase theophylline plasma concentrations
-
Immunizations
- Update immunization per guidelines before initiating methotrexate if possible
- May be ineffective during therapy and live virus vaccines are not recommended due to risk of infection
- Disseminated infections following administration of live vaccines reported
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
Based on published reports and mechanism of action, can cause embryo-fetal toxicity and fetal death when administered to pregnant women
Advise pregnant women with neoplastic diseases of potential risk to fetus; preservative benzyl alcohol can cross placenta; when possible, use preservative-free formulation when methotrexate Injection needed during pregnancy to treat a neoplastic disease
Verify pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential before initiating
Contraindicated in pregnant women with nonmalignant disease
Contraception
-
Females
- Can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women;
- Use effective contraception during and for 6 months after final dose
-
Males
- Can cause chromosomal damage to sperm cells
- Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during and for at least 3 months after final dose
Infertility
- Females: Can cause impairment of fertility and menstrual dysfunction during and after cessation of therapy; unknown if infertility may be reversed in all affected females
- Males: Can cause oligospermia or infertility during and after cessation of therapy; unknown if infertility may be reversed in all affected males
Lactation
Limited published literature report the presence of methotrexate in human milk in low amounts; no information is available on the effects on breastfed infants or milk production
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, including myelosuppression, from methotrexate in breastfed infants, advise women not to breastfeed during therapy and for 1 week after final dose
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits dihydrofolic acid reductase; inhibits purine and thymidylic acid synthesis, which in turn interferes with DNA synthesis, repair, and cellular replication; cell cycle specific for S phase of cycle
May inhibit rapid proliferation of epithelial cells in skin
Absorption
Bioavailability (PO): 60% at PO doses <30 mg/m², bioavailability is significantly less at doses >80 mg/m²
Bioavailability (SC, Otrexup): 17, 13, 31, and 36% greater than PO methotrexate at doses of 10, 15, 20, and 25 mg respectively
AUC (SC, Rasuvo): 35%, 49%, 51%, and 68% greater than PO methotrexate at doses of 7.5 mg, 15 mg, 22.5 mg, and 30 mg respectively
Peak plasma time: PO, 1-2 hr; IM, 30-60 min
Distribution
Protein bound: 50%
Vd: Initial, 0.18 L/kg; steady-state, 0.4-0.8 L/kg
Metabolism
Metabolized by liver and intracellularly
Metabolites: Polyglutamated forms
Elimination
Half-life: Psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and low-dose cancer treatment, 3-10 hr; high-dose treatment, 8-15 hr
Excretion: Urine (80-100% within 24 hr), feces (small amounts)
Administration
IV Incompatibilities
Additive: Bleomycin
Syringe: Droperidol, metoclopramide (may be compatible at low concentrations of metoclopramide)
Y-site: Chlorpromazine, dexamethasone sodium phosphate(?), droperidol(?), gemcitabine, idarubicin, ifosfamide, midazolam, nalbuphine, promethazine, propofol
IV/IM Preparation
Reconstitute with D5W or NS: 20-mg vial, up to 25 mg/mL; 1-g vial, up to 50 mg/mL
May dilute further for IV infusion
IV/IM Administration
Administer by IM, IV push, or IV infusion
Regular IV given with no more than 25 mg/mL
IV push: Administered at 10 mg/min
IV infusion (usually >100 mg): Administered over 30 minutes to 4 hours, or according to institutional protocol
High-dose therapy (uses 1-g vial): Administered over 4 hours
Specific dosing schemes vary, but high doses should be followed by leucovorin 24 hours after initiation of therapy to prevent toxicity
IT Administration
Use only preservative-free product
May dilute further with preservative-free 0.9% NaCl
Before administration, equal volume of CSF is usually withdrawn; administer drug only if easy flow of blood-free CSF is noted
SC Administration
Otrexup is a single-dose auto-injector available in doses between 10 to 25 mg (in 5-mg increments) for once-weekly SC use only
Rasuvo is a single-dose auto-injector available in doses between 7.5 and 30 mg (in 2.5-mg increments) for once-weekly SC use only
RediTrex is a single-dose prefilled syringe available in doses between 7.5 and 25 mg (in 2.5-mg increments) for once-weekly SC use only
Use another formulation in patients who require PO, IM, IV, intra-arterial, or IT dosing
Visually inspect for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration; do not use if seal is broken
Administer SC in abdomen or thigh
May self-inject if determined appropriate by a physician and have received proper training on preparation and administration; a trainer device is available
Handling and disposal consistent with recommendation for cytotoxic drugs
Oral Administration
Oral solution (Xatmep)
- Intended for oral use only
- Instruct patients and caregivers that the recommended dose should be taken weekly, as directed, and that mistaken daily use of the recommended dose has led to fatal toxicity
- Measure dose with an accurate measuring device to provide the correct dose, such as an oral syringe provided by the pharmacist (do NOT use a household teaspoon)
- May take with or without food; food does not affect AUC, but decreased maximum concentration levels by 50% and delayed the absorption
Storage
Store intact vials at room temperature
Protect from light
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xatmep oral - | 2.5 mg/mL solution | 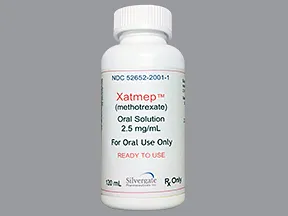 | |
| Xatmep oral - | 2.5 mg/mL solution |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.




